
Harvard scientists uncover affordable supplement that reverse ageing

A recent major study reveals that daily supplementation with vitamin D3 may significantly slow the biological aging process by preserving telomere length, offering a promising avenue for anti-aging strategies and healthy aging interventions.

-
Preservation of Telomere Length: Participants who took vitamin D3 showed a notable reduction in telomere shortening compared to those who received a placebo. This indicates that vitamin D supports the maintenance of chromosome integrity and delays cellular aging.
-
Biological Age Reduction: The results suggested an effective "reversal" of biological age by approximately three years, as measured by telomere length and associated biomarkers.
-
Additional Health Benefits: Supplementation with vitamin D3 was also linked to reduced inflammation and a decreased risk of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers.
News in the same category


Teen's Warning: Ch3st Pain Symptoms Could Be a Sign of Something More Serious

The B@nned Bible: A Controversial Book Featuring Teachings of Jesus That Contradict the Church

15-year-old teen diagnosed with stage 3 melan0ma reveals doctors initially dismissed warning signs as "puberty"
Experts raise alarm on irreversible lung damag3 caused by vap!ng, known as ‘popcorn lung’

Early puberty in girls on the rise — Researchers may have pinpointed the reason behind it

What Happens When You Eat Sweet Potatoes Every Day: Benefits, R!sks, and How to Enjoy Them

Warning issued to anyone using this smiley face emoji: You may have been sending it wrong
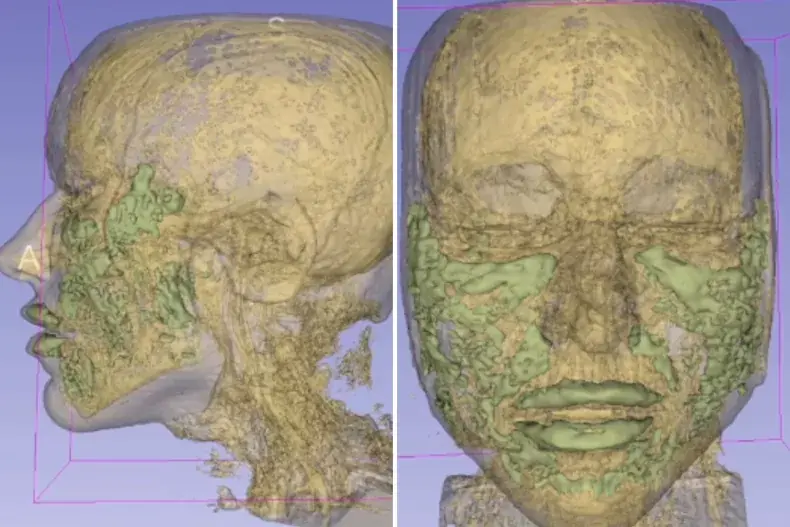
Detailed MRI maps out exactly where a 33-year-old woman's filler ended up in her face
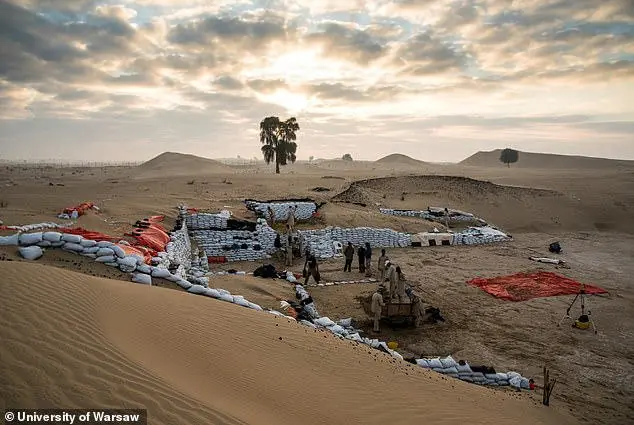

Mysterious ancient city built 5,000 years ago by lost advanced civilization found beneath vast desert

New study finds Vitamin K supplement slows progression of pr0state canc3r cells
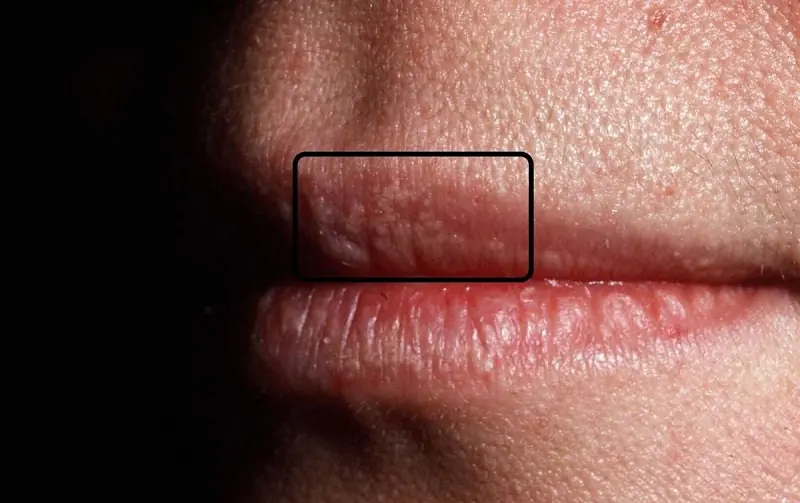
Understanding White Bumps on Lips: Causes, Sympt0ms, and Tre@tment Options

Diabetes and Sleep: Early Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore

Recognizing the Early Warning Signs of C@ncer: What You Should Know

Why You Should Never Leave a Water Bottle in Your Car: F!re Risk and Safety Tips

The Ultimate Guide to Brushing Your Teeth: Before or After Breakfast?

What Happens to Your Body During a 36-Hour Fast? A Comprehensive Science-Based Exploration
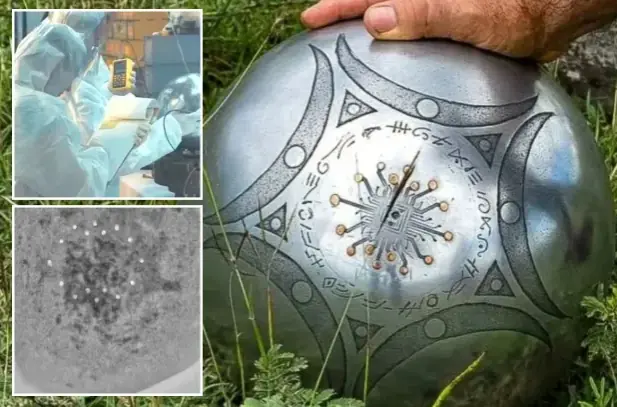

AI deciphers the meaning of fallen ‘alien orb’ in Colombia, revealing chilling message

Morning vs. Night Showers: Scientists Finally Reveal Which Is Best for Your Hygiene and Health
News Post

My Son Befriended a Garbage Man He Called 'Mr. Tomorrow' Until I Learned Who He Really Was
Every morning, my son handed juice to a garbage man he called “Mr. Tomorrow.” I thought he was a stranger until I learned he held a secret tied to our family.

My Mother-in-Law’s Latex Gloves Hid a Terr!fying Secret: The Mystery That Shook Our Family to Its Core
Discover the chilling secret behind a mother-in-law’s latex gloves in this suspenseful tale of hidden pain, family secrets, and resilience. A gripping story of fear, betrayal, and healing unfolds.

6 Skin Glow Juices for Naturally Radiant, Youthful Skin: Ultimate Guide to Nourish Your Complexion from Within
These six powerful juice recipes harness nature’s best ingredients to detoxify, hydrate, and protect your skin—leading to a clearer, firmer, and more luminous complexion.

John Rendez opens up about feeling unwelcome at Nora Aunor’s burial
Singer-rapper reflects on loss and shares heartfelt memories of late “soulmate” Nora Aunor

Are Gerald Anderson and Julia Barretto still together?

Apply This Flaxseed Gel Daily to Naturally Erase Wrinkles and Reveal Youthful, Radiant Skin
By incorporating this DIY elixir into your daily routine, you nourish your skin deeply, smooth fine lines, and restore a radiant, youthful complexion without exposure to harsh chemicals.
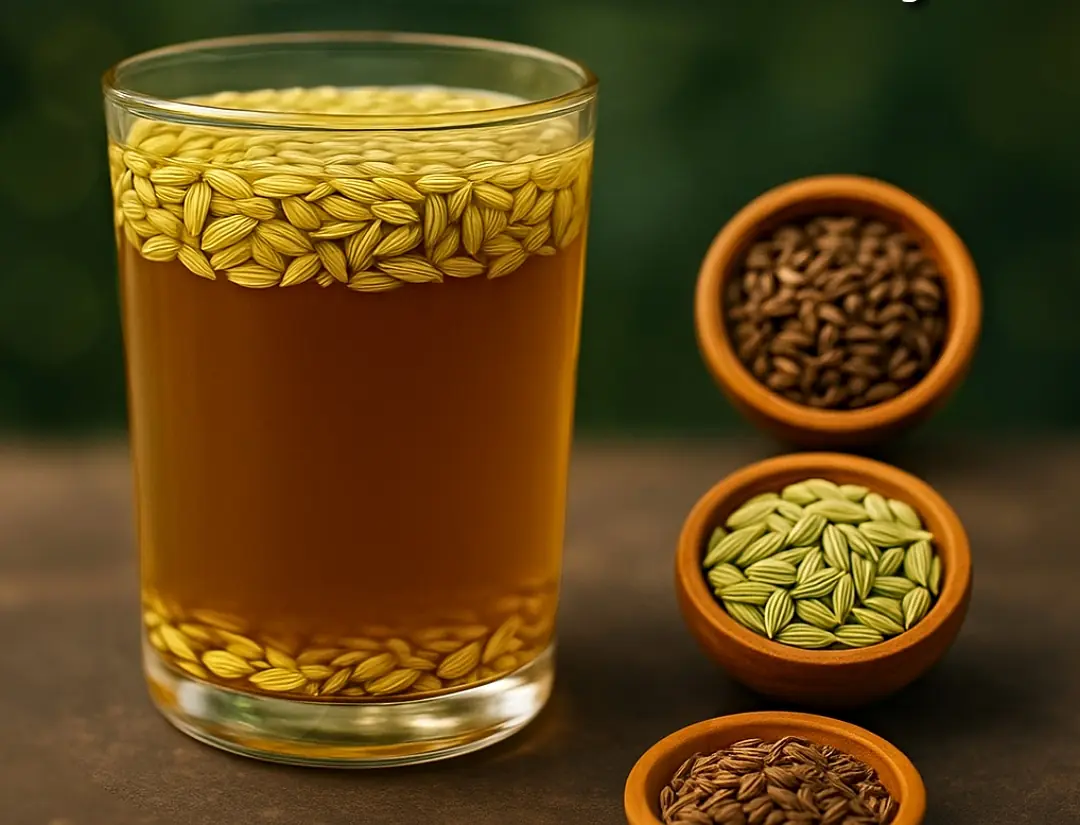

How to make Fennel Seeds Water/ Tea – Benefits of Fennel Seeds for Weight Loss & Health
Fennel seed water is more than a refreshing beverage—it’s a holistic health tonic with the power to transform your metabolism, digestive health, skin radiance, and overall vitality.
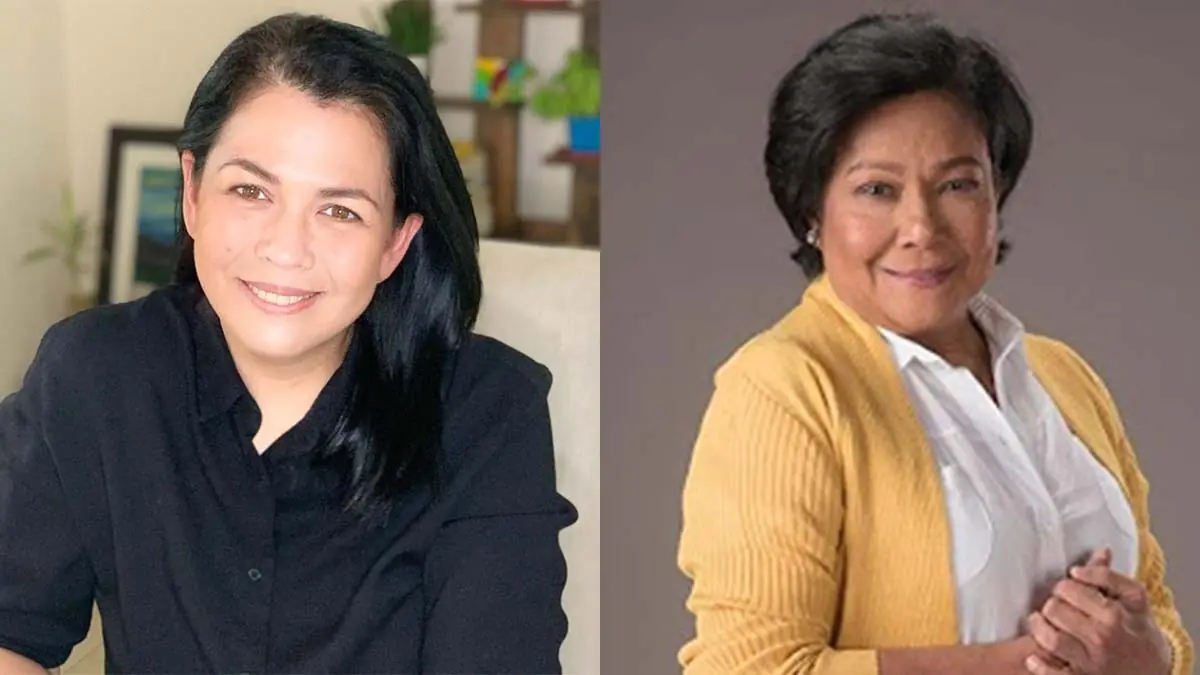

Lotlot de Leon’s cryptic Instagram posts spark conversations on truth and deception
Actress Lotlot de Leon recently stirred speculation online after posting cryptic messages about lies and truth on her Instagram Stories
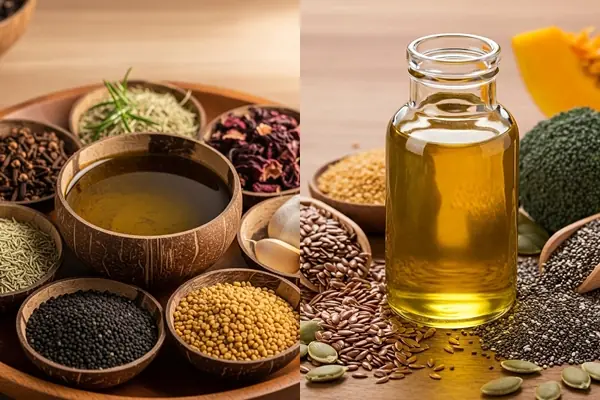

The Ultimate DIY Herbal Oil for Extreme Hair Growth: Natural Remedies for Healthier, Thicker Hair
Packed with powerful ingredients like cloves, rosemary, garlic, and hibiscus, this oil helps nourish your scalp, stimulate hair follicles, and encourage thicker, healthier hair.
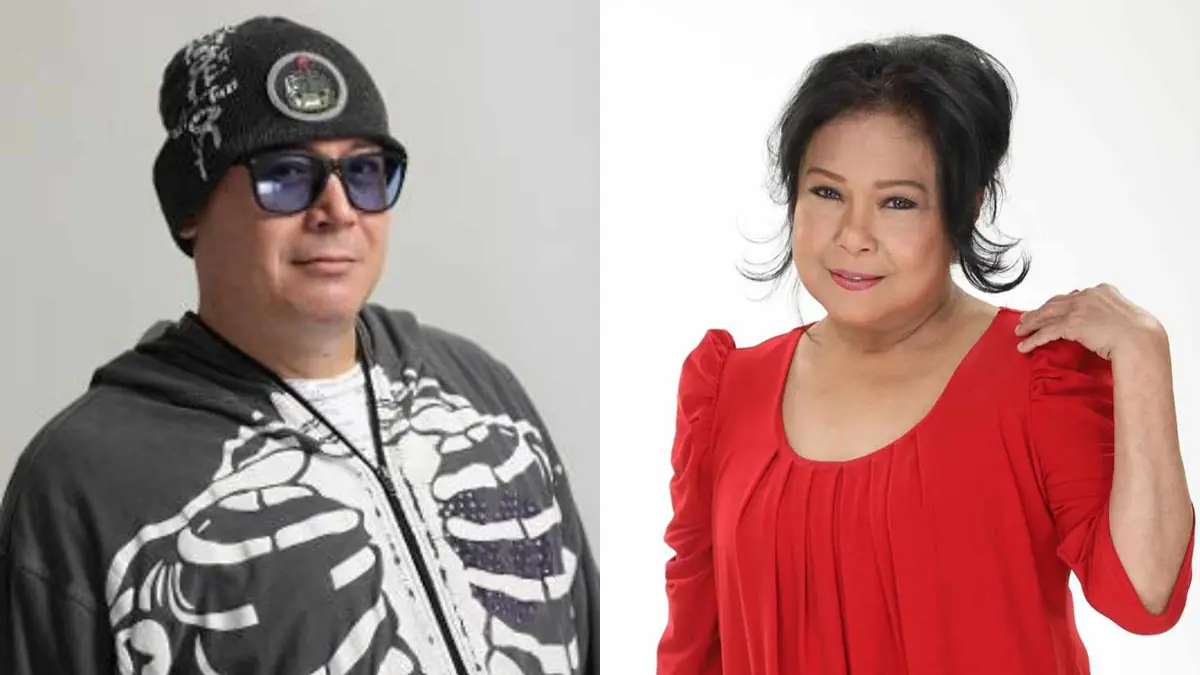

John Rendez, still grieving the loss of Nora Aunor: “I’ll never forget you”
John Rendez expresses deep sorrow over the passing of his dear friend and beloved superstar, Nora Aunor. Despite the passage of time, the loss remains a painful reality that he continues to cope with.
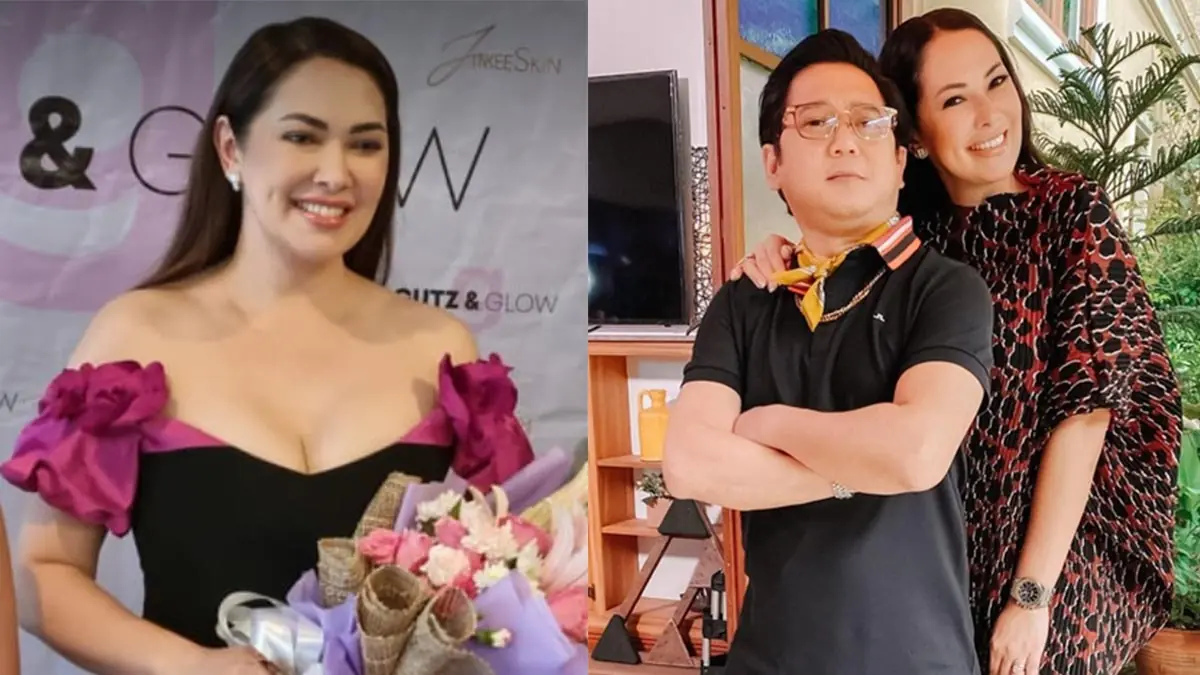

Ruffa Gutierrez talks about love, marriage, and family priorities: “I’m not closing my doors”
Ruffa Gutierrez opens up about her perspective on marriage and her current relationship with Herbert Bautista
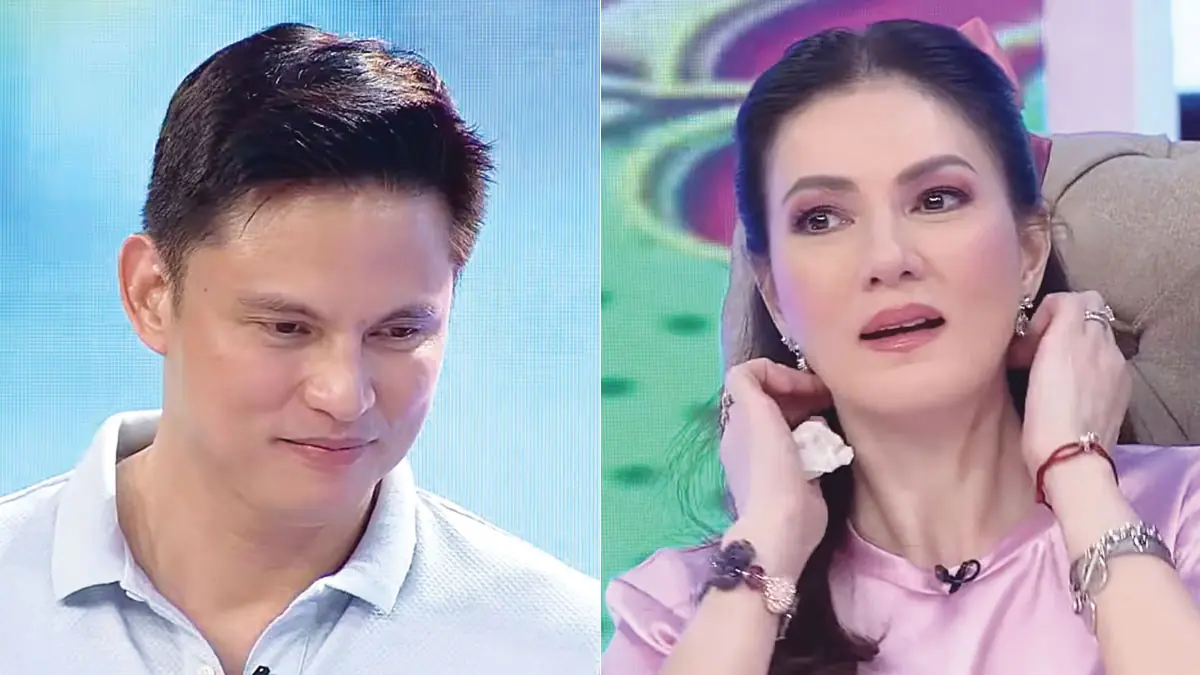

Zoren Legaspi put on the spot by wife Carmina Villarroel over question about ex-girlfriends
During a playful yet challenging segment on Sarap Di Ba?, Zoren Legaspi faced a tricky question about his ex-girlfriends posed by his wife Carmina Villarroel, leading to a humorous but revealing exchange.

35 Genius Baking Hacks You Didn’t Know You Needed
Ready to transform your baking game? These 35 clever hacks will save you time, fix common baking problems, and make your treats taste even better!

How Often Should You Clean Everything? The Ultimate Guide to Household and Personal Item Care
Knowing how frequently to clean your belongings can boost your health and keep your home fresh—discover the best cleaning schedules for everyday items.

My Husband F@ked His De@th on Our Wedding Day And Left Me Heartbr0ken and Betrayed
A heart-wrenching story of betrayal and love as Polina discovers her husband f@ked his de@th on their wedding day. After the sh0ck and heartbre@k, can she ever trust him again?

17 Surprising Foods You Didn’t Know You Could Cook or Prepare in the Microwave
Unlock the full potential of your microwave with these clever hacks to save time and make meal prep easier than ever.

14 Powerful Vaseline Uses and Benefits for Skin, Lips, and Hair: Timeless Beauty Hacks You Need to Know
Still, for many, Vaseline offers simple, effective beauty care that doesn’t break the bank. When paired with natural ingredients, it becomes even more powerful - proving that skincare doesn’t have to be complicated to be effective.

3 Highly Effective Natural Mould Removers: Safe and Powerful Alternatives to Bleach
Discover natural, non-toxic ways to eliminate mould from your home using simple ingredients that are just as effective as harsh chemicals.

The Power of Silence: How Listening to Your Inner Voice Can Transform Your Life
In a noisy world filled with distractions, embracing silence can restore your focus, clarity, and emotional balance.

My Husband Went on Vacation Instead of Helping Me with My Mom’s Funeral: His Bl00d Froze When He Returned
After losing her mother, Elanor faces emotional neglect from her husband Jasper, who chooses vacation over support. Her bold response forces change in their fractured marriage. A powerful story of grief, resilience, and reclaiming love.