
7 supermarket sale items employees advise against buying, no matter how cheap
7 Items Supermarket Staff Advise Against Buying, No Matter How Big the Discount, Due to Concerns Over Quality.


7 Items Supermarket Staff Advise Against Buying, No Matter How Big the Discount, Due to Concerns Over Quality.

As consumers become increasingly cautious about the quality of cooking oils, many are turning to animal fats as a complete alternative. But is this truly a wise decision for health?

A woman from Guadeloupe has been identified as the only person in the world with a completely new blood type

It’s not the air conditioner, but the refrigerator that’s the real culprit behind your skyrocketing electricity bills. Improper placement of this appliance can also lead to increased energy consumption.

Heavy metal pollution has become an invisible threat to modern human health. Studies reveal that up to 87% of people have varying levels of heavy metals lingering in their bodies.
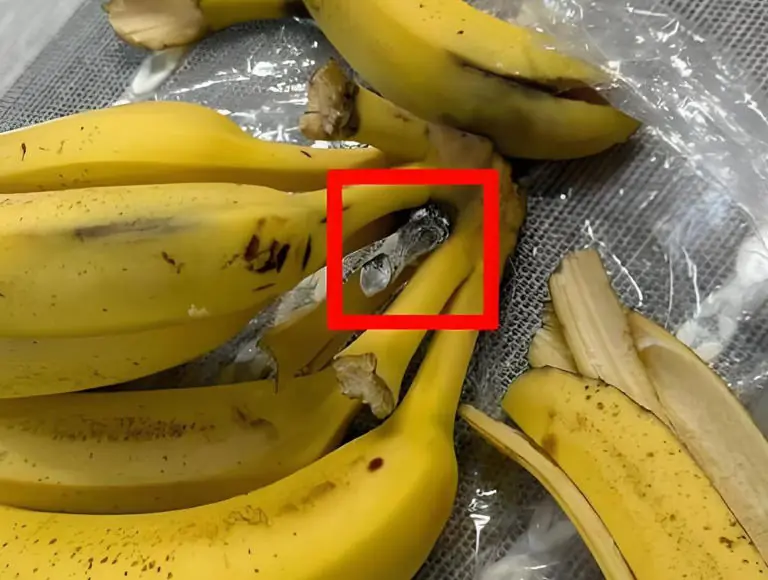


Not All Bananas Are Worth Buying: 4 Types You Should Avoid, Even at Discounted Prices
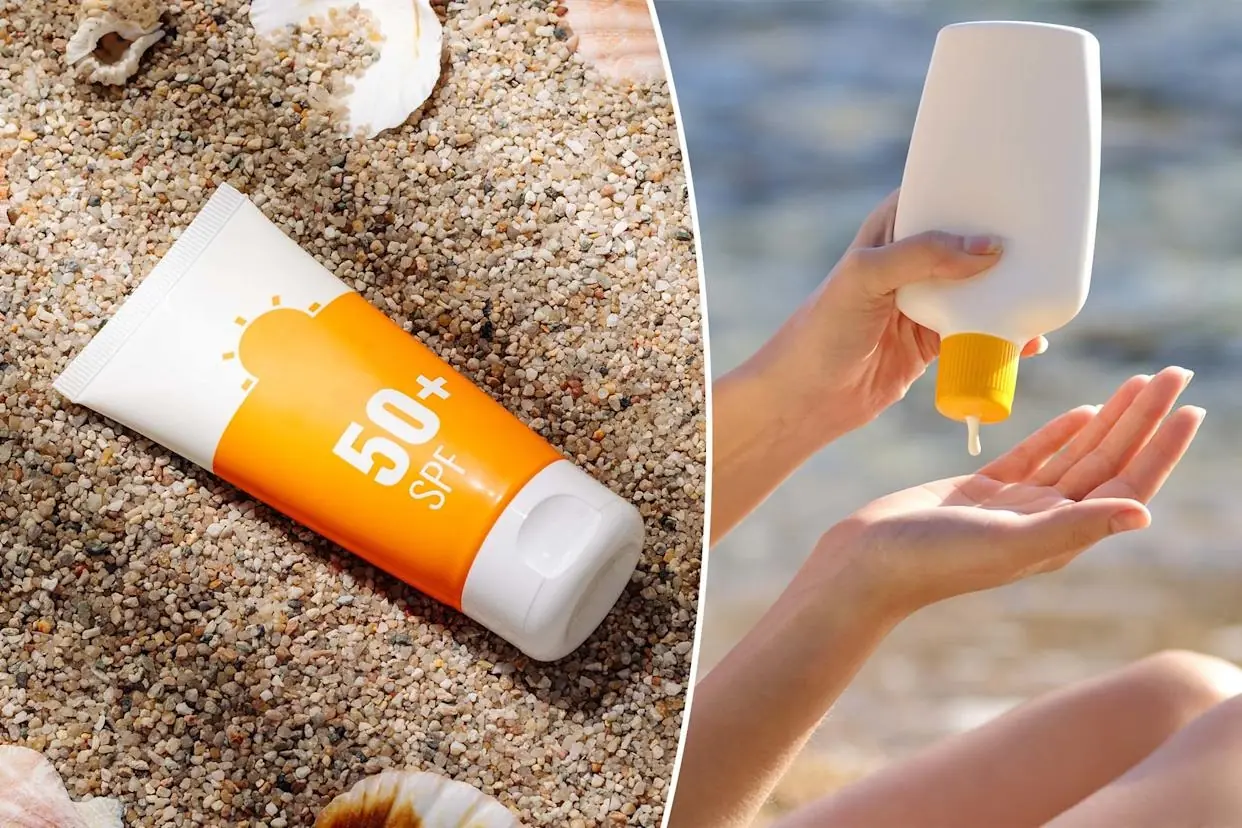

While many popular brands promise superior protection, the reality is that some products fail to meet the standards necessary to effectively safeguard your skin.
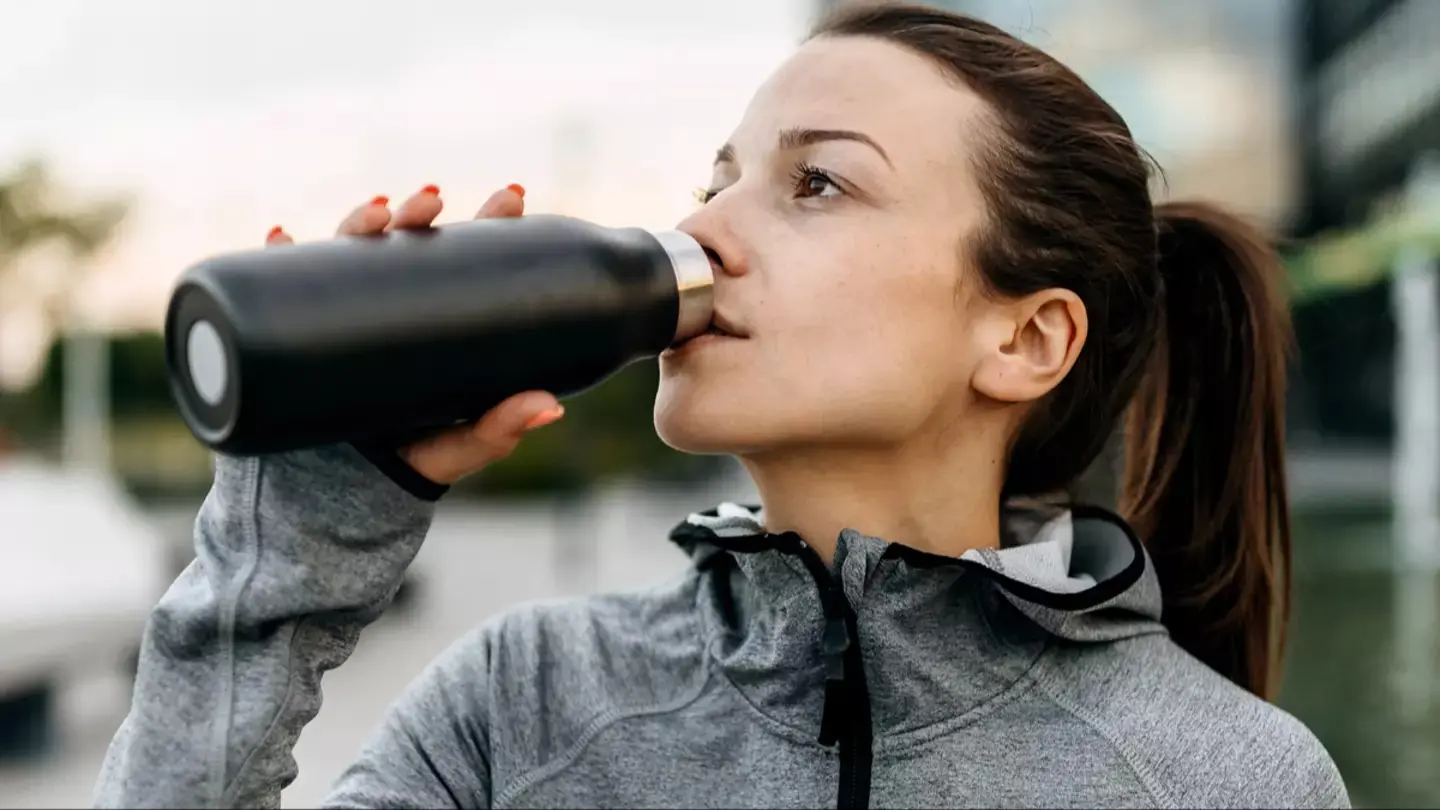

The recent case of lead poisoning from a metal water bottle serves as a stark reminder of the potential health risks associated with using old or damaged bottles.
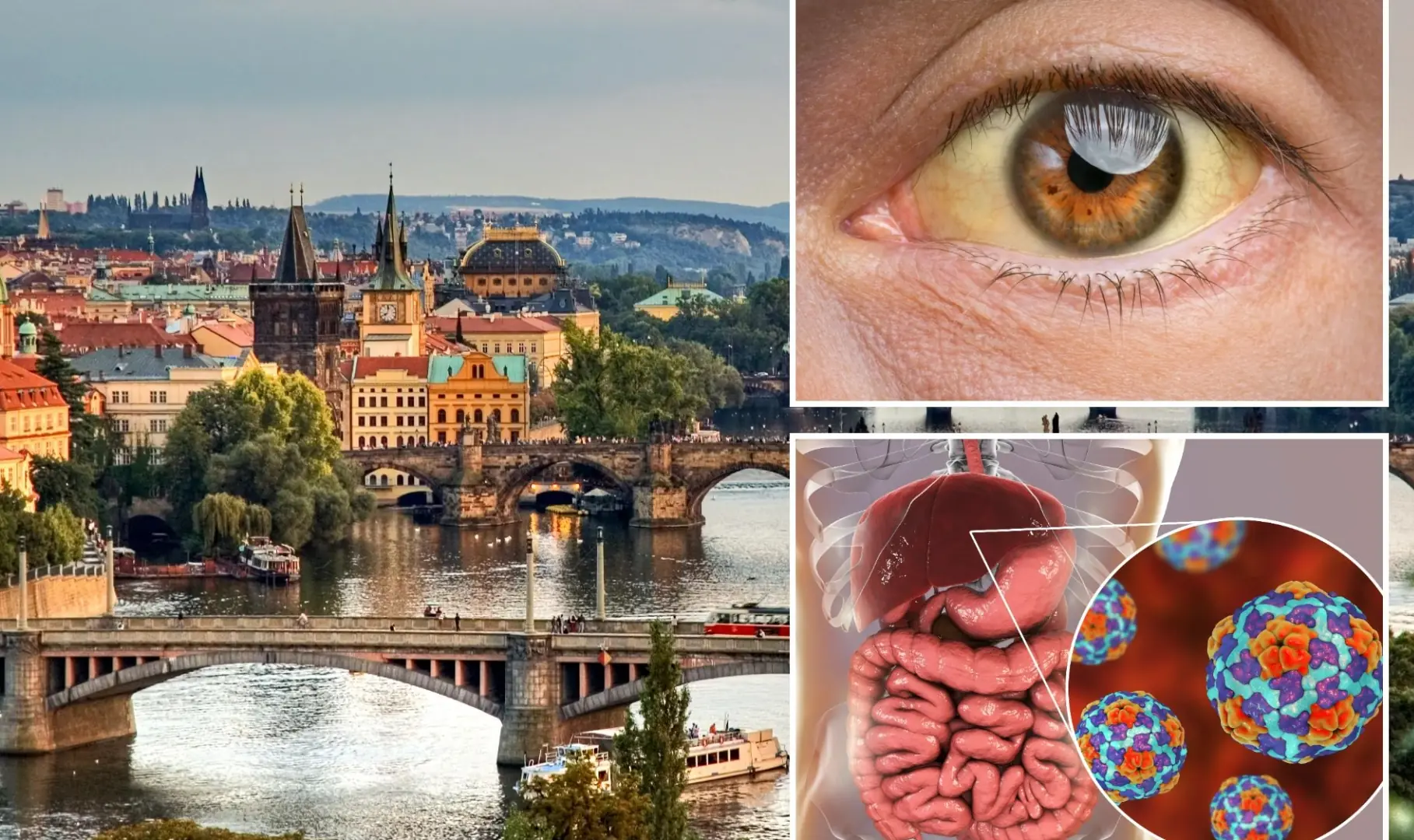
The recent surge in hepatitis A infections across Europe and the UK serves as a reminder of the importance of proper food hygiene and vaccination, especially when traveling to regions with higher risks of the virus.
Discover the fascinating world of marine viruses and their vital role in ocean ecosystems. With up to 10 million virus particles in a single drop of seawater, learn how these tiny entities influence microbial populations, nutrient cycles, and the environm
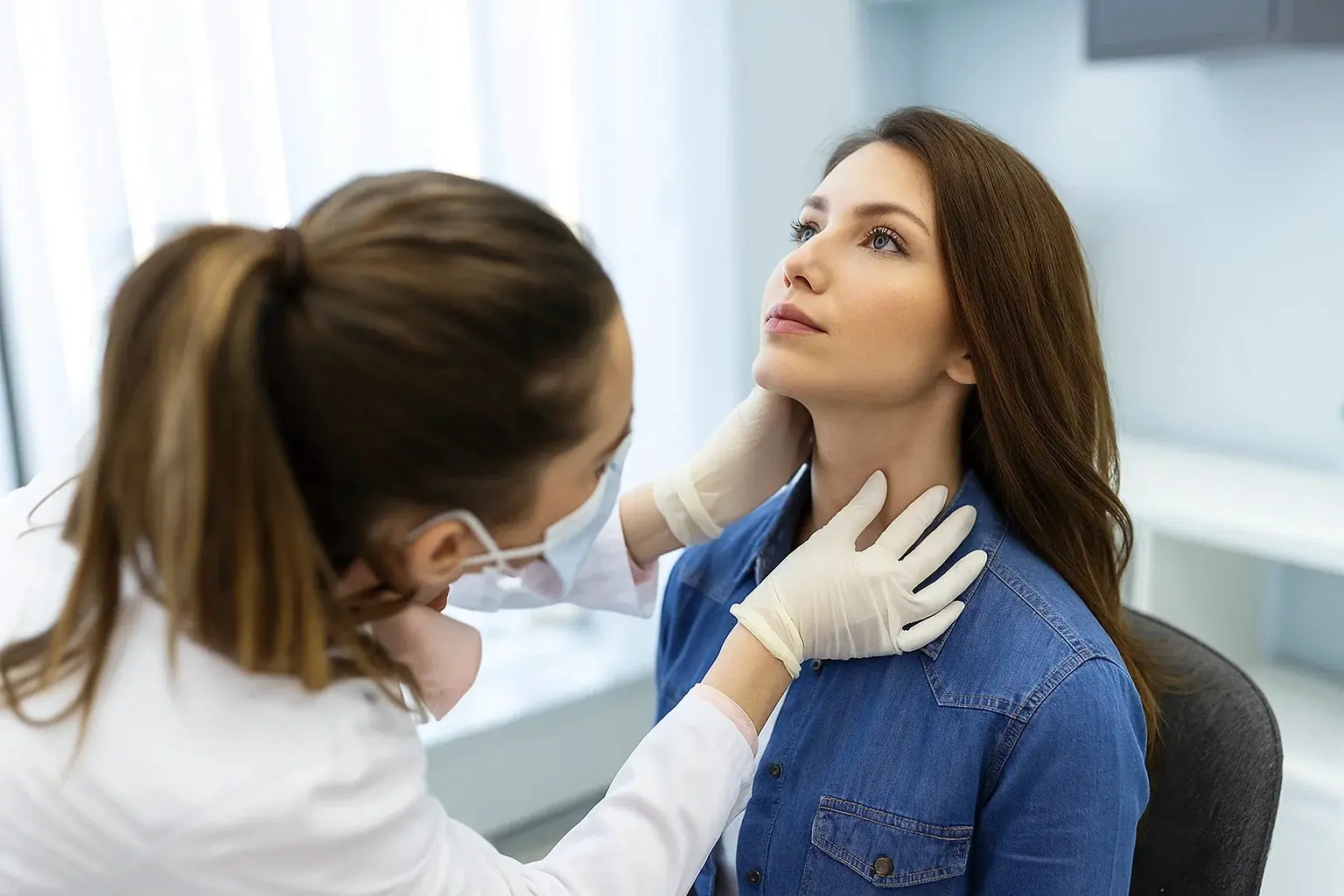
While turkey neck can be a cosmetic concern, there are several non-invasive treatments and lifestyle changes that can help improve the appearance of sagging neck skin.
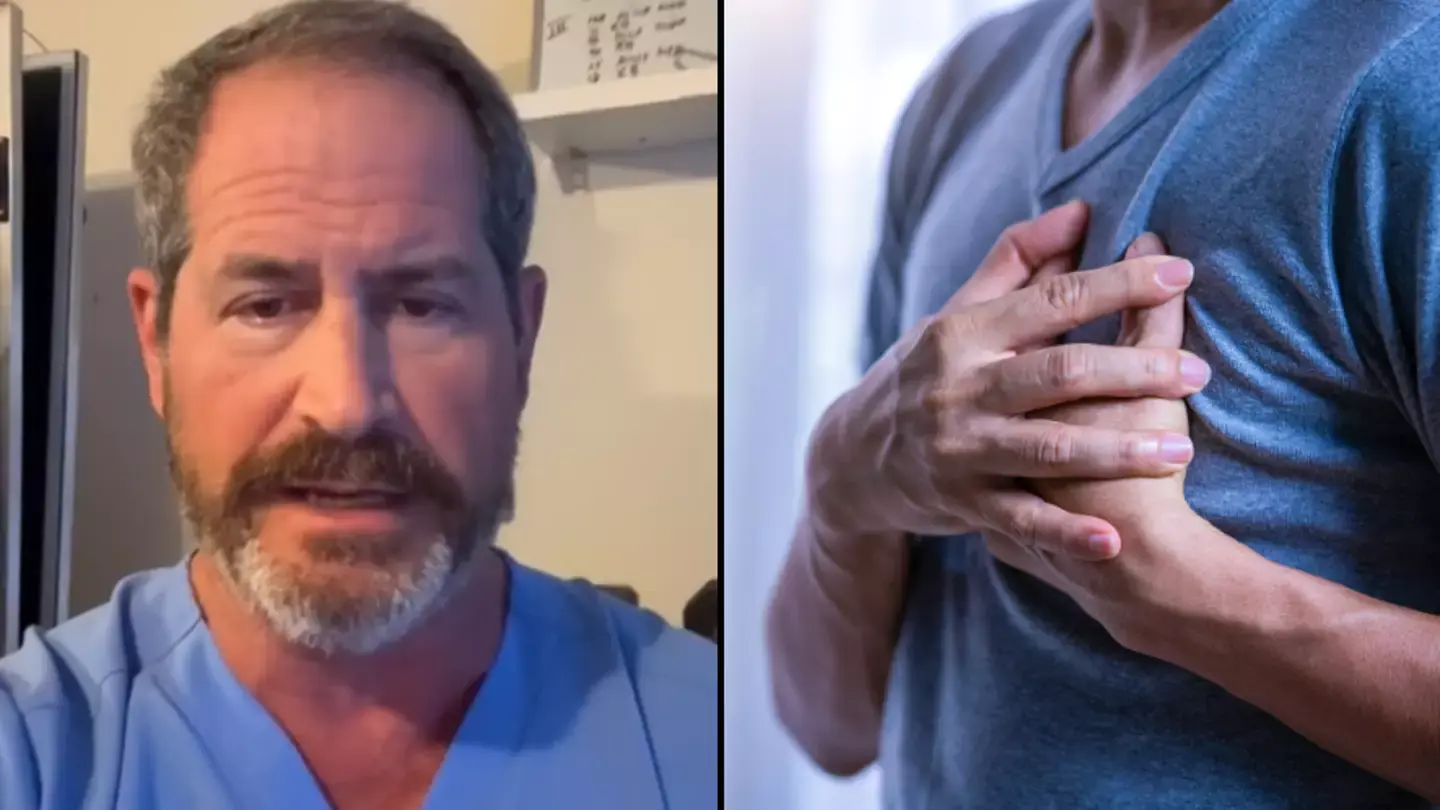
Discover the foods you should avoid for a healthy heart, including trans fats, excess sugar, and processed meats.

Struggling with leg cramps at night? Learn about common causes of night leg cramps and effective solutions to prevent and relieve them.

Discover the amazing health benefits of eating bananas every day. From improved digestion and heart health to boosting mood, find out how this simple fruit can transform your body. Learn more in our comprehensive guide.
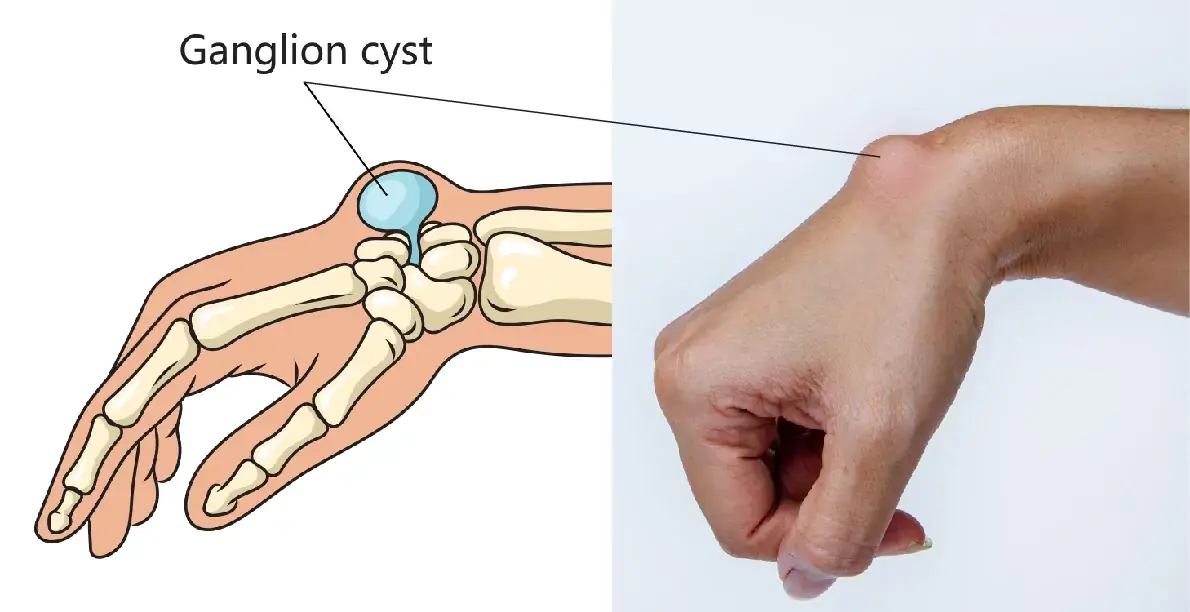
Learn about ganglion cysts, including their causes, how daily activities like repetitive movements and poor posture can make them grow, and expert tips on prevention. Discover when to seek medical attention and ensure proper joint health.

Learn how magnesium supports bone health, blood sugar management, anxiety relief, and digestive health. Find out the best forms, dosages, and foods rich in magnesium to boost overall well-being and manage health conditions.

Discover the health benefits of cabbage, from its anti-cancer properties to digestive support. Learn who should avoid cabbage due to thyroid issues, blood clotting disorders, and more. Understand its nutritional value and side effects for a healthier diet


7 Items Supermarket Staff Advise Against Buying, No Matter How Big the Discount, Due to Concerns Over Quality.

As consumers become increasingly cautious about the quality of cooking oils, many are turning to animal fats as a complete alternative. But is this truly a wise decision for health?

A woman from Guadeloupe has been identified as the only person in the world with a completely new blood type

It’s not the air conditioner, but the refrigerator that’s the real culprit behind your skyrocketing electricity bills. Improper placement of this appliance can also lead to increased energy consumption.

Heavy metal pollution has become an invisible threat to modern human health. Studies reveal that up to 87% of people have varying levels of heavy metals lingering in their bodies.
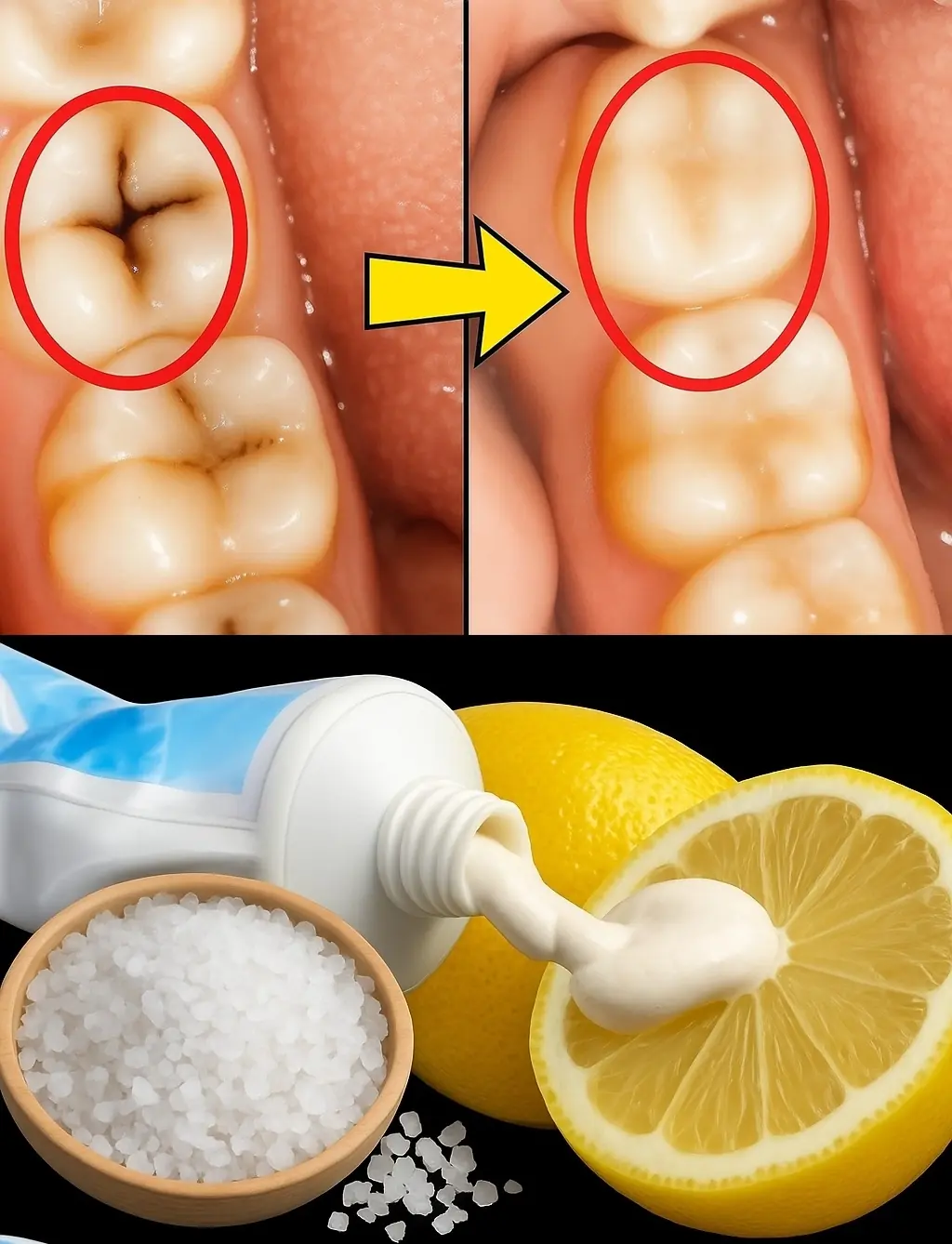
By incorporating these natural methods into your daily routine, you can strengthen your teeth, support your gums, and prevent further decay.


Agatha Christie, the Queen of Crime Fiction, vanished for 11 days in 1926, leaving the world in suspense. Discover how personal heartbreak led to her greatest creative revival and the birth of her most iconic works.

Parents of tweens and teens, listen up! Discover the powerful 'Add 20% Rule' for effective communication. Learn why assuming your child knows more than you think about topics.

Yvette Kahn’s tragic story is a powerful reminder of innocence lost during the Holocaust. Despite the horrors she faced, Yvette found music in a world that tried to silence her. Remembering her is a call to preserve the beauty and resilience of childhoo

This DIY flaxseed-based skincare routine offers a natural, affordable, and effective way to combat wrinkles and promote a more youthful appearance.
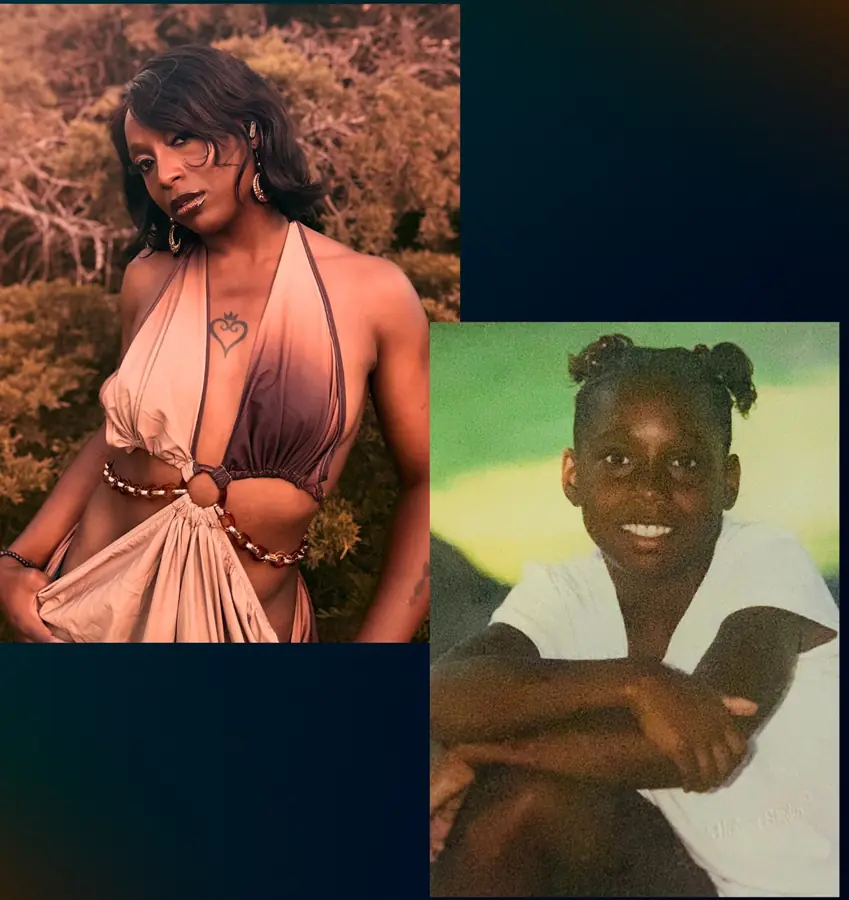

Kandice Pritchard-Harmon's adoption as a preteen began a journey filled with identity struggles and cultural shifts. Discover how her quest for freedom led to a transformative enlistment in the U.S. Army, building resilience, global experiences, and a pow


Try these simple, effective remedies and enjoy the benefits of natural hair care. O

Carla’s curiosity led her to follow two lonely twin girls in the park, but what she uncovered about their tragic home life sh0cked her to the core.

Natural remedies, on the other hand, provide a safe, affordable, and effective way to promote thicker, longer, and healthier eyelashes over time.

After years of looking down on his ex-wife, Anton's world is turned upside down when he sees her in a luxurious mansion, living a life he never imagined. A gripping tale of pride, revenge, and the consequences of underestimating someone’s strength.

Packed with skin-loving nutrients like vitamin C, antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and collagen-boosting compounds, this gel can transform your skin, providing deep hydration, elasticity, and a youthful glow.

Not All Bananas Are Worth Buying: 4 Types You Should Avoid, Even at Discounted Prices