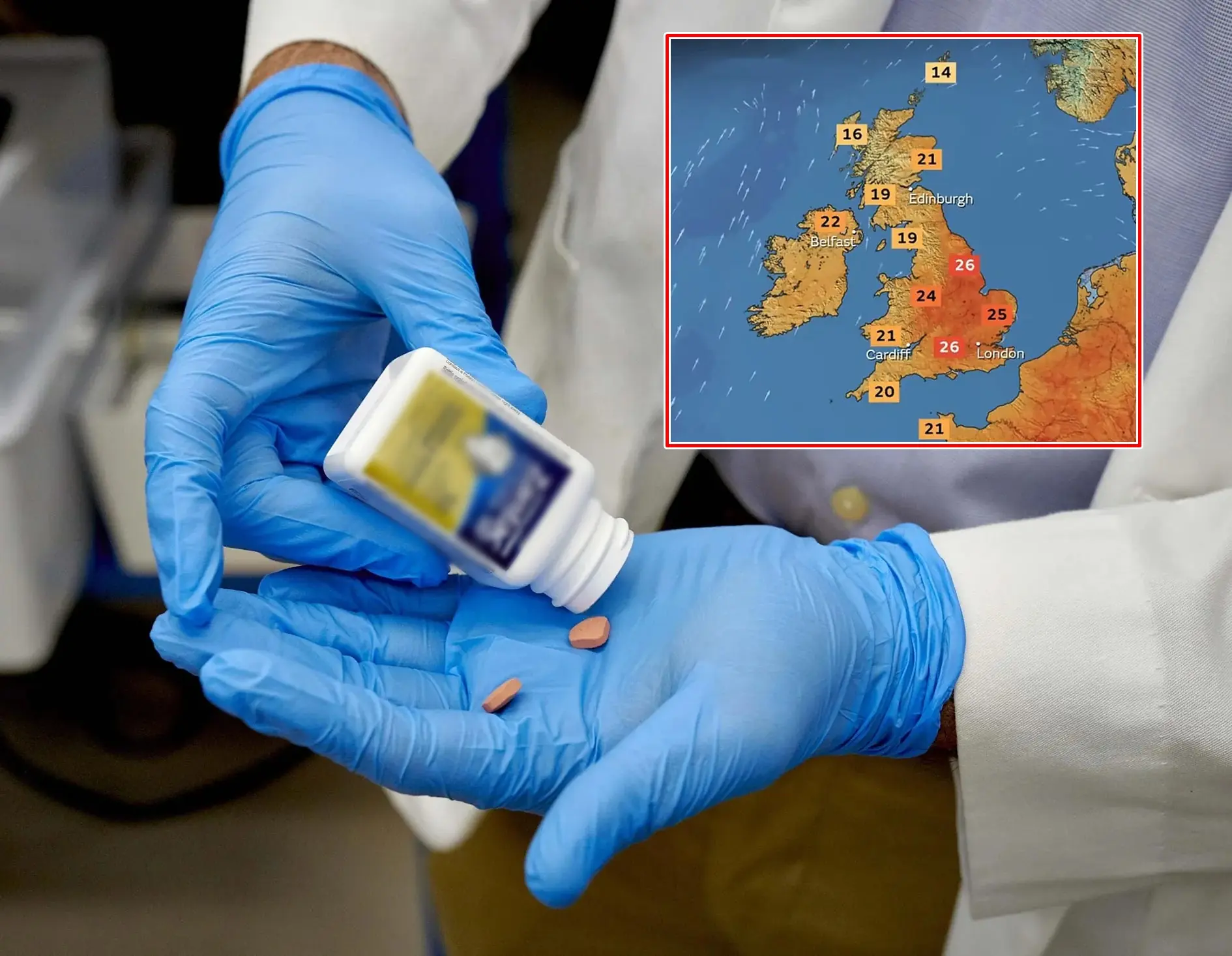

Warning over common over-the-counter drug that can fuel cancer in warm weather
It is crucial for individuals taking these medications to be aware of the potential risks and to take appropriate steps to protect their skin from harmful UV radiation.

In a groundbreaking clinical trial, Japanese scientists have achieved a significant advancement in Parkinson's disease treatment. Researchers at Kyoto University have successfully implanted lab-grown dopamine-producing neurons into Parkinson's patients using induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, a process that could potentially revolutionize treatments for Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases like ALS and Alzheimer’s.
This new method, developed by Kyoto University in collaboration with Sumitomo Pharma, marks the most advanced use of iPS cells in human neurology to date. The results are promising: patients showed significant motor improvements and increased dopamine activity, with minimal side effects.
Unlike previous attempts using fetal tissue, this new method uses genetically reprogrammed adult cells, addressing both ethical concerns and safety issues. The lab-grown neurons are implanted in patients' brains, with some showing up to a 63.5% increase in dopamine production. Importantly, the increased dopamine activity is localized precisely where the cells were implanted, reducing the risk of unwanted side effects.
The ability to produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is severely depleted in Parkinson's patients, could restore lost brain function and improve motor skills. This breakthrough marks a critical step in Parkinson's treatment, as it not only targets the symptoms of the disease but also works towards restoring the brain’s natural function.
This treatment’s impact could go beyond Parkinson’s disease. The success of this approach offers hope for treating other neurodegenerative diseases like Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, which share similar challenges in brain function. Scientists believe that this technology may serve as a model for developing treatments for a variety of conditions where brain function is impaired.
The next goal for the Japanese research team is regulatory approval, with plans to seek approval by late 2025 in Japan. If successful, this will make it the second approved iPS-based therapy in Japan, further cementing the country’s position as a global leader in regenerative medicine. With continued positive results and safety profiles, this treatment could redefine how we approach brain disorders and offer a beacon of hope for millions living with neurodegenerative diseases.
One of the key differences between this approach and previous methods is the use of adult cells rather than fetal tissue, which brings ethical concerns and risks. By using induced pluripotent stem cells, which are genetically reprogrammed adult cells, researchers have sidestepped these concerns while improving safety and efficacy. This breakthrough paves the way for personalized medicine and offers a sustainable solution to the ethical dilemma of using fetal tissue in medical treatments.
This new stem cell-based Parkinson’s treatment represents a significant milestone in medical science. With the potential to improve the quality of life for patients and offer a safer alternative to traditional treatments, this therapy is one step closer to regulatory approval. The results of this study have the potential to change the landscape of neurodegenerative disease treatment for years to come, offering hope for patients globally.
Kyoto University, Stem Cell Research Group
Sumitomo Pharma, Collaboration in Regenerative Medicine
"Parkinson’s Disease Treatment: A New Hope" — Published in Nature Medicine
Clinical Trial Reports by the Japan National Institute of Health and Medicine

It is crucial for individuals taking these medications to be aware of the potential risks and to take appropriate steps to protect their skin from harmful UV radiation.

Instead of relying on sleep aids or medications, individuals may be able to improve their sleep naturally by making small, sustainable changes to their diet.

With the rising temperatures and the potential for bacteria growth in the heat, it’s essential to adjust your food storage practices to ensure your meals remain safe and enjoyable.
While protein shakes have become a staple for many individuals looking to maintain muscle mass or lose weight, recent research suggests that these seemingly innocent supplements may pose significant risks to long-term health.



While many of these foods may be considered indulgent or "fancy," the risks they pose are very real and can have life-threatening consequences.











A groundbreaking app, Circadian AI, developed by a 14-year-old, uses machine learning to analyze heart sounds and detect early signs of heart disease with 96% accuracy in just seven seconds.

Mary's inspiring story of overcoming a turbulent childhood, discovering her roots, and finding love and happiness. A tale of resilience, self-discovery, and the power of family.

At 100, Layne Horwich faced bre@st canc3r with bravery. Learn how her active lifestyle, strong will, and a decision to undergo surgery helped her beat canc3r and inspire others to prioritize their health.

Inspired by Sandra Bullock's profound wisdom, this piece explores the power of choosing peace over retaliation. Learn how empathy, silent strength, and the courage to move forward define true resilience and foster personal growth in the face of disrespect

Mason Wartman’s Rosa’s Fresh Pizza turned $1 slices into a kindness movement. Read his story! ❤️🍕

Discover the history and beauty of Hàng Trống paintings, one of Vietnam's three most iconic folk art traditions. Learn about its cultural significance and lasting impact, showcased through the eyes of an artisan at work.

Ada Blackjack survived alone in the Arctic for two years, a forgotten hero. Discover her incredible story! ❤️❄️

Found tied up and heartbroken, one dog's life changed forever. Discover his journey from abandonment to a loving home, a powerful story of rescue, unconditional love, and the profound joy of giving a second chance to a deserving soul.

Discover the incredible journey of a family from hardship to success. From being placed in a Catholic orphanage to serving in WWII, this family's resilience and love for each other became their strength.

It is crucial for individuals taking these medications to be aware of the potential risks and to take appropriate steps to protect their skin from harmful UV radiation.

A wealthy father goes undercover as a poor man to test the sincerity of his son’s fiancée and her wealthy parents. Tension builds as the family tries to humiliate him, but an unexpected revelation leaves everyone speechless.

After being unfairly blamed for a mess at the office, Valya finds an unexpected ally in her office rival, Marianna. Together, they confront the CEO, and Valya learns the power of standing up for herself. A story of empowerment, confrontation, and self-wor

Instead of relying on sleep aids or medications, individuals may be able to improve their sleep naturally by making small, sustainable changes to their diet.

Lonely pensioner, Brenda, has spent most of her life providing shelter cats with a forever home. When her newest pet, Lucky, starts bringing home dollar bills, Wendy quickly realizes something suspicious is happening in her neighborhood.

With the rising temperatures and the potential for bacteria growth in the heat, it’s essential to adjust your food storage practices to ensure your meals remain safe and enjoyable.

While protein shakes have become a staple for many individuals looking to maintain muscle mass or lose weight, recent research suggests that these seemingly innocent supplements may pose significant risks to long-term health.



A strange sound from the bathroom on a cross-country flight gives flight attendant Lenna a terrible fright. Little does she realize that the kid inside will forever change her life.

While many of these foods may be considered indulgent or "fancy," the risks they pose are very real and can have life-threatening consequences.
