
If You Have These Tiny Red Dots On Your Arm, Do Not Ignore The Warning Signs
In the UK, doctors have issued an urgent health warning about a concerning increase in the incidence of scabies, a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites. Recently, more and more individuals have reported developing tiny red dots on their skin, often appearing on their arms and wrists, as a result of scabies. Though not typically a life-threatening condition, scabies can cause significant discomfort, with symptoms including severe itching, skin rashes, and even secondary infections if left untreated. Given the growing number of cases in northern England, experts are stressing the importance of seeking medical attention if you notice these red spots on your skin, as well as taking proper precautions to prevent spreading the infection to others.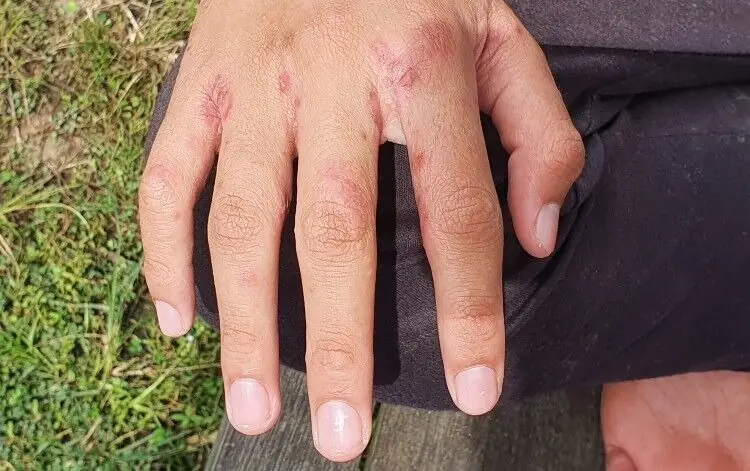
This warning comes in the wake of an alarming increase in scabies cases, as well as a rise in other infectious diseases affecting individuals in the UK. With more people experiencing symptoms like headaches, muscle aches, and diarrhea, it is vital to address these symptoms early to avoid serious complications. In this article, we will explore what scabies is, its symptoms, how it spreads, and why it's important to seek treatment promptly.
What is Scabies and What Are the Symptoms?
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by microscopic mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These tiny mites burrow under the skin, where they lay eggs that hatch into larvae, causing irritation and itching as they move through the skin’s layers. The condition is primarily characterized by the appearance of small, red dots or bumps on the skin, as well as intense itching that typically worsens at night.
Professor Kamila Hawthorne, chairwoman of the Royal College of GPs, explained, “While not a serious condition, scabies can be very itchy and irritating. If not properly treated, it can spread and increase a patient’s risk of complications, such as secondary skin infections, or make existing skin conditions worse.”
The most common symptoms of scabies include:
- Intense Itching: This is often the first and most noticeable symptom, particularly at night when the mites are most active.
- Rashes and Red Spots: Scabies typically causes small red dots, similar to insect bites, to appear on the skin, especially around the wrists, elbows, and between the fingers.
- Sores or Crusted Skin: If the condition progresses, scratching the itchy spots can cause sores and potentially lead to secondary bacterial infections.
- Blisters or Pustules: In some cases, blisters or pustules may form around the affected areas, causing more discomfort.
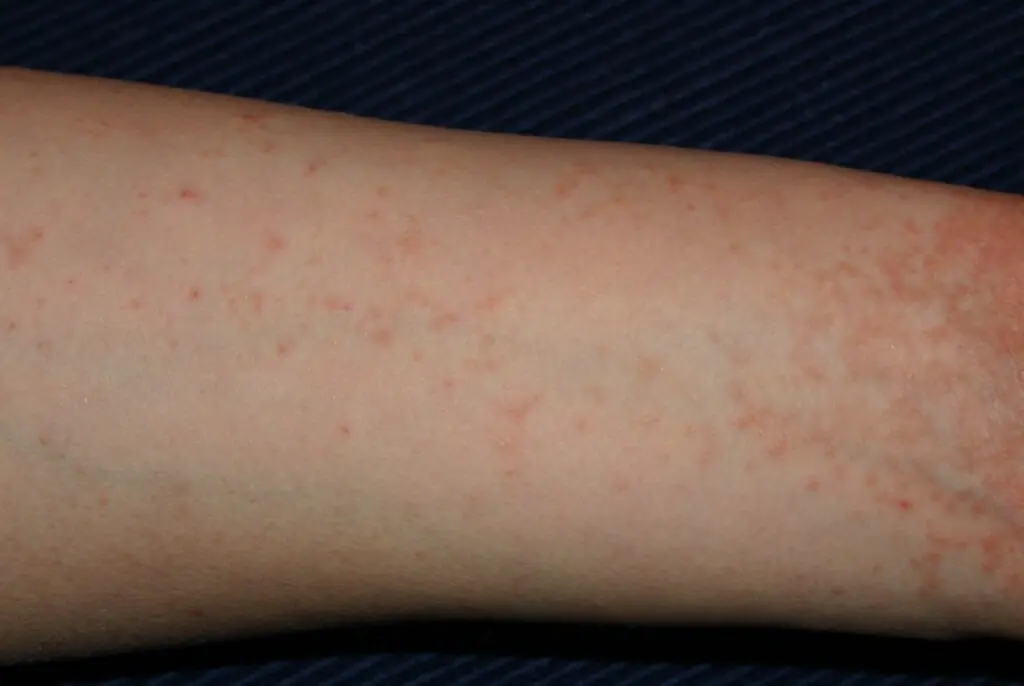
As scabies can spread rapidly through close physical contact, it is important to be aware of its signs and seek treatment as soon as possible. If left untreated, scabies can cause significant distress and complications, making early detection essential.
How Can Scabies Be Contracted?
Scabies is highly contagious and spreads through prolonged physical contact, particularly in environments where people are in close contact with one another, such as schools, dormitories, and crowded living situations. The mites are transferred from person to person through skin-to-skin contact, making individuals in close proximity-such as family members, classmates, or sexual partners-more susceptible.
One of the reasons for the rising number of cases in northern England, as reported by health professionals, is the high rate of social interaction among young adults and schoolchildren. "Schools and young adults are particularly susceptible to scabies because of their high social interaction rates," said Professor Hawthorne. "Given how intimate you’re becoming with others in such a situation, it can also be detected if you have several sexual partners."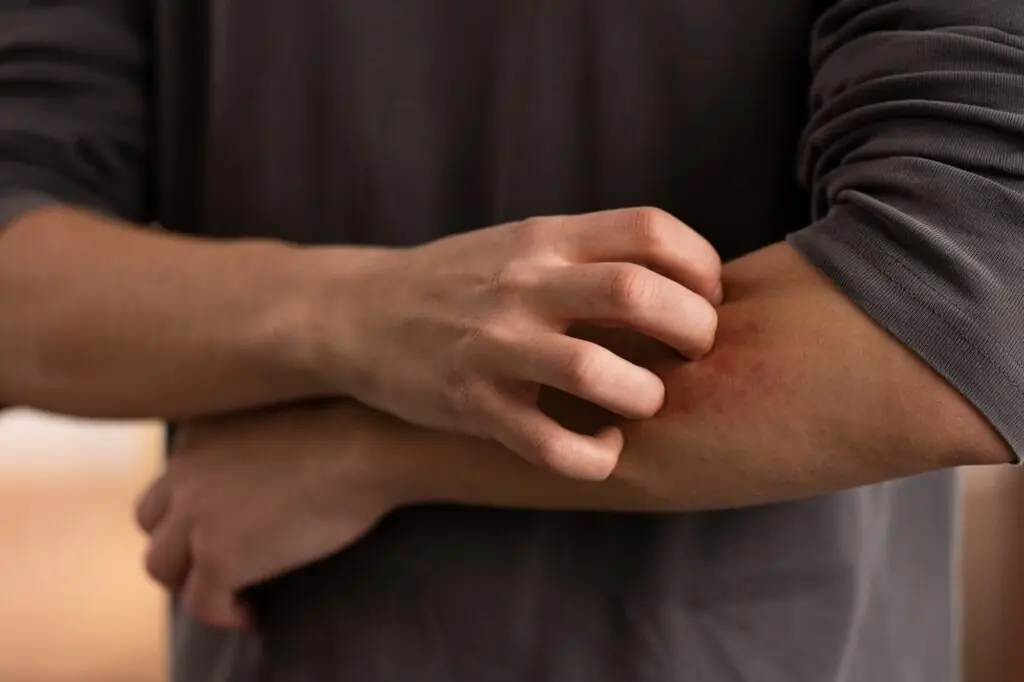
In addition to direct skin contact, scabies can also be transmitted by sharing clothing, bedding, or towels with an infected person. The mites can survive on clothing and bedding for up to 72 hours, so it's essential to wash these items thoroughly in hot water (around 60 degrees Celsius) to kill any remaining mites.
If washing clothing and bedding at such high temperatures is not possible, it's advisable to place the items in a sealed bag for at least three days to ensure the mites are eliminated.
The Importance of Seeking Treatment
While scabies is not life-threatening, it can lead to significant discomfort and, if left untreated, can cause more serious complications. Professor Hawthorne emphasized that despite the social stigma often associated with scabies, individuals who believe they may be infected should not hesitate to seek medical attention. “We recognise that patients may be apprehensive to seek treatment given the social stigma that surrounds the condition, but it is important that they don’t ignore their symptoms as this could lead to them getting worse and risks transmitting the condition to other people,” she stated.
The initial stages of scabies are typically manageable with prescribed treatments, such as topical creams or lotions that kill the mites. However, if left untreated, scabies can lead to secondary infections, such as impetigo, which may require more aggressive treatment, including antibiotics. In severe cases, if the skin becomes infected or if individuals scratch the affected areas excessively, the risk of complications such as cellulitis (a skin infection) or sepsis (a life-threatening infection) increases.
It is also crucial to treat all individuals who have had close contact with the infected person to prevent further spread of the condition. "Don’t hide away if you have scabies," Professor Hawthorne advised. "It is really uncomfortable, but you can get creams and lotions to help ease the pain. In addition, if the bites worsen, the illnesses may cause something more serious."
The Social Stigma of Scabies
One of the primary challenges in addressing scabies is the social stigma that often surrounds it. Many people mistakenly associate scabies with poor hygiene or unclean living conditions, which is simply not true. Anyone can get scabies, regardless of their cleanliness, and it is a common misconception that scabies only affects people who live in unhygienic environments.
This stigma can discourage people from seeking help, leading to untreated cases and the spread of the condition. Professor Hawthorne emphasized the importance of breaking the stigma, stating, "Although there is a 'social stigma' associated with the illness, this shouldn’t stop those who are affected from getting the assistance they may require."
Public awareness campaigns and open discussions about scabies are essential in reducing the stigma and encouraging individuals to seek treatment when they experience symptoms. Health professionals must continue to educate the public about the importance of early intervention and the effectiveness of treatment options.
Preventing the Spread of Scabies
Preventing the spread of scabies requires a combination of personal hygiene and environmental measures. If you or someone in your household is diagnosed with scabies, it’s important to follow these steps to minimize the risk of transmission:
- Seek Medical Treatment: If you experience symptoms of scabies, such as itching, red spots, or rashes, consult a healthcare provider promptly to get the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
- Wash Clothing and Bedding: Wash all clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water to kill any mites. If washing at high temperatures is not possible, seal items in a bag for three days.
- Avoid Close Contact: Limit physical contact with others until you have completed the necessary treatment. This helps prevent the spread of scabies to others.
- Treat Close Contacts: If you have scabies, ensure that anyone who has had close contact with you, such as family members or sexual partners, also seeks treatment to prevent reinfection.
Conclusion
Scabies is a common but highly contagious skin condition that can cause significant discomfort and distress if left untreated. While it is not a life-threatening condition, its symptoms-such as intense itching, rashes, and small red dots-should not be ignored. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing scabies and preventing complications, such as secondary infections.
Despite the social stigma surrounding scabies, it is essential for individuals who suspect they have the condition to seek medical attention promptly. By following appropriate treatment protocols, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with others, individuals can effectively manage scabies and reduce the risk of transmission.
If you experience any of the symptoms of scabies, such as itching, red spots, or rashes, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider as soon as possible. With the right treatment, scabies can be easily managed, and the discomfort associated with the condition can be alleviated. Don’t let the stigma prevent you from seeking help-your health and well-being are worth it.
News in the same category

An unusual abdominal sign warns of severe fa:tty l!ver: If you see it, get checked immediately.
A gastroenterologist has suggested how to recognize fatty liver disease from an unusual sign in the abdomen.

A 33-year-old woman with metastatic canc3r is healthy 3 years later thanks to consistently doing one thing: "If I'd waited longer, things would be different."
Stunned after receiving the health check results, the 33-year-old woman still felt fortunate because she had detected the dangerous disease in time and still had a chance for treatment.

Don't buy these 3 kinds of oysters; even seafood shop owners won't let their families consume them.
If you want to buy good and clean oysters to eat, you must immediately avoid these types.

Straight vs. curved cucumbers: Which tastes better? My mother, with 40 years of farming experience, shares 3 key secrets.
The 'beautiful' things may have deceived you!

Beyond superstition: 5 items placed at your bedside secretly "drain" your health, leaving you more tired the more you sleep.
Green pots, plush bears, and small decorative items are all commonly seen objects in the bedrooms of many families. However, they can completely affect your health.

Is showering 2-3 times a day good in hot weather? Doctors warn certain bathing habits increase stroke risk.
In hot weather, many people have the habit of showering 2-3 times a day to cool down their bodies. However, is this habit good for health?
A 22-year-old man developed k!dney failure, fa:tty l!ver, and gout simultaneously, regretting drinking one type of beverage for four years.
A 22-year-old young man named Wang Yi, from Taiwan (China), went for a check-up and was unexpectedly diagnosed with kidney failure, fatty liver disease, and gout.

Eating too much of these 5 vegetables is like "poisoning" your liver, and the first one is on almost every family's dinner table.
The liver is an important detoxifying organ of the body. However, some familiar vegetables in daily meals can become silent 'enemies,' harming the liver if not used properly.

Woman suffers severe consequences after using bee stings to treat breast canc3r
Having breast cancer but not going to the hospital for treatment, instead opting for honeybee stings at home, the woman in Ho Chi Minh City has to bear the heavy consequences as the tumor complicates and metastasizes to many places.

Everyone knows canc3r can be hereditary, but which types of cancer have a higher risk?
Some hereditary cancers related to genetic mutations, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer, can be managed and screened early thanks to genetic counseling.

Prolonged "minor ailments" could indicate canc3r, so beware of these 7 signs.
If you continuously experience headaches, loss of appetite, dry cough, and continuous weight loss... you need to see a doctor immediately as this could be a sign of cancer.
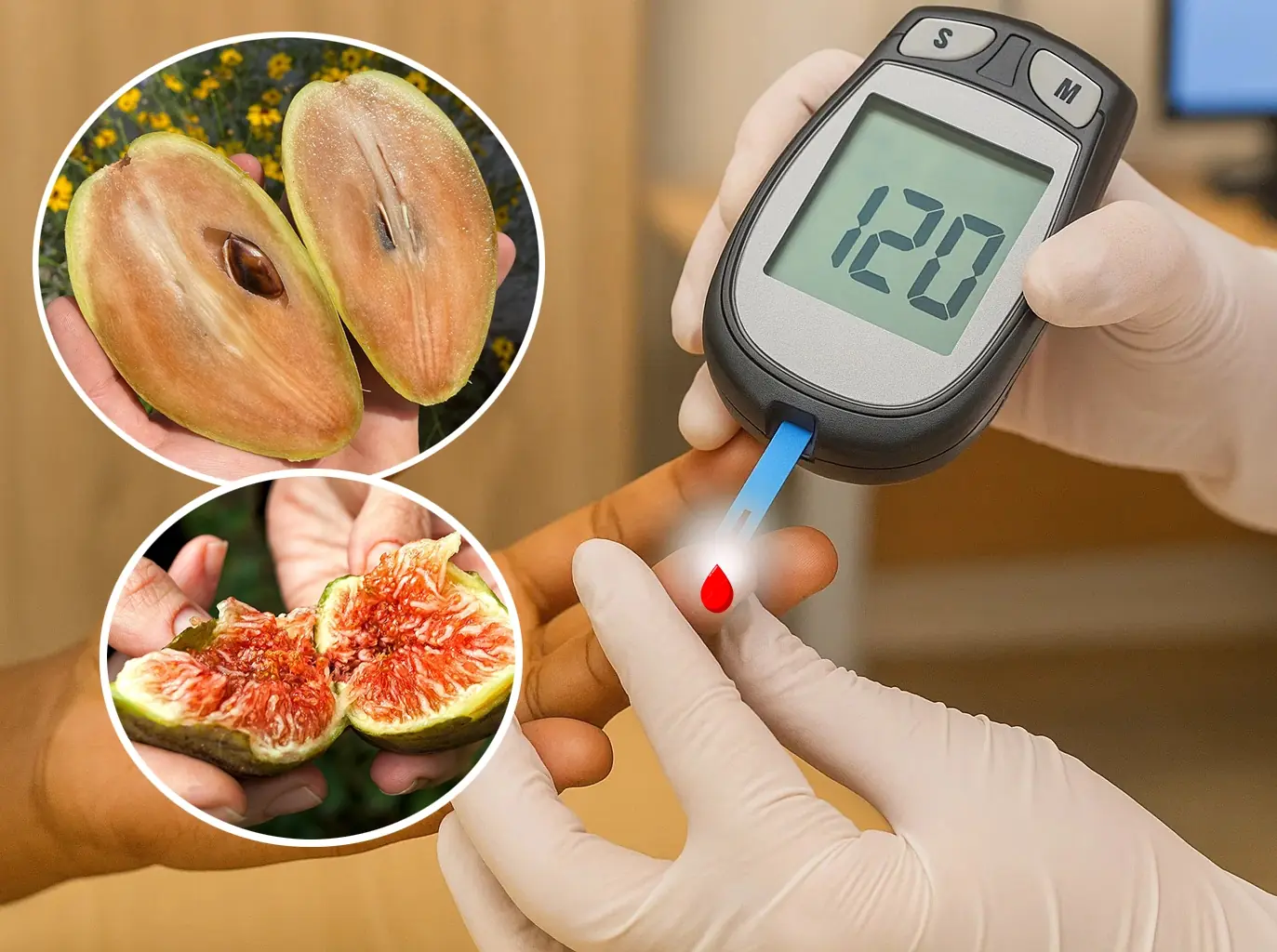
8 types of fruit that contain a lot of sugar should be limited to reduce the risk of diabetes and protect health
Fruit is good for you, but certain kinds contain a lot of sugar. Overeating can impact your health by raising blood sugar levels.

Hidden St0mach Canc3r Risk: How H. Pylori Infection Can Lead to Silent Canc3r and What You Need to Know
Learn about the link between Helicobacter pylori infection and stomach canc3r. Discover how this common food and waterborne bacteria could lead to silent canc3r and how early detection and treatment can help prevent it.
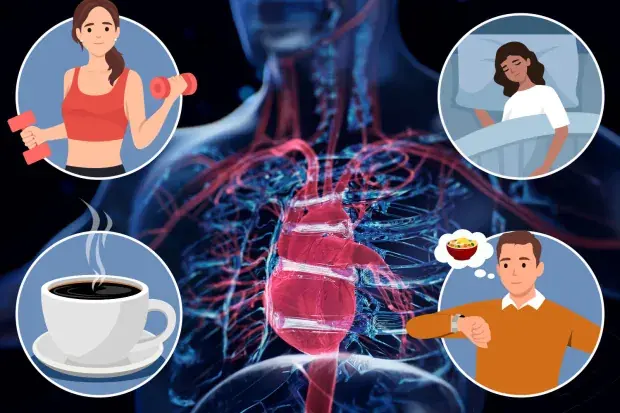
5 Simple Habits to Slash Heart Att@ck and Stroke Risks - Experts Reveal the Secrets
Discover 5 easy daily habits that can significantly reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. From exercise to diet, learn how small lifestyle changes can protect your heart and improve overall health.
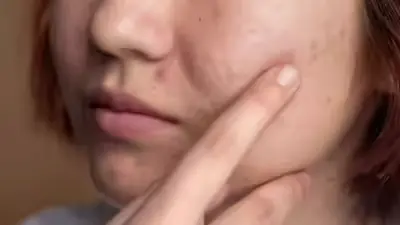
4 Visible Signs of Fatty Liver Dise@se on Your Face and How to Recognize Them
Discover the 4 common facial signs of fatty liver disease (NAFLD) like puffiness, skin discoloration, and acne. Learn how liver health affects your skin and when to seek medical help.
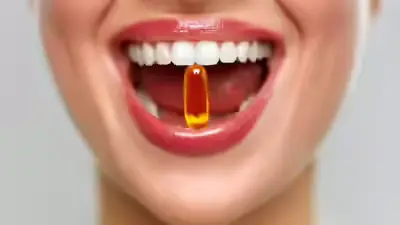
Vitamin D Can Reduce Tooth Decay by 50%, Study Finds: A Natural Solution to Dental Health
Discover how vitamin D can reduce tooth decay by 50%. Learn about its role in preventing dental caries, the link between vitamin D and oral health, and more in this detailed guide.
3 habits that "destroy blood vessels" faster than eating fatty meat: Many people still do them carelessly every summer
There are other causes of "damaging blood vessels" besides eating a lot of fatty meat and fatty foods. Three frequent summertime activities can also damage blood vessels, according to physicians.

Top 3 Seeds and 3 Drinks to Reduce Bloating, According to a Renowned Gastroenterologist
Discover the top seeds and drinks recommended by Dr. Saurabh Sethi to reduce bloating. Learn about sesame, flax, chia seeds, and drinks like ginger tea, kefir, and more.

There's a secret on b33r bottle caps: Target this point to open them easily by hand.
Many people have used their teeth, the edge of a table, or the armrest of a chair to open beer bottle caps – both dangerous and likely to cause damage. In fact, there is a special 'weak point' on beer bottle caps. Just aim correctly at this spot, and yo
News Post

When washing dishes, follow this method to remove all chemicals: Don't rush and risk "eating" detergent.

An unusual abdominal sign warns of severe fa:tty l!ver: If you see it, get checked immediately.
A gastroenterologist has suggested how to recognize fatty liver disease from an unusual sign in the abdomen.

A 33-year-old woman with metastatic canc3r is healthy 3 years later thanks to consistently doing one thing: "If I'd waited longer, things would be different."
Stunned after receiving the health check results, the 33-year-old woman still felt fortunate because she had detected the dangerous disease in time and still had a chance for treatment.

Don't buy these 3 kinds of oysters; even seafood shop owners won't let their families consume them.
If you want to buy good and clean oysters to eat, you must immediately avoid these types.

Straight vs. curved cucumbers: Which tastes better? My mother, with 40 years of farming experience, shares 3 key secrets.
The 'beautiful' things may have deceived you!

Beyond superstition: 5 items placed at your bedside secretly "drain" your health, leaving you more tired the more you sleep.
Green pots, plush bears, and small decorative items are all commonly seen objects in the bedrooms of many families. However, they can completely affect your health.

Is showering 2-3 times a day good in hot weather? Doctors warn certain bathing habits increase stroke risk.
In hot weather, many people have the habit of showering 2-3 times a day to cool down their bodies. However, is this habit good for health?

A 22-year-old man developed k!dney failure, fa:tty l!ver, and gout simultaneously, regretting drinking one type of beverage for four years.
A 22-year-old young man named Wang Yi, from Taiwan (China), went for a check-up and was unexpectedly diagnosed with kidney failure, fatty liver disease, and gout.

2-Step Korean-Inspired Glowup Routine: Achieve Radiant, Youthful Glass Skin At Home
The combination of rice, flaxseed, and other nourishing ingredients offers numerous benefits, from boosting hydration to fighting free radicals and improving skin texture. Follow this routine consistently, and you’ll be on your way to achieving the cove

Eating too much of these 5 vegetables is like "poisoning" your liver, and the first one is on almost every family's dinner table.
The liver is an important detoxifying organ of the body. However, some familiar vegetables in daily meals can become silent 'enemies,' harming the liver if not used properly.
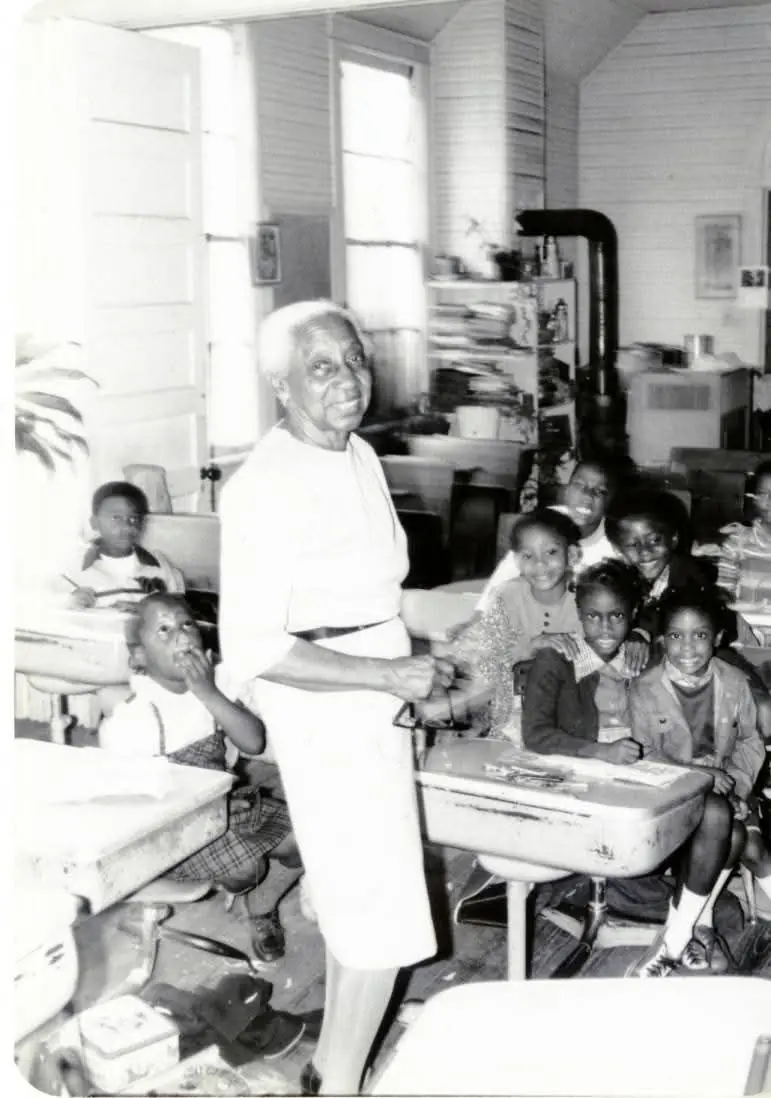

The Legacy of Ruby Middleton Forsythe: A Lifelong Advocate for Education and Civil Rights
Discover the inspiring life of Ruby Middleton Forsythe, a dedicated educator who shaped the future of African-American children in South Carolina, teaching for over six decades despite adversity.

A 14-Year-Old’s Work Ethic: How One Young Girl’s Determination is Shaping Her Future
Discover the inspiring story of a 14-year-old girl who took the initiative to get a job, worked hard, and is saving for her future. Learn how determination and responsibility are shaping her dream to become a doctor.

Woman suffers severe consequences after using bee stings to treat breast canc3r
Having breast cancer but not going to the hospital for treatment, instead opting for honeybee stings at home, the woman in Ho Chi Minh City has to bear the heavy consequences as the tumor complicates and metastasizes to many places.
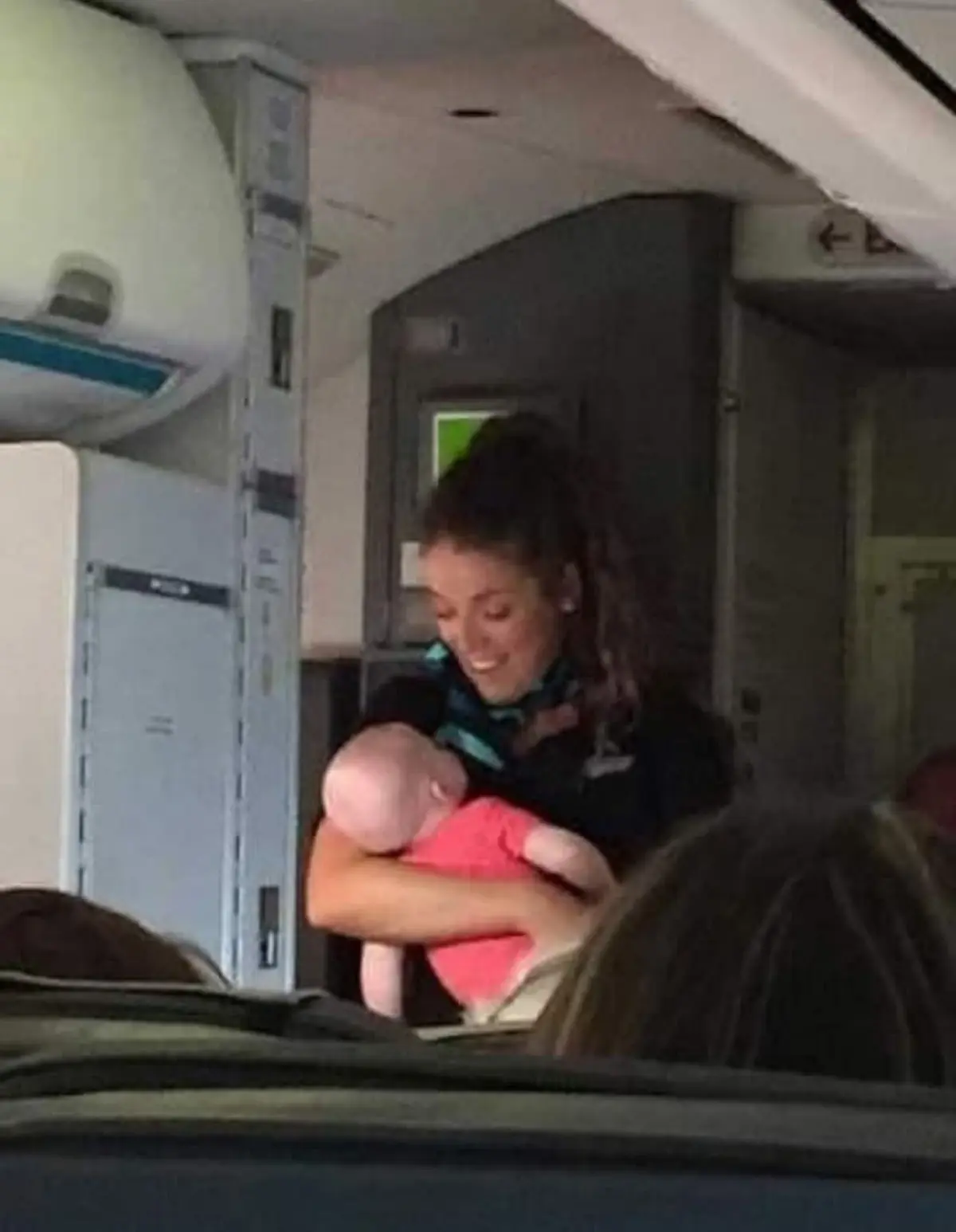

Mid-Flight Miracle: How a WestJet Flight Attendant Became a Baby-Whispering Hero
A family's challenging flight with a crying 4-month-old was transformed by the extraordinary kindness of a WestJet flight attendant. Discover this heartwarming story of empathy and going above and beyond in customer service.
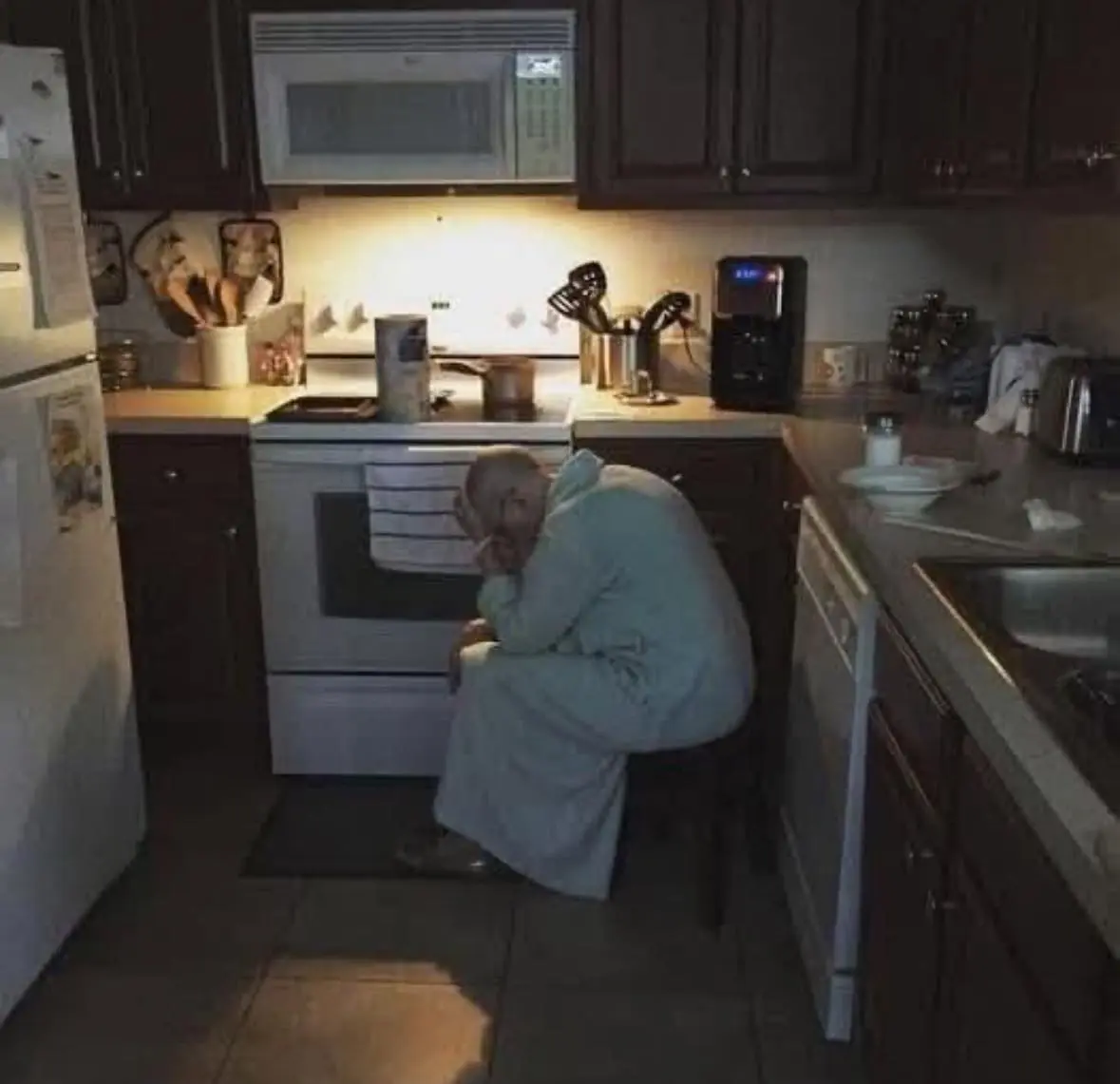

Quiet Strength and Southern Grace: The Unseen Heroism of a Mother-in-Law Named Sharon
Discover the powerful story of Sharon, a mother-in-law whose quiet resilience and unwavering love carried her family through cancer, caregiving, and grace under pressure.
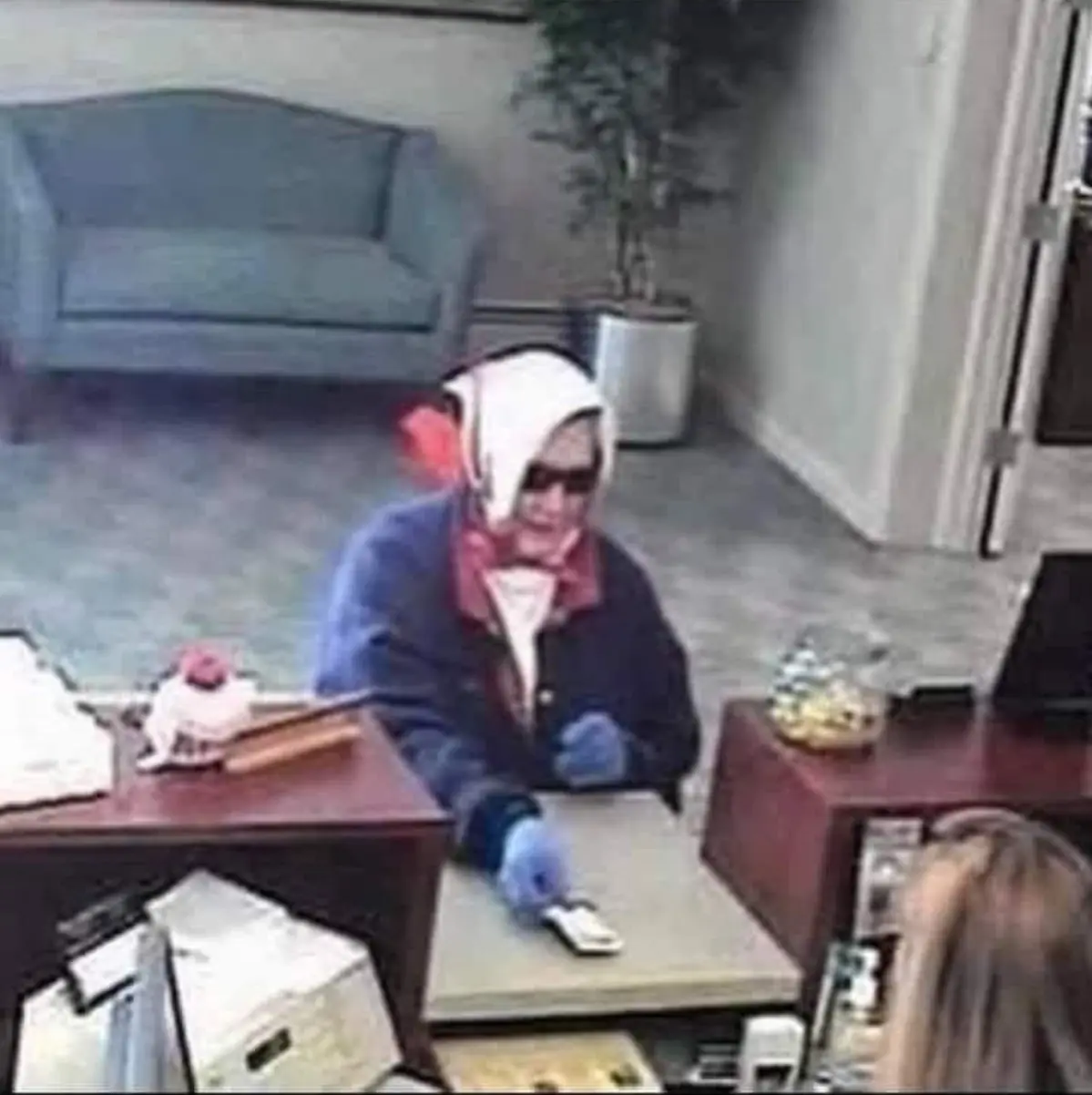

The Wisdom of Experience: How a $10 Withdrawal Taught a Bank Teller a Priceless Lesson
An elderly customer's request for a $10 withdrawal led to a viral moment of hidden wisdom. This compelling story reveals how patience and respect for elders can transform interactions, offering a powerful lesson in customer service and human dignity.

DIY Flaxseed Gel & Okra Hair Gel for Natural Hair Growth and Frizz-Free Shine
By incorporating these DIY treatments into your routine, you can achieve healthier, shinier, and fuller hair—without relying on harsh chemicals or expensive products.

Everyone knows canc3r can be hereditary, but which types of cancer have a higher risk?
Some hereditary cancers related to genetic mutations, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer, can be managed and screened early thanks to genetic counseling.
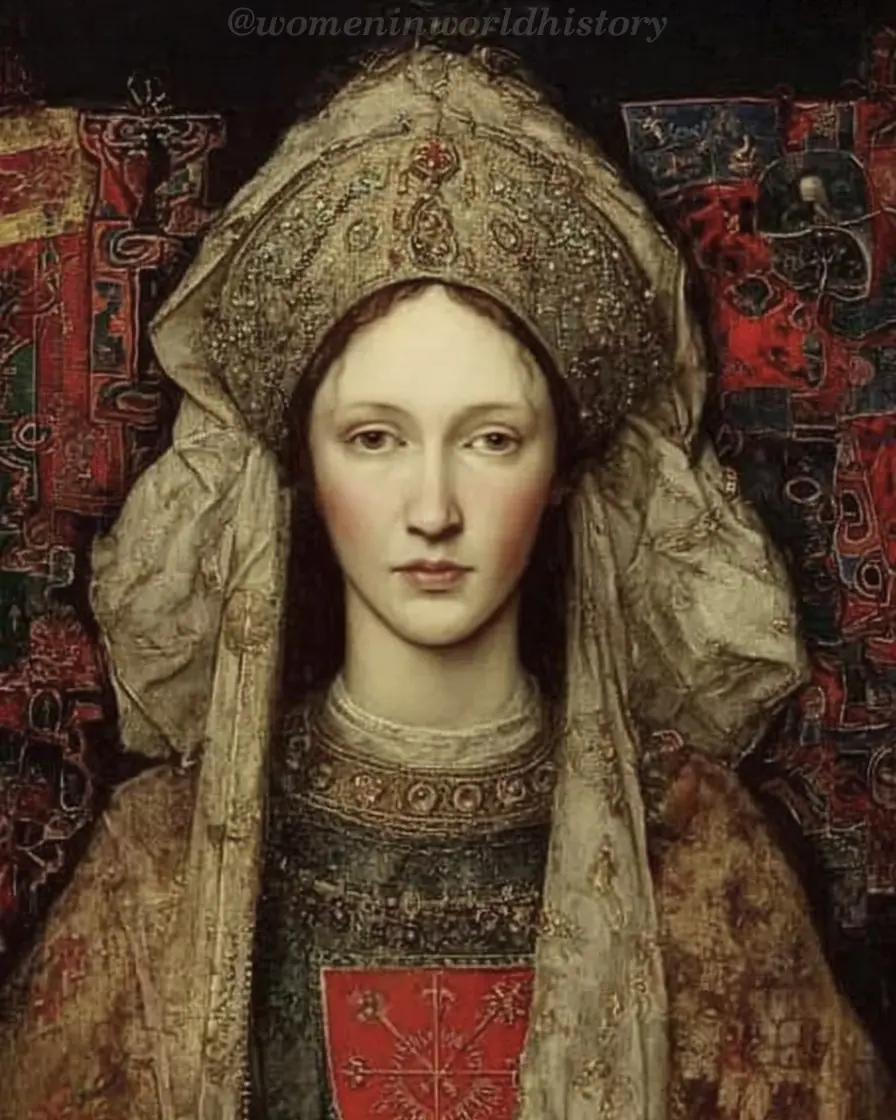

Katherine Swynford: From Mistress to Duchess and the Legacy of Love and Power
Discover the extraordinary life of Katherine Swynford, from a lady-in-waiting to a duchess, her deep love story with John of Gaunt, and the lasting impact of her children, the Beauforts, on English history.

Prolonged "minor ailments" could indicate canc3r, so beware of these 7 signs.
If you continuously experience headaches, loss of appetite, dry cough, and continuous weight loss... you need to see a doctor immediately as this could be a sign of cancer.