10 Brilliant and Budget-Friendly Pet Hacks to Make Life Easier
Caring for pets doesn’t have to be expensive or stressful—these 10 easy hacks make life better for you and your furry friends!
Collagen is often called the "glue" that holds our bodies together. It’s a vital protein that keeps our skin youthful, joints flexible, and organs strong. But did you know there are many types of collagen, each with unique roles? In this guide, we dive into the history of collagen discovery, explain why Roman numerals are used, and explore the 5 most common types found in supplements and your body.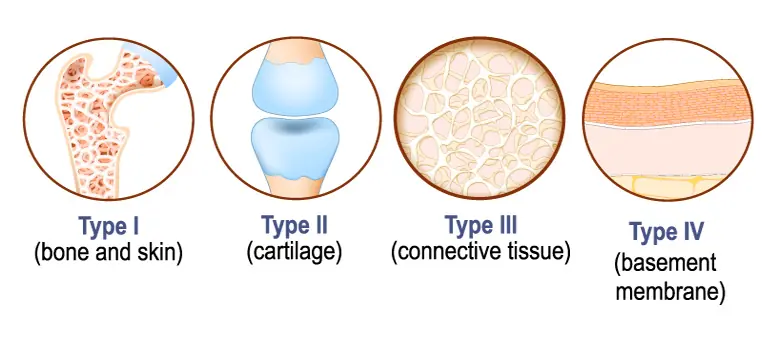
A Brief History: Collagen Discovery and the Roman Numeral Tradition
Nearly 100 years ago, histologists—scientists who study tissues—first identified Type I collagen. The early researchers, working in dimly lit basement labs, chose to label collagen types using Roman numerals—a tradition that continues today. Why Roman numerals? According to Dr. Cate, a collagen expert, it’s simply the style preferred by these pioneering scientists.
How Many Types of Collagen Are There?
The exact number of collagen types in the human body is still debated. Some studies suggest 16 types, others 28, and some claim there could be as many as 183 different forms. Mark Moyad, MD from the University of Michigan Medical Center, calls the science “in its infancy.”
Despite the uncertainty, we know collagen is critical to many bodily functions. In nutrition and supplements, five types stand out as most important—and these are the focus of our discussion.
The 5 Most Common Types of Collagen in Your Body and Supplements
Collagen supplements often highlight these types using Roman numerals:
Type I
Type II
Type III
Type V
Type X
Let’s explore each type’s unique role, sources, and benefits.
Type I Collagen: The Superstar of Collagens
Type I collagen accounts for approximately 90% of the collagen in your body. It is found throughout your skin, hair, nails, bones, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, organs, and even your eyes.
Think of Type I as the “Homecoming Queen” of collagen types, the most abundant and most sought after in supplements. Its primary function is to provide strength and structure, keeping tissues firm and resilient.
Best sources: Beef, bone broth, eggs.
Type II Collagen: The Joint Protector
Type II collagen is primarily found in cartilage, joints, and the gut lining. It plays a vital role in cushioning joints and supporting digestive health.
Studies, though small, have shown promising effects of Type II collagen supplements in alleviating rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Whether or not you believe anecdotal evidence, many users report relief and improved joint function.
Best sources: Chicken, bone broth.
Type III Collagen: The Structural Sidekick
Type III collagen often works alongside Type I and is a key component in organs, blood vessels, and muscle structure. It’s essential for maintaining the flexibility and integrity of blood vessels and organs.
A small study found that lack of Type III collagen was linked to vascular diseases, highlighting its importance in arterial health.
Best sources: Beef, bone broth, fish.
Type V Collagen: The Placenta and Cornea Contributor
Less known but incredibly important, Type V collagen is found in the placenta and the cornea of the eyes. It supports fetal development during pregnancy and contributes to eye health.
Pregnant women can safely take collagen supplements containing Type V, offering nutritional support for their growing baby.
Best sources: Eggs, multi-collagen supplements.
Type X Collagen: The Bone and Joint Builder
Type X collagen plays a critical role in the health of bones and joints, working behind the scenes to support cartilage and bone development.
Because Type X collagen is often sourced from eggshells and chicken cartilage, getting sufficient amounts from diet alone can be challenging.
Best sources: Eggs (especially eggshell membranes), chicken.
Lesser-Known Collagen Types
Other types, such as Type IV collagen, exist and serve specialized roles. For instance, Type IV supports the skin’s basement membrane and helps filter blood in kidneys. However, these are rarely included in supplements.
Collagen vs. Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
When shopping for supplements, be aware that most products contain hydrolyzed collagen peptides—broken-down forms that are easier for your body to absorb. Not all collagen types are equally represented in these products, so choosing a multi-collagen blend ensures you get a broad spectrum.
Final Thoughts: Why Collagen Matters
Whether for skin elasticity, joint comfort, or organ support, collagen is fundamental to our health. While science continues to uncover more about its many types, current research and customer testimonials affirm the benefits of collagen supplementation.
If you want the convenience of all five key types, look for multi-collagen products sourced from diverse animal origins like beef, chicken, fish, and eggs.

Caring for pets doesn’t have to be expensive or stressful—these 10 easy hacks make life better for you and your furry friends!

Certain foods can naturally help your body fight parasites while a holistic approach offers personalized care.

Feeling stuck in a rut? It’s time to reclaim your motivation and unlock your full potential.

Master the art of home cleaning by knowing exactly what to clean—and when—to keep your living space fresh and organized effortlessly.

Beat the heat with these nutritious and delicious beverages perfect for tropical climates and sunny days.

Master your cleaning routine by knowing exactly what tasks to tackle—and when—to keep your home fresh and inviting all year round.

Your diet plays a crucial role in immune health—learn which common foods might be harming your defenses and how to strengthen them naturally.

Incorporate these nutrient-packed foods into your diet to maintain electrolyte balance and promote optimal health.
Hormones play vital roles in regulating your body’s functions, affecting both physical and mental well-being.

Understanding the wide-ranging effects of sugar can help you make healthier choices and protect your well-being.

Discover how vinegar’s versatility can simplify cleaning, pest control, and even personal care in your daily life.

Discover easy homemade vinaigrette recipes that add a burst of freshness and zest to your meals.

Discover simple, effective ways to clean and care for your jewelry at home—no expensive trips needed!

Learn simple daily routines that calm inflammation and help protect your body from chronic diseases.

Never let a missing ingredient stop your baking — discover reliable swaps for spices, liquids, flours, and more!

Discover how the perfect marinade can transform simple salmon into a flavorful culinary delight.

Keep your plants thriving by understanding common signs of deficiencies and how to effectively treat them.

Learn how syncing your vitamin intake with meals and your daily schedule can improve nutrient absorption and boost your health

Discover houseplants that require minimal sunlight and are perfect for darker corners, offices, or rooms with limited natural light.





Caring for pets doesn’t have to be expensive or stressful—these 10 easy hacks make life better for you and your furry friends!

Certain foods can naturally help your body fight parasites while a holistic approach offers personalized care.


A woman’s kind act at T.J. Maxx helps a homeless woman with jeans, thanks to a caring program. Read the story! ❤️🛍️


Feeling stuck in a rut? It’s time to reclaim your motivation and unlock your full potential.

Barbie said David often expresses his love through acts of service and gift-giving.

Feeling invisible in a crumbling marriage, Jennifer plans a surprise getaway for her husband, only to face heartbre@king betrayal. Read how she finds strength and starts anew.

After years of struggle, a young couple finally secures their dream apartment—only to face unexpected family pressure. Discover how standing up for their new home becomes a powerful journey of independence and self-respect.

Tiana's life unravels when she notices a birthmark on her best friend Melisa's adopted son that's identical to the one her deceased son had. As she struggles to understand this impossible coincidence, Tiana uncovers a harrowing truth.

A runaway bride escapes an abu$ive wedding only to uncover a cr:u:el family plot. With unexpected help, she f!ghts for her future and reclaims her life in this gripping, emotional journey of betrayal and hope.
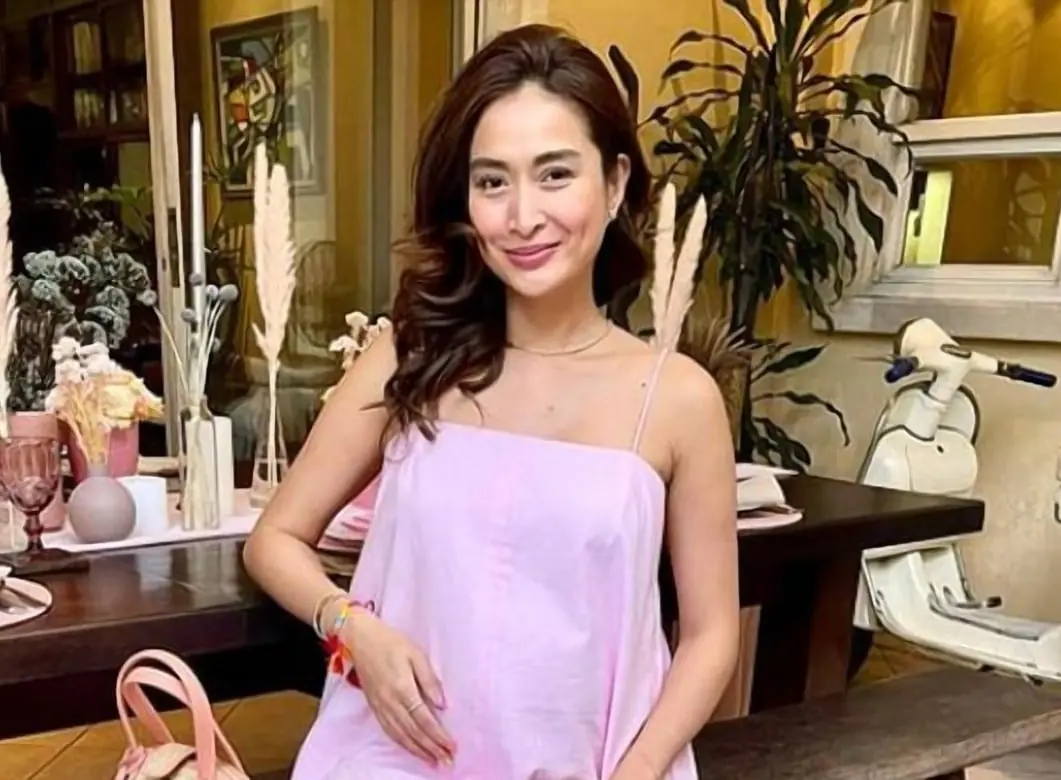



Phoemela’s career began in the world of modeling at just 14 years old. She joined the Pink Soda Club at 13, which paved the way for numerous projects, including commercials locally and internationally.
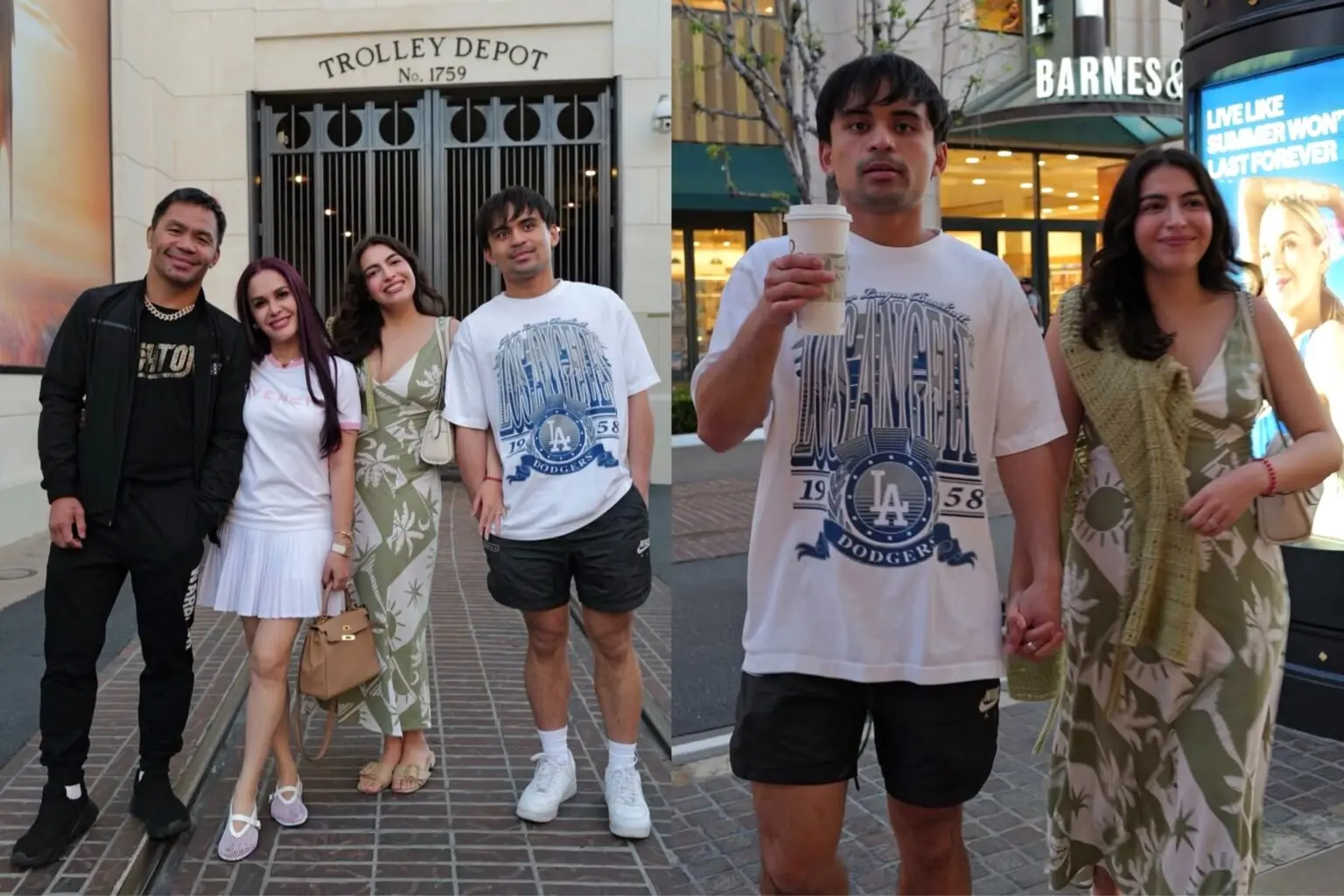

As of this time, Jimuel has not made any public statements regarding his alleged new romance.
