
Washing cauliflower with water alone isn't enough - Learn this trick to completely get rid of all dirt and grime
You need to know the following trick to wash the cauliflower really clean before cooking it.
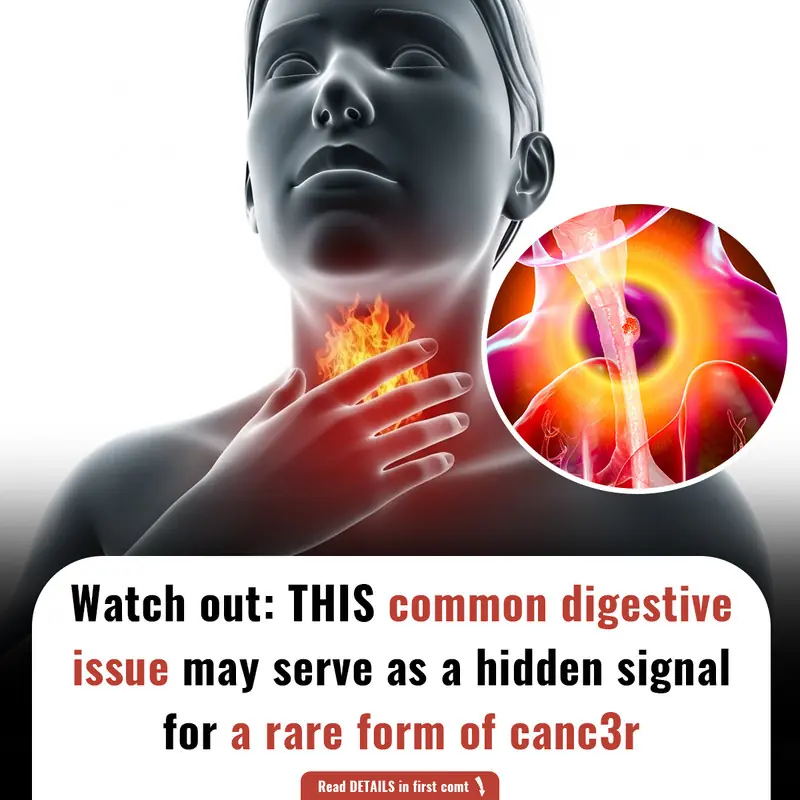
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This cancer begins in the flat cells lining the esophagus.
Adenocarcinoma: This cancer starts in cells that produce mucus and other fluids.
Pain in the throat, back, behind the breastbone, or between the shoulder blades
Difficulty swallowing
Chest pain
Vomiting or coughing up blood
Heartburn
Hoarseness
Unexplained weight loss
Tobacco use
Alcohol consumption
Obesity
Barrett’s esophagus and chronic acid reflux
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Previous cancer history
Other health conditions (e.g., achalasia, tylosis)
Occupational exposure to certain chemicals

You need to know the following trick to wash the cauliflower really clean before cooking it.

A US doctor warned of this common symptom on TikTok

Many people go outside to use sunscreen to protect their skin. However, be mindful of this to avoid harming your health.

Specialized tools show that the actual room temperature is vastly different from the temperature set on the air conditioner.

Washing machines are very convenient but they also have limitations; not everything can just be thrown in there and it's done.
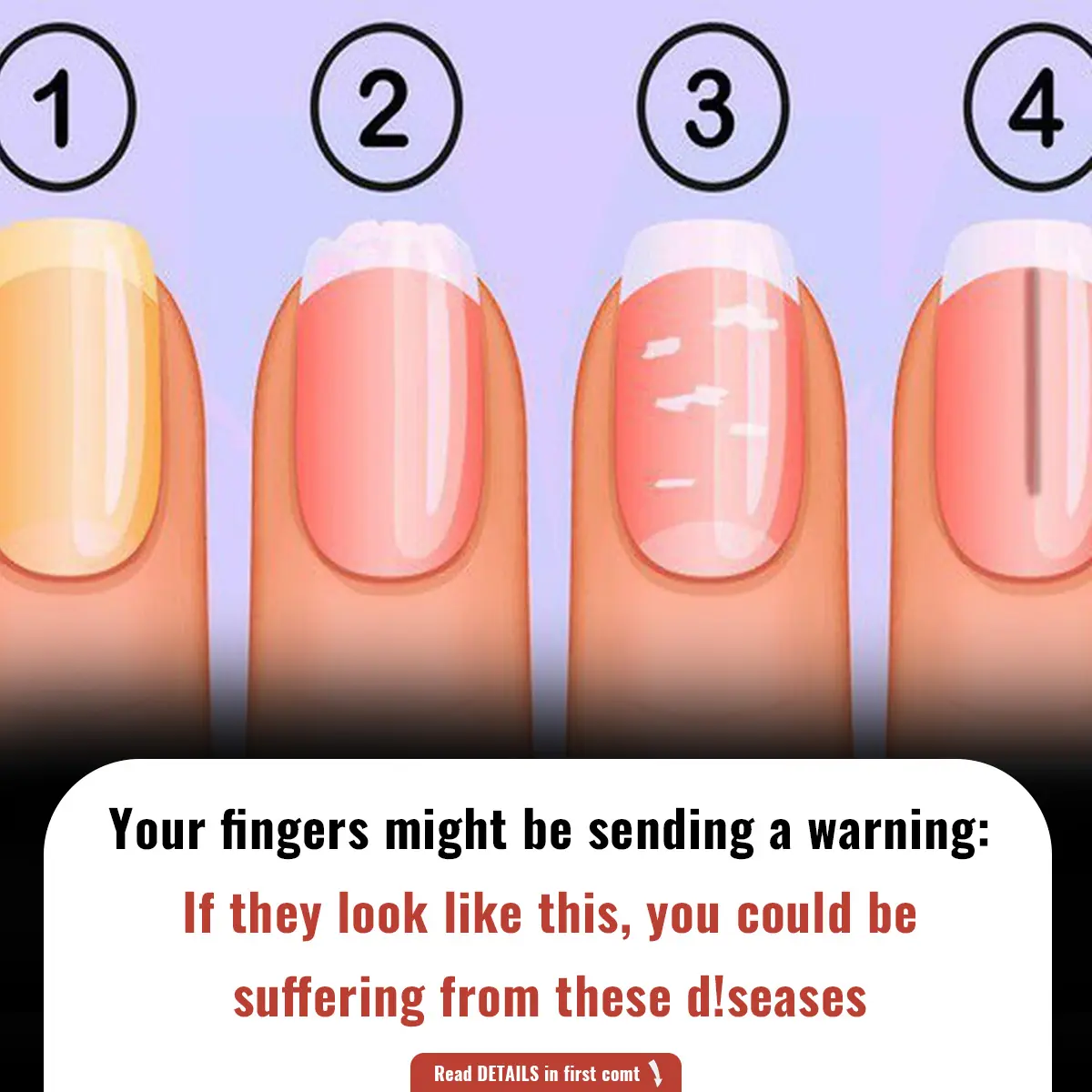
5 Health Conditions Your Nails May Reveal

"I have no choice just to get on with it and keep fighting," Leah Hughes said

Despite being on a ventilator and undergoing continuous dialysis, the 15-year-old female student has died due to severe septic shock from popping her pimples.

Knowing the 6 tips below will help you choose good honey, becoming a smart consumer in a market filled with real and fake products.

Be careful with this when drinking iced coffee if you don't want to experience the same situation.
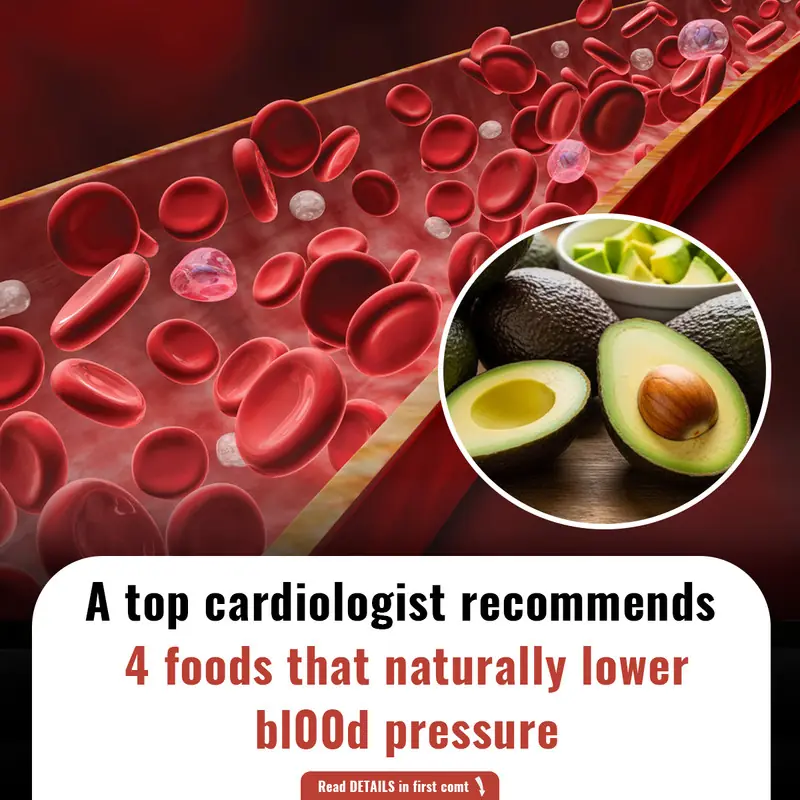
Dr. Sanjay Bhojraj, a cardiologist, highlights the significance of diet in managing high blood pressure, a major contributor to chronic illnesses. He recommends incorporating foods like avocados, bananas, leafy greens, and garlic into a balanced diet. The
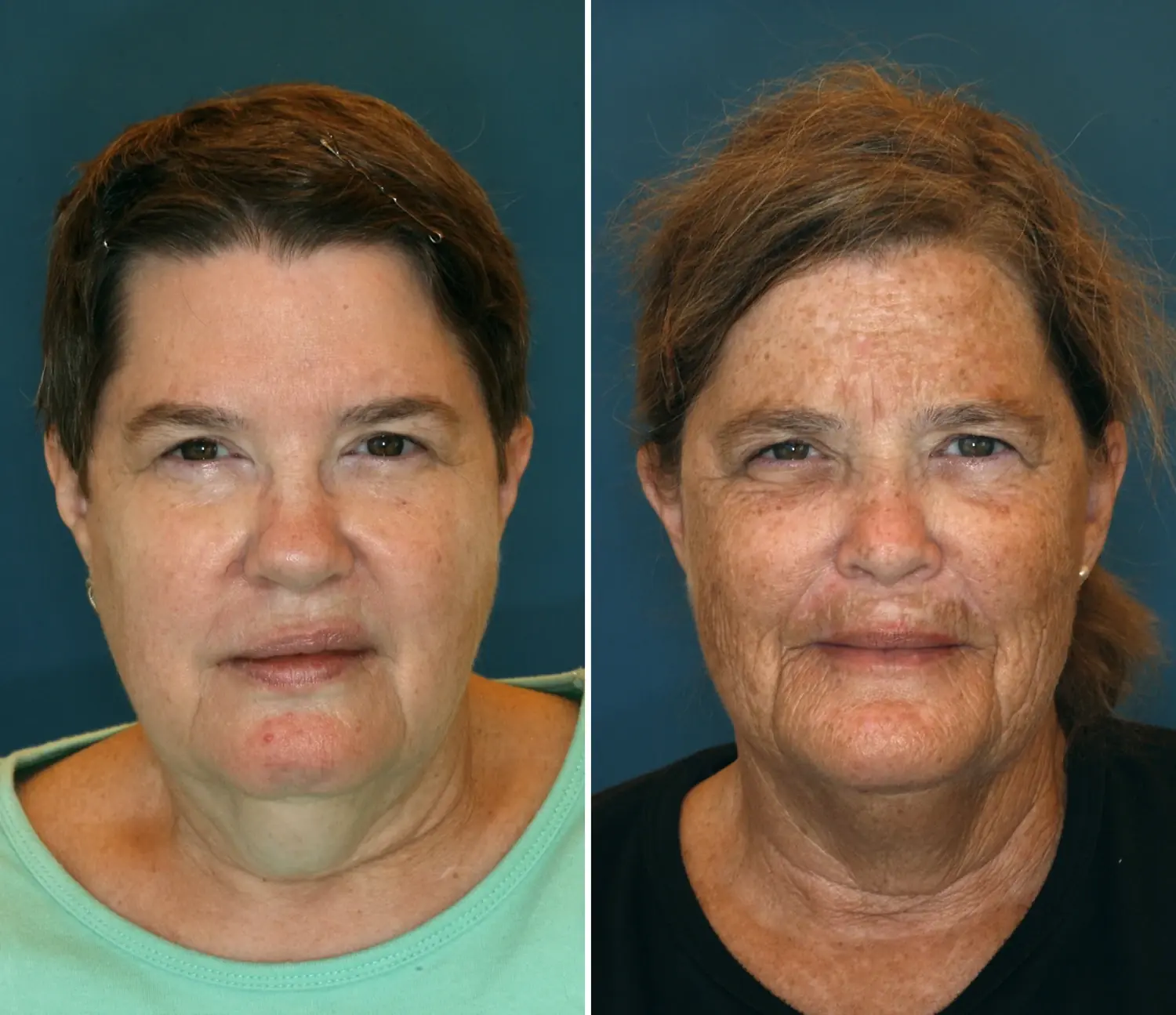
A twin study reveals how sm0king and tanning accelerate skin aging by damaging collagen and elastin. Learn how lifestyle choices impact aging and why sunscreen and healthy habits are key to preserving your skin.
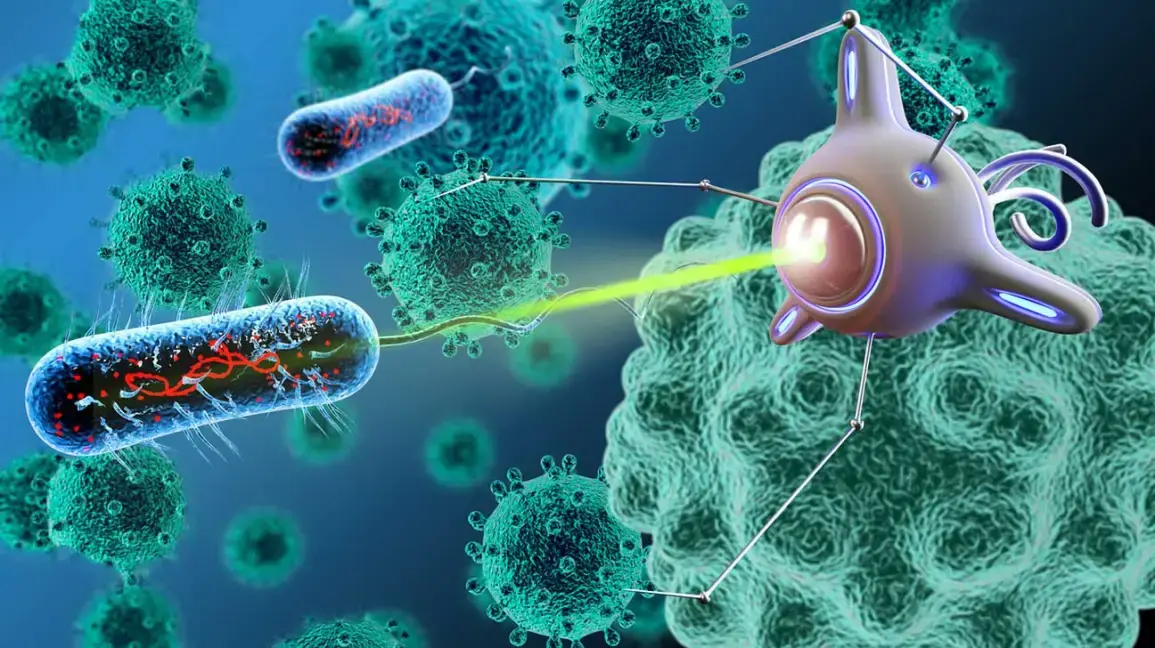
Discover how a groundbreaking mRNA-based treatment uses nanoparticles to turn your own immune cells into cancer-fighting CAR-T cells, offering a faster, safer, and more affordable alternative to traditional CAR-T therapy.

Scientists transform plastic waste into acetaminophen (paracetamol) in 24 hours! Explore this eco-friendly innovation turning pollution into pain relief.

Discover how rapamycin, a drug originally used for organ transplants, may mimic the life-extending effects of calorie restriction and its potential role in anti-aging treatments. Learn more about the early research and risks.

New research reveals how a specific brain region regulates alcohol consumption, offering hope for targeted treatments for alcohol addiction. Discover how this breakthrough could transform alcohol dependency therapies.

Discover how oxytocin, the "love hormone," stimulates heart stem cells and aids in regenerating heart tissue after injury. This new research brings hope for future heart attack treatments.

At 18 years old, associated with the bright days of youth, this girl received a diagnosis of premature ovarian failure, making it very difficult to conceive.

Although the air conditioner can still operate, when noticing the following signs, it is advisable to conduct timely inspections and repairs to avoid affecting the usage needs and the health of users.

Discover the deep, quiet bond between George Harrison and Stevie Nicks. Their connection, built on mutual respect and shared creativity, left a lasting impact on both their personal lives and the music world.

Discover how Carol Burnett, with the help of a $1,000 gift, transformed her career from struggling actress to one of America’s most beloved entertainers, leaving a legacy of laughter and love.

You need to know the following trick to wash the cauliflower really clean before cooking it.

A US doctor warned of this common symptom on TikTok
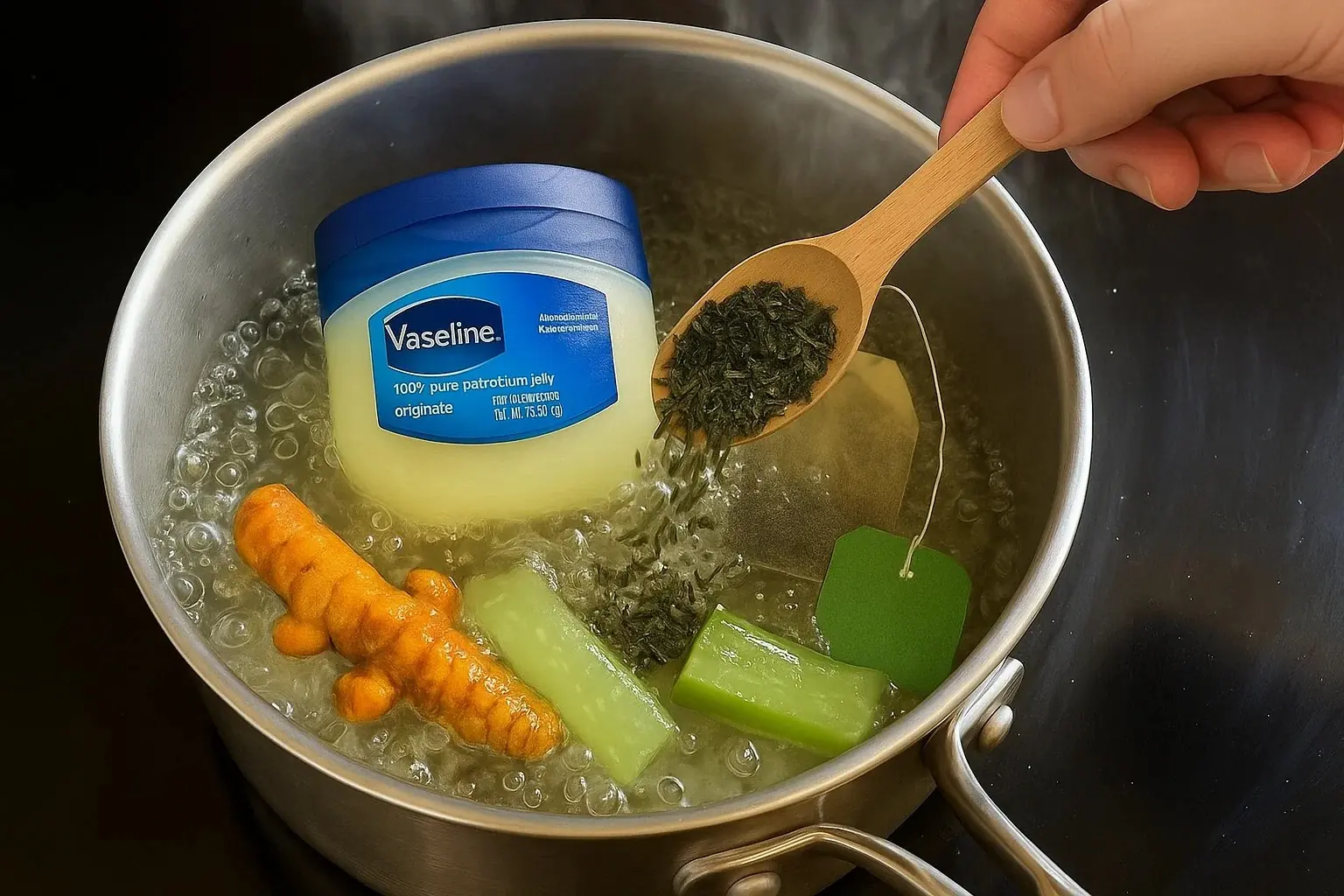

This DIY Botox serum using Vaseline and potent natural ingredients like rosehip oil, turmeric, and vitamin E is an affordable and effective alternative to expensive Botox treatments.
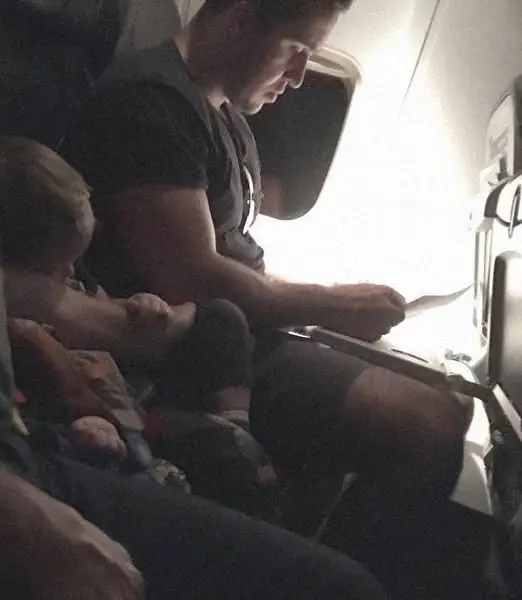

An anxious mother's late-night flight with her toddler became a testament to human kindness. Discover how a stranger's unexpected compassion and patience transformed a potentially stressful journey into a heartwarming lesson in empathy for all.

Many people go outside to use sunscreen to protect their skin. However, be mindful of this to avoid harming your health.

Specialized tools show that the actual room temperature is vastly different from the temperature set on the air conditioner.
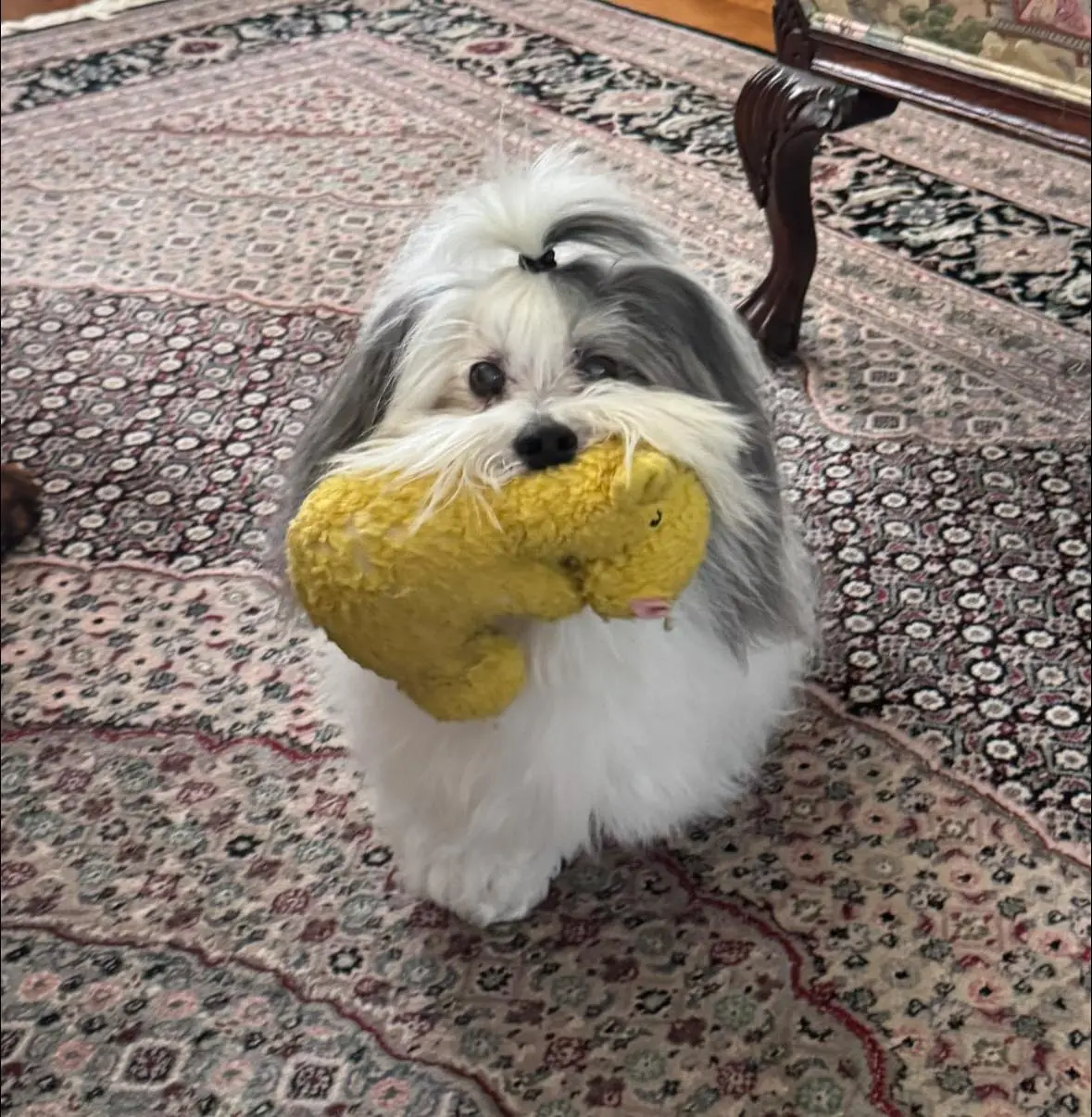

A heartfelt story about family, routine, and a loyal pup named Gordon who never forgets to show off his favorite toy—even when his best friend, Papa, is away in the hospital.

Washing machines are very convenient but they also have limitations; not everything can just be thrown in there and it's done.

D-Day 1944: Private Hillman found his mother's initials on his parachute. A heartwarming WWII story of maternal love and an unexpected connection.

5 Health Conditions Your Nails May Reveal

By drinking this tea daily, you provide your body with the essential nutrients needed to stimulate collagen production and protect the skin from oxidative stress.
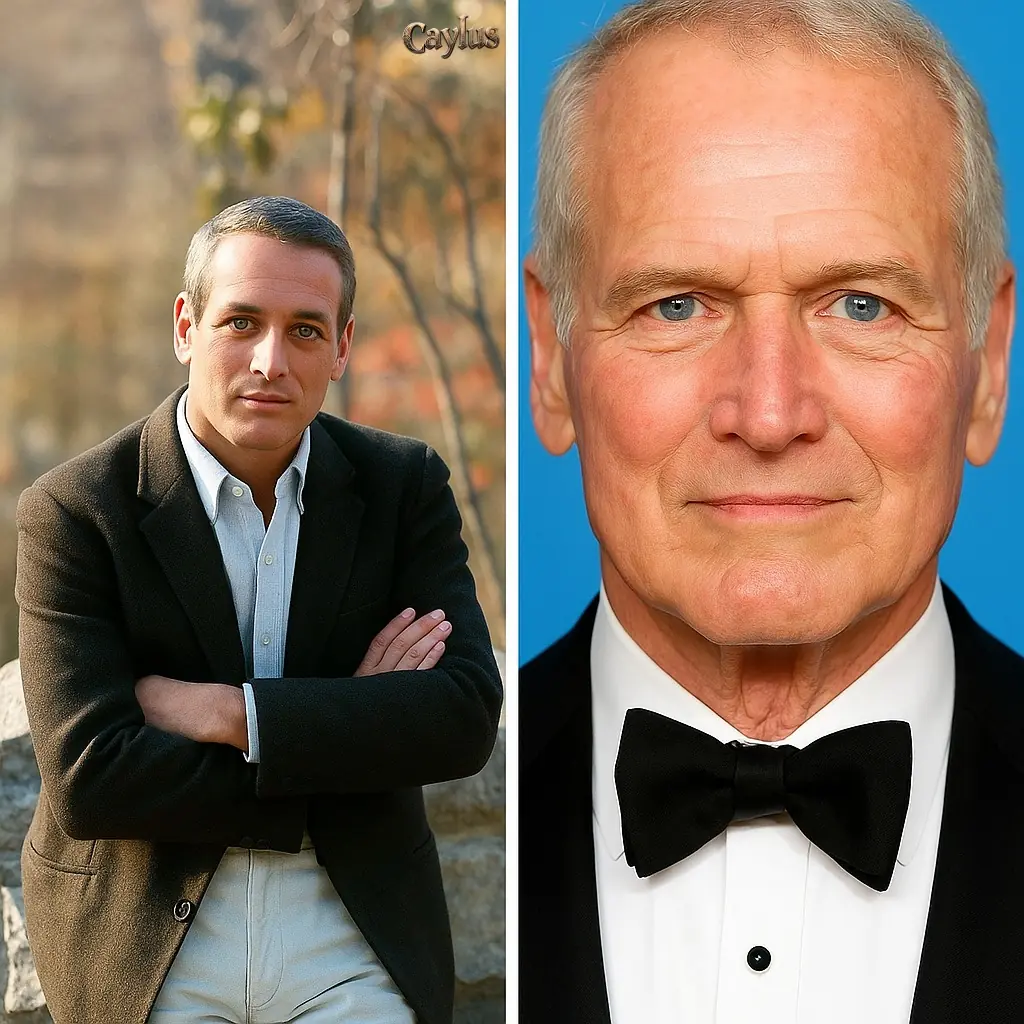

Discover how Paul Newman quietly redirected his movie perks to fund children’s hospitals, transforming his privilege into purposeful generosity, away from the spotlight.
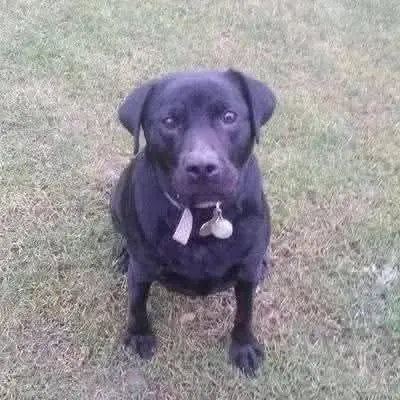

Meet Mollie, the sweet dog whose powerful instincts made her a fearless protector. This heartwarming story reveals her unwavering loyalty during a park incident and a medical emergency, a true testament to the human-animal bond and canine guardianship.
In this compelling story, Sonia Kovaleva overcomes class prejudice and mockery to prove her worth, showing that strength, resilience, and self-belief can overcome even the harshest of judgments.
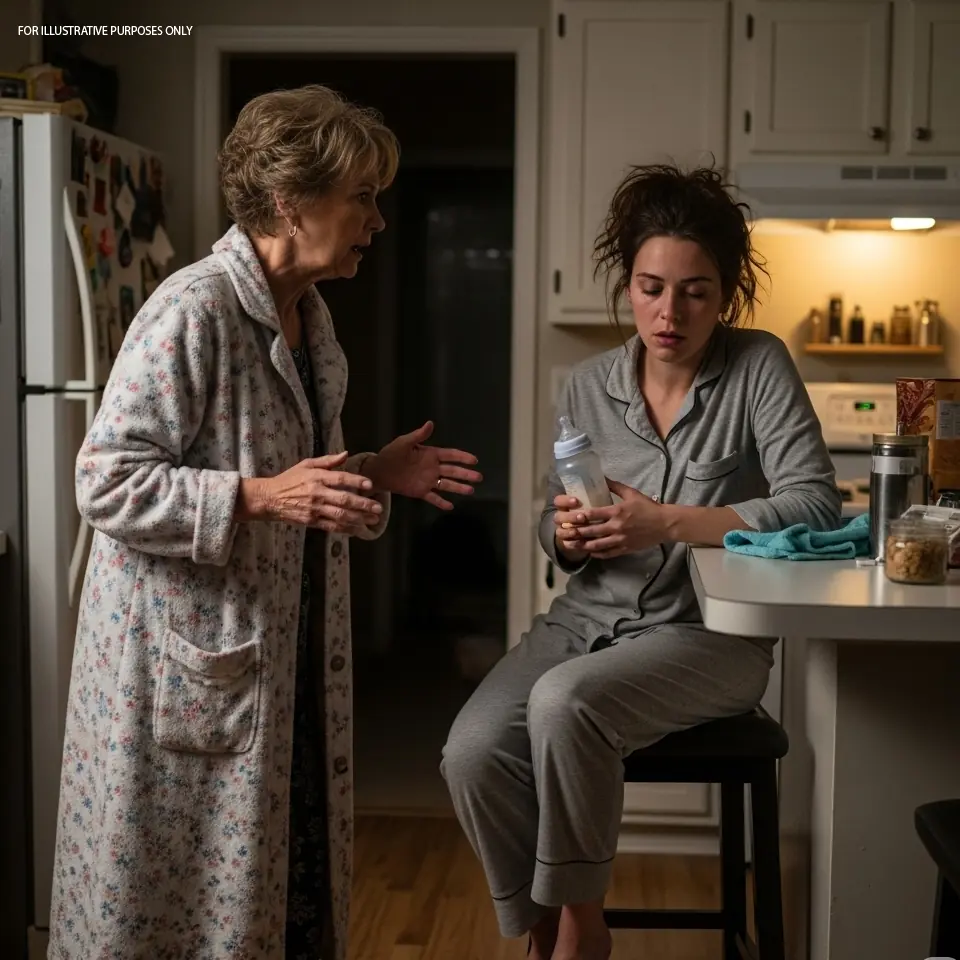

In this deeply emotional story, a mother-in-law learns to truly see her daughter-in-law and stands by her during the toughest moments. A journey of unconditional support, understanding, and healing that transforms their relationship.
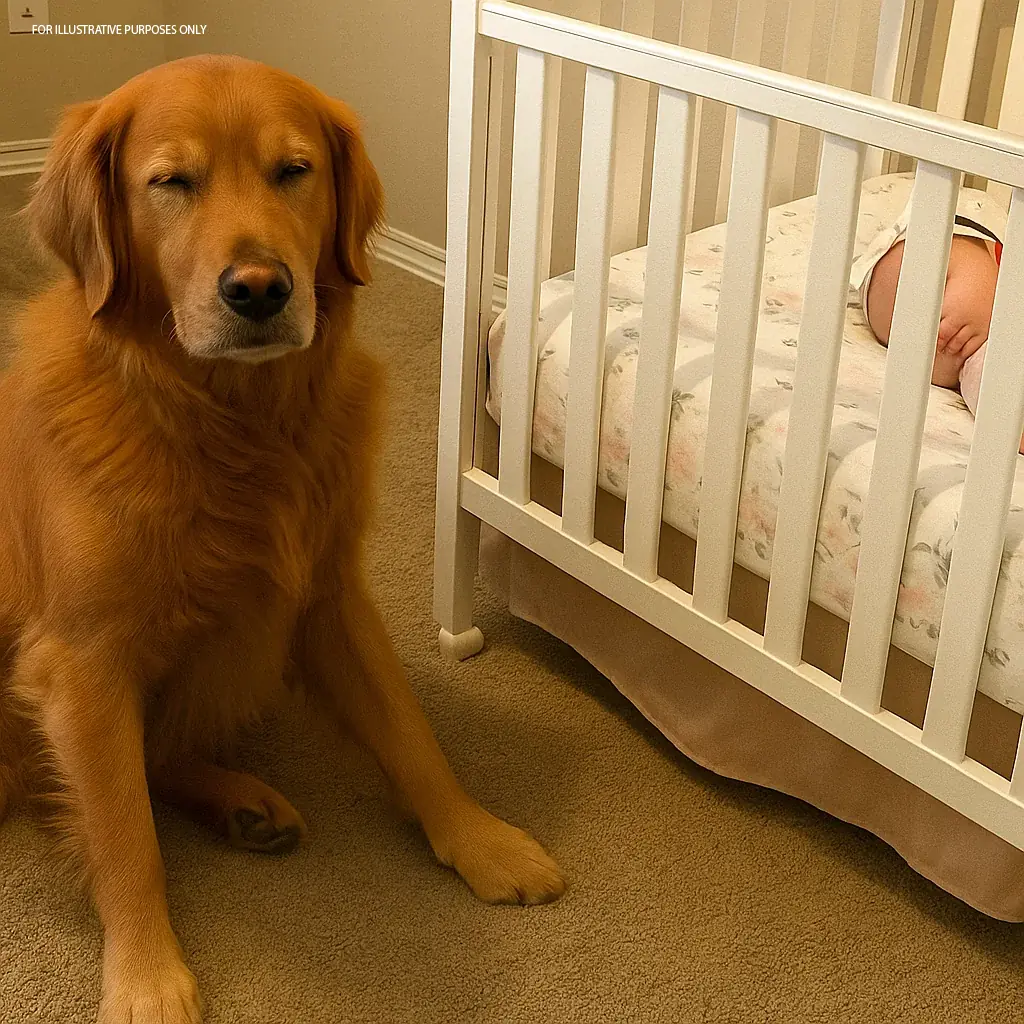

When our golden retriever, Beau, wouldn't stop barking at the nanny, we thought he was just being territorial. Maybe jealous. We even talked about rehoming him. But the night I checked the security footage, I saw something that made my stomach twist. Beau

By stimulating collagen production, improving circulation, and offering anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, clove oil helps reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin
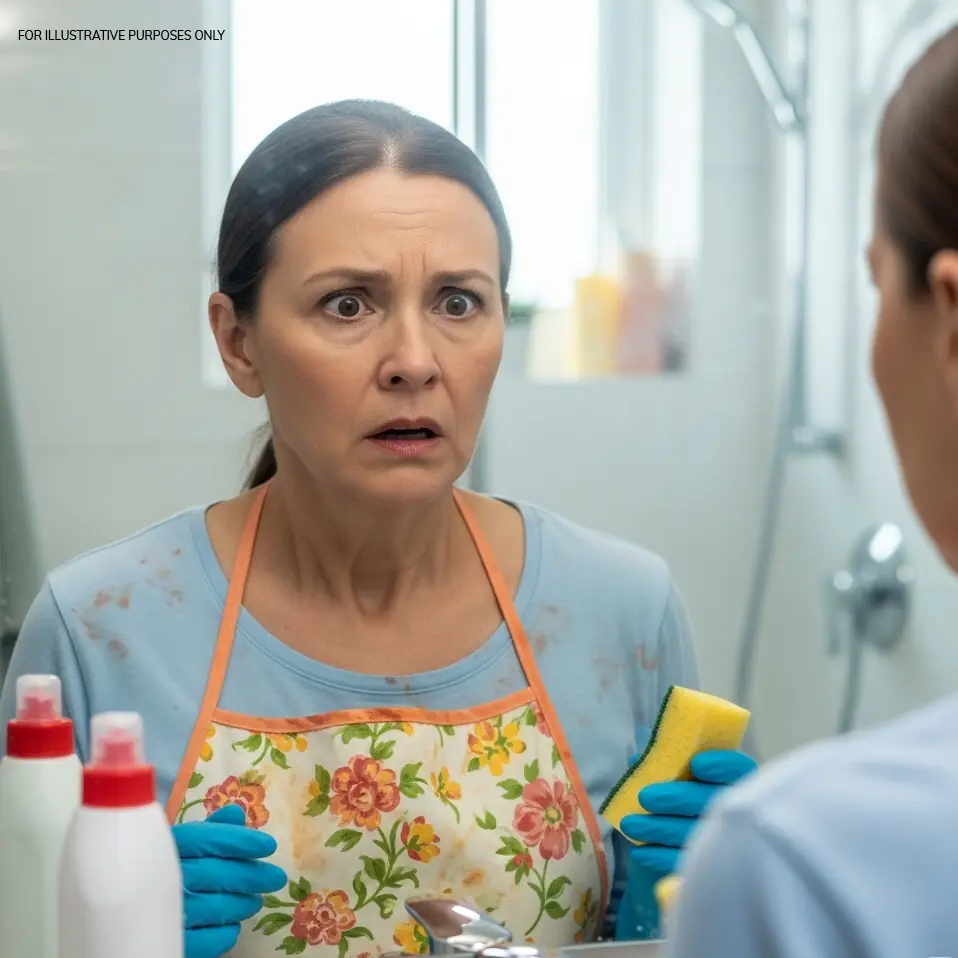

After years of neglect, a wife’s heartfelt request for a date leads to a painful realization for her husband. As they rediscover each other, they learn that true love starts with self-respect and self-care, transforming not just their relationship, but