Experts reveal what drinking too much caffeine does to your body and how much you should actually consume in one day
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive substances in the world, found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and even chocolate. It's a staple in many people's daily routines, providing that much-needed boost of energy and alertness. But beyond just keeping us awake and stimulated, caffeine has been linked to several health benefits when consumed in moderation. However, like anything, excessive caffeine consumption can have negative effects on our health, especially on sleep patterns. In this article, we explore the pros and cons of caffeine, how it impacts our body, and how much is the ideal amount for reaping its benefits without suffering from unwanted side effects.
The Benefits of Caffeine: More Than Just Keeping You Awake
Caffeine is widely known for its ability to keep you awake and alert, especially when you're feeling fatigued. But did you know that moderate caffeine intake has been associated with several health benefits, particularly in relation to cardiometabolic diseases?
According to various health studies, moderate caffeine consumption can lower the risk of conditions such as type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and stroke. The caffeine in coffee and other beverages is believed to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and even support heart health when consumed in appropriate amounts.
The beneficial effects of caffeine are thought to arise from its ability to stimulate certain biological processes. It’s a central nervous system stimulant, which means it activates your brain and body, improving focus and energy levels. But there's more to caffeine than just its wakefulness-promoting effects.
How Does Caffeine Affect the Body?
To understand the full scope of caffeine’s effects, it’s essential to know how it interacts with the body. One of the key players in the caffeine-adenosine interaction is a naturally occurring compound in our bodies called adenosine.
Adenosine is responsible for promoting relaxation and sleepiness. As the day progresses, adenosine levels naturally build up, signaling to our bodies that it's time to wind down. This process helps regulate our sleep-wake cycle and is critical for maintaining energy balance throughout the day.
“Adenosine is one of the naturally produced substances in the body to cause a quieting of activity in various organs that are under stress or in need of lowering energy demand,” said Kenneth Jacobson, chief of the molecular recognition section at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
When adenosine levels increase, it encourages sleep and a general feeling of tiredness. However, when we consume caffeine, it works by blocking adenosine from attaching to its receptors. This prevents the "sleepy" signal from being sent to the brain, which is why caffeine makes us feel more alert and energetic.
Too Much Caffeine: The Potential Downsides
While caffeine offers several benefits, it’s important to remember that there can be too much of a good thing. Excessive caffeine intake can lead to a range of negative effects, the most prominent being sleep disturbances.
Caffeine typically peaks in the bloodstream around one hour after consumption, and its stimulating effects can last for several hours. According to Damian Bailey, professor of physiology at the University of South Wales in the UK, “Caffeine levels build up in the bloodstream in around 20 minutes, and ‘peak’ caffeination is around an hour after having caffeine.” This means that drinking caffeine late in the afternoon or before bedtime can significantly disrupt your ability to fall asleep, as it blocks the calming effects of adenosine.
Sleep Disturbances: A Common Consequence of Overconsumption
The most immediate and common issue with excessive caffeine consumption is sleep disturbance. If you find yourself tossing and turning at night or waking up feeling restless, caffeine may be the culprit. This is particularly true if you consume caffeine later in the day, as the stimulating effects can last long enough to interfere with your natural sleep cycle.
It’s essential to understand the timing of caffeine consumption in order to avoid disrupting your sleep. Most experts recommend avoiding caffeine for at least 6 hours before bedtime. For example, if you plan to sleep at 10 p.m., it’s best to avoid caffeine after 4 p.m. to ensure that it doesn't affect your ability to fall asleep.
Finding the Ideal Amount of Caffeine: How Much Is Enough?
So, how much caffeine should you consume in order to benefit from its positive effects without facing negative consequences such as poor sleep or heightened anxiety?
According to studies, the sweet spot for caffeine consumption is between 200mg and 300mg per day. This is roughly equivalent to two to three cups of coffee, depending on the strength and type of coffee you drink. For instance, an average cup of instant coffee contains around 100mg of caffeine, so having two to three cups a day will keep you within the recommended limit.
“A cup of coffee typically has around 100mg of caffeine in it, so two or three cups should do the job,” states a recent report from MailOnline. However, it's important to be cautious with energy drinks, as some brands contain much higher caffeine concentrations.
The Risks of Energy Drinks
Energy drinks have become increasingly popular, especially among young adults and athletes. However, these drinks can be far more potent than regular coffee or tea. For example, some energy drinks, like Prime Energy, contain around 160mg of caffeine per 330ml can. Consuming multiple energy drinks in a short period can quickly push you past the recommended caffeine limit, leading to negative side effects such as jitters, anxiety, and sleep disruption.
Additionally, energy drinks often contain other ingredients, such as high levels of sugar and artificial additives, which can further contribute to health problems when consumed in excess. It's important to be mindful of the total amount of caffeine you consume throughout the day, particularly when combining coffee, tea, and energy drinks.
The Health Benefits of Caffeine Beyond Energy
While caffeine is primarily known for its ability to boost energy and improve mental alertness, it also offers a range of health benefits when consumed in moderation.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Caffeine has been shown to improve memory, focus, and cognitive performance. It stimulates the central nervous system, helping you stay alert and focused, especially when performing mentally demanding tasks.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: Caffeine can improve physical performance by increasing adrenaline levels in the body. This makes it a popular choice for athletes, as it can enhance endurance and strength during exercise.
- Reduced Risk of Certain Diseases: Research suggests that moderate caffeine consumption is linked to a lower risk of certain diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and some types of cancer. Studies have also found that caffeine may help reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity.
- Mood Enhancement: Caffeine stimulates the release of dopamine and serotonin, neurotransmitters that are associated with mood regulation. This can help improve mood, reduce feelings of depression, and even boost motivation.
Conclusion: Moderation is Key
Caffeine can be a powerful ally in maintaining mental alertness, enhancing physical performance, and improving overall health, but like any substance, it’s most beneficial when consumed in moderation. Too much caffeine can lead to sleep disturbances, increased anxiety, and other health issues, which is why it’s important to find the right balance.
The general recommendation is to keep caffeine intake between 200mg and 300mg per day, which is equivalent to two or three cups of coffee. Be cautious with energy drinks, as they often contain much higher amounts of caffeine, along with added sugars and artificial ingredients. Remember, the timing of your caffeine consumption also plays a critical role in minimizing its negative effects on sleep.
If you find yourself feeling jittery, anxious, or experiencing difficulty sleeping, it might be time to reassess your caffeine habits. By understanding the effects of caffeine on your body and following the recommended guidelines, you can enjoy its benefits while minimizing the risks.
News in the same category


36-Year-Old Teacher Passed Away From Diabetes Doctors Say Was Triggered By Everyday Foods
Diabetes is a dangerous condition with numerous complications, and diet is a key factor.
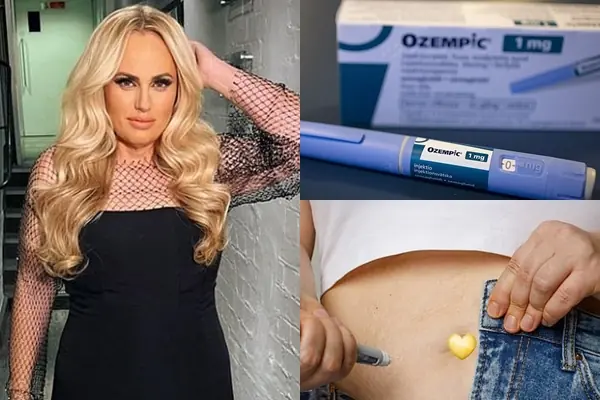
Experts issue urgent warning about terrifying hidden symptom from taking Mounjaro and Ozempic
Experts have issued an urgent warning about a symptom that can come to light from taking drugs such as Mounjaro and Ozempic.

The Benefits of Epsom Salt Foot Soak: A Natural Remedy for Foot Pain and Health
Discover the health benefits of Epsom salt foot soaks, including pain relief, exfoliation, fungal infection treatment, and more. Learn how to safely use Epsom salt for foot health.

What Causes Blue Veins? Understanding the Reasons and When to Seek Help
Blue or green veins are common, but when should you worry? Learn the possible causes of visible veins, from genetics to lifestyle factors, and when it may indicate a medical condition.

7 Early Warning Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore: Act Now for Better Health
Learn about 7 early warning signs of diabetes that could be easily overlooked. Early detection can help manage diabetes, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Read on for expert insights.

Genetic Link Between Endometriosis and Autoimmune Diseases Revealed in New Study
A new study has identified a shared genetic link between endometriosis and autoimmune conditions. Women with endometriosis are at a higher risk for diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis.

People Warned to See a Doctor After Sharing Photo of Concerning Dark Line on Finger
A Reddit user received warnings to see a doctor immediately after posting an image of a dark line on their finger. Learn about melanonychia and why nail discoloration can be a serious health concern.
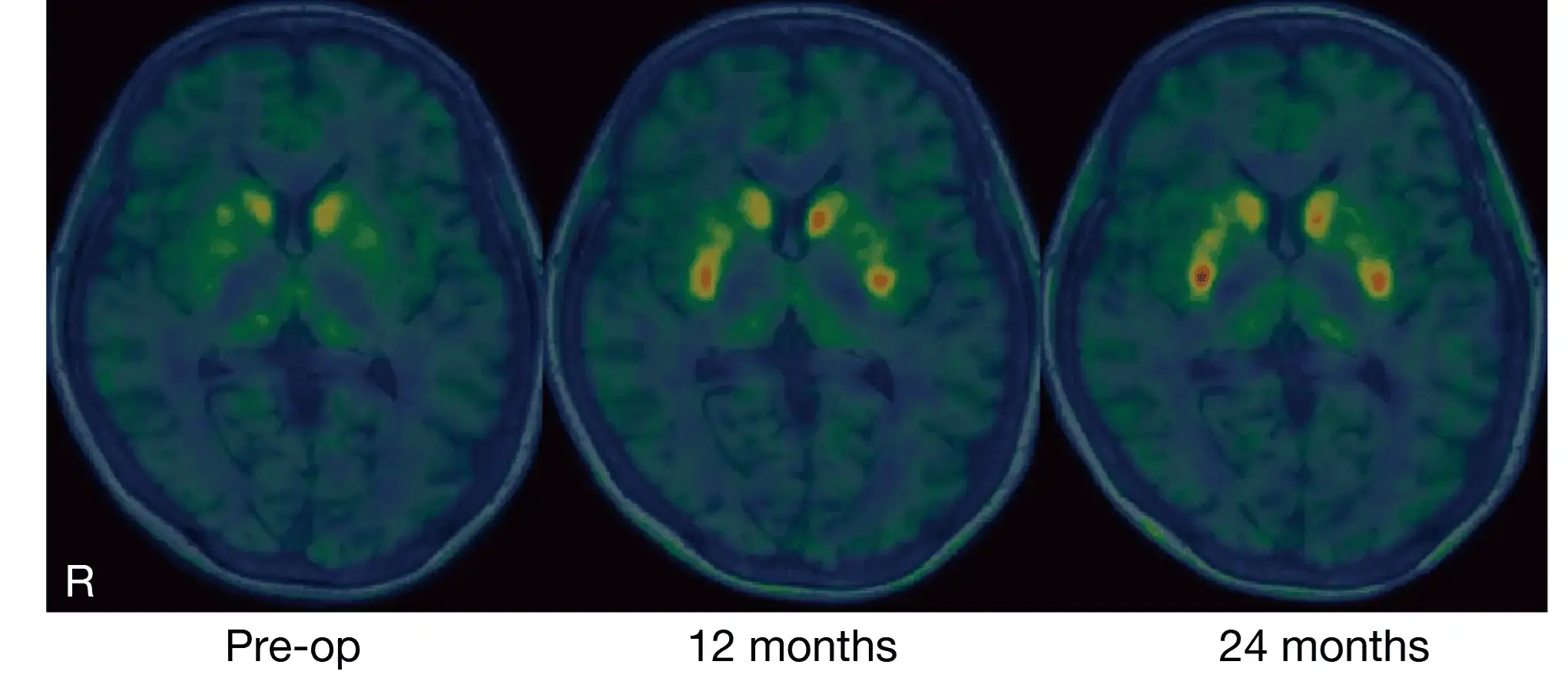
Breakthrough in Parkinson’s Treatment: Japanese Scientists Successfully Implant Lab-Grown Brain Cells
Japanese researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery in Parkinson’s treatment using lab-grown brain cells. Early results from the clinical trial show promising improvements in movement and dopamine production.

4 Simple Steps to Cool Your Home Faster and Save on Electricity Before Turning on the Air Conditioner

3-Blade vs. 5-Blade Fans: Which Cools Better? The Truth Behind Common Misconceptions

The Alarming Rise of Bowel C@ncer in Young Adults: Is Your Diet to Blame

United Airlines Passenger Punches Gate Agent, Kn0cking Them Out

Should You Close or Leave the Toilet Lid Open After Use? 90% of People Get It Wrong — Here's Why Your Bathroom Always Smells

4 Everyday Foods That Fuel C@ncer Cells
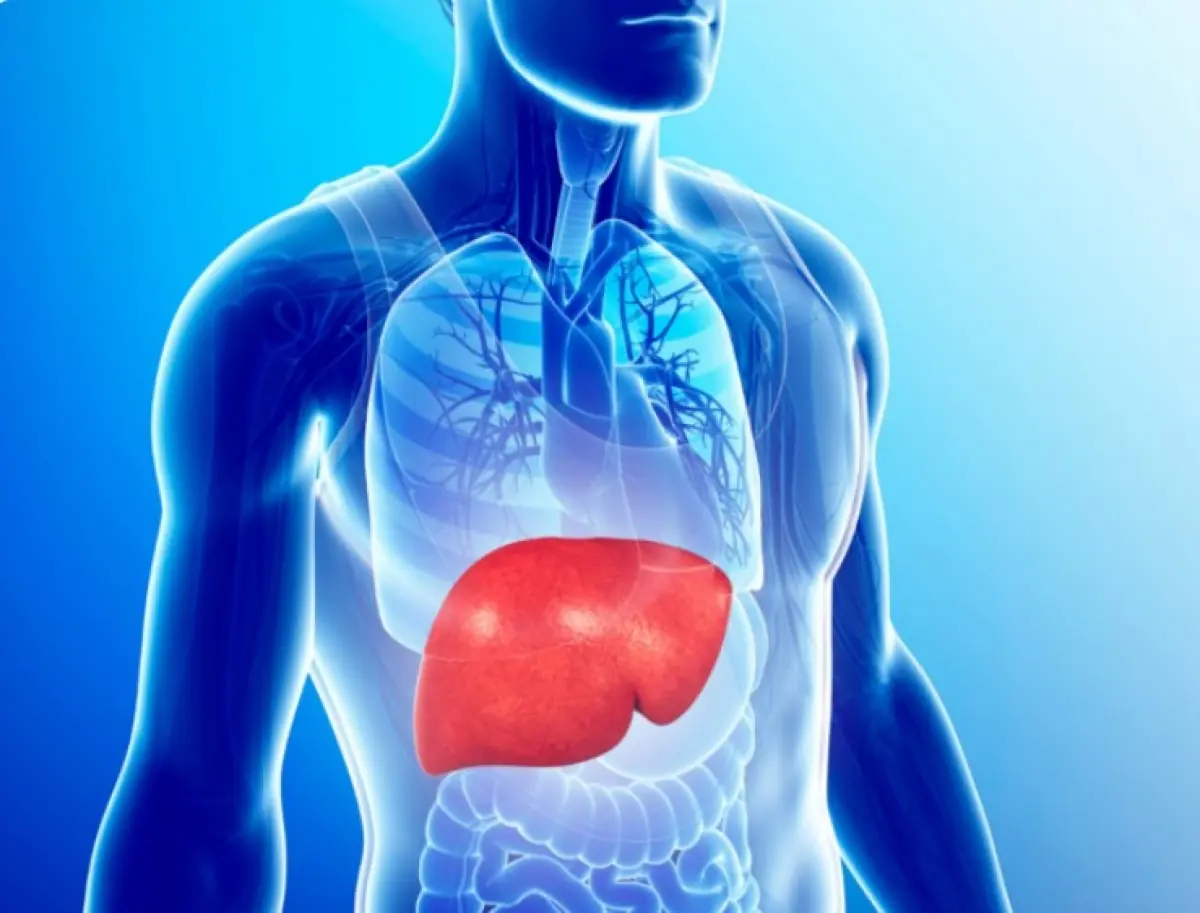
Fatty Liver Disease: A Silent Pathway to Liver C@ncer
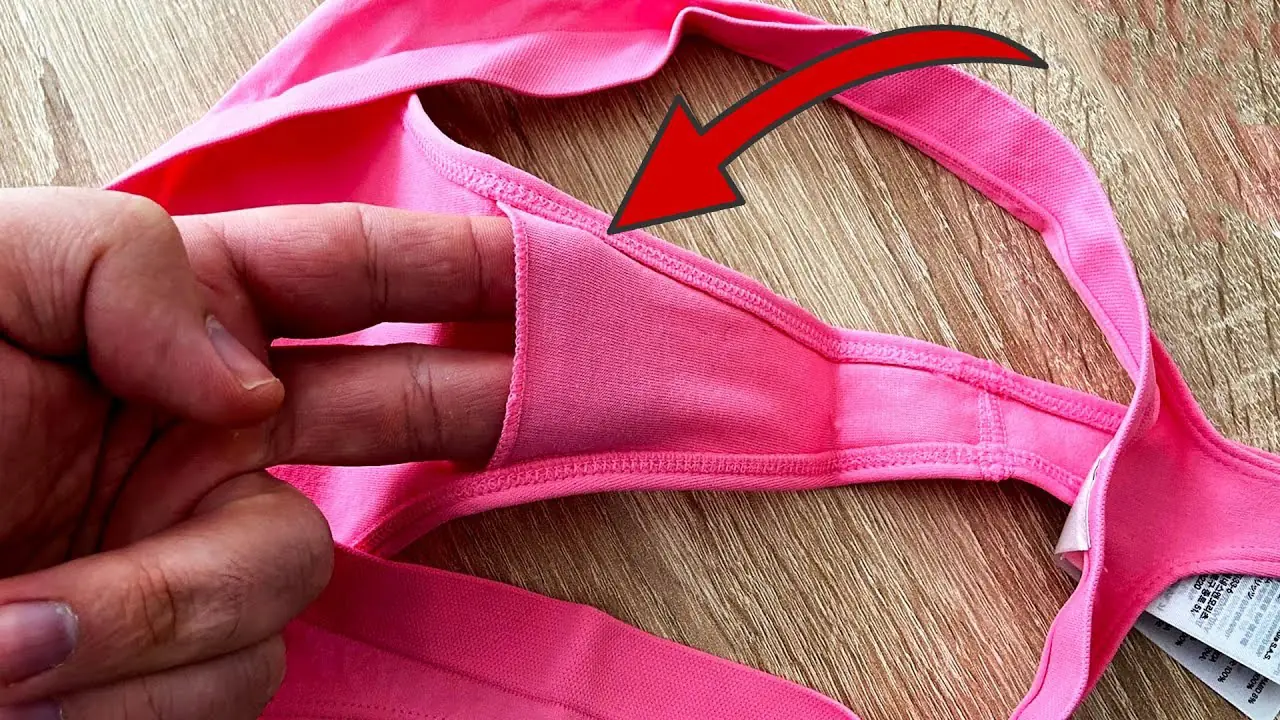

The Hidden Purpose of the Pocket in Women's Underwear: More Than Just a Design Feature
In actuality, the "pocket" in women's underwear is actually a gusset, which serves a number very valid purposes.

This quick 'cup of tea' test could be a simple way to spot early signs of dementia in a loved one
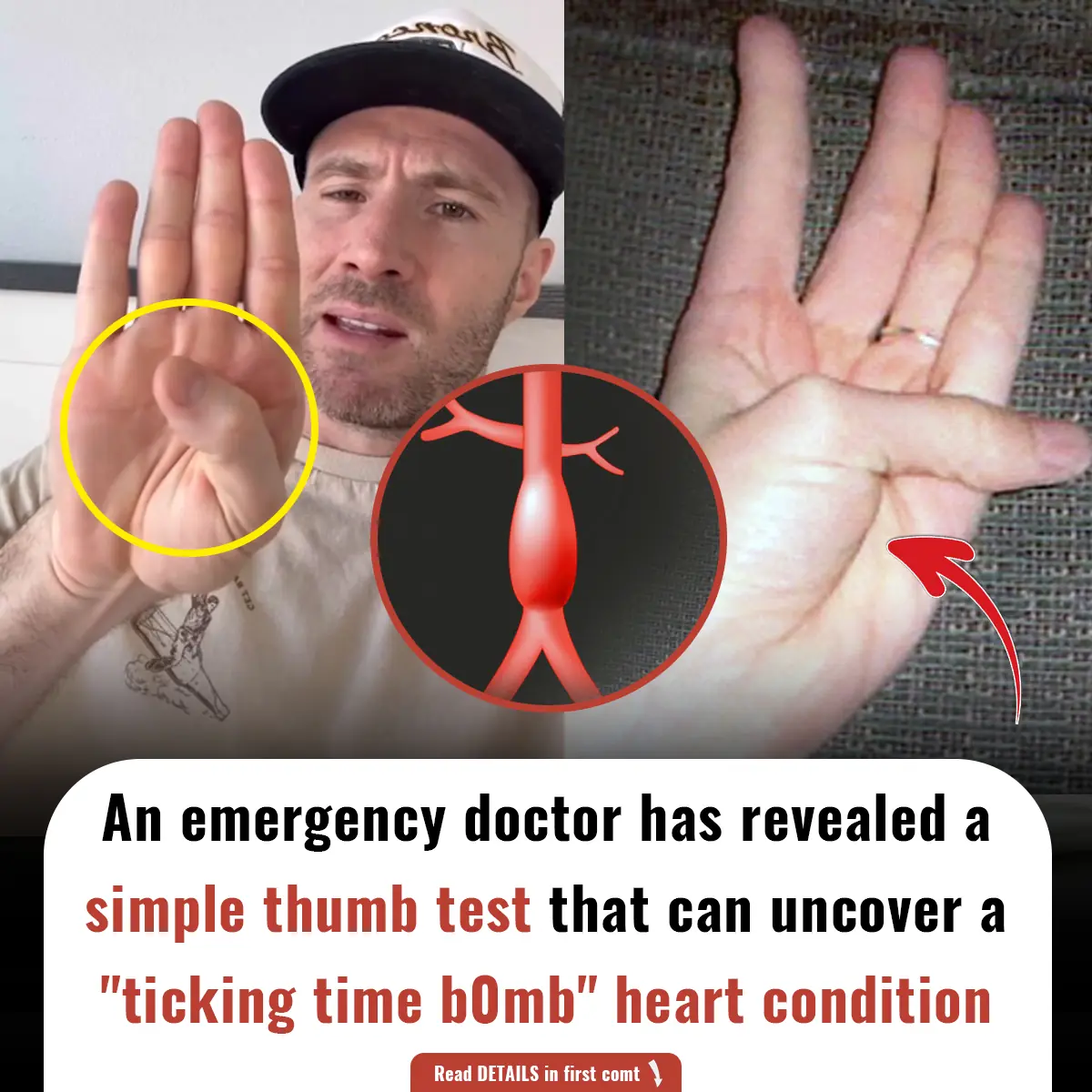
A doctor has revealed a simple thumb test that can uncover a "ticking time b0mb" heart condition

Avocados are incredibly healthy, if using them incorrectly in these 3 common ways could actually have adverse effects
News Post

The Woman Who Walked Away: A Journey of Self-Discovery and Empowerment
A powerful tale of self-realization as Alina breaks free from a toxic relationship, finding strength and confidence after a painful breakup. Discover how she chooses her own path towards happiness and independence.

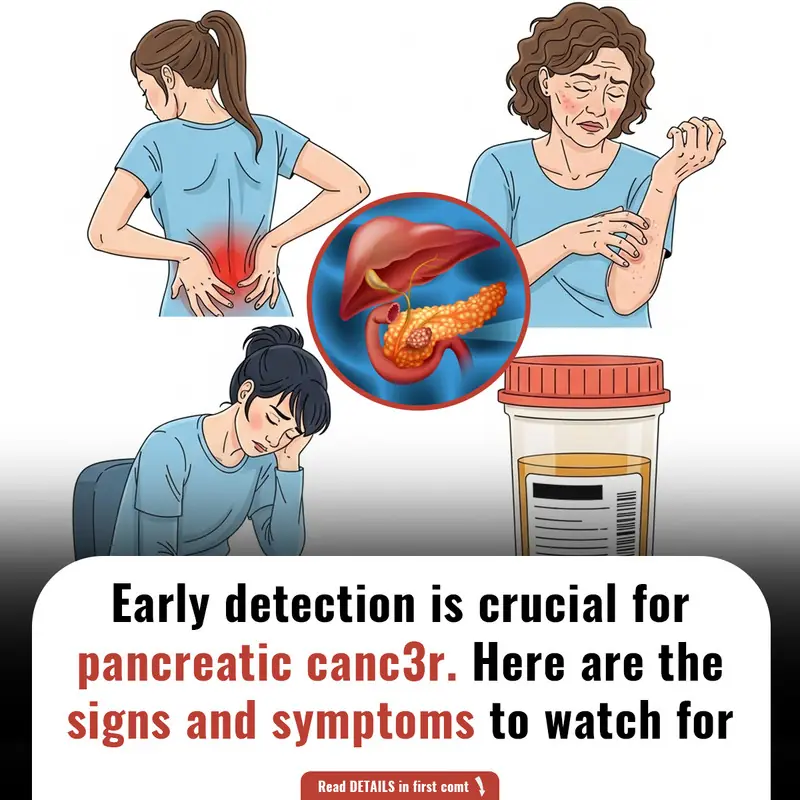
Silent Signals: Recognizing the Subtle Symptoms of Pancreatic C@ncer
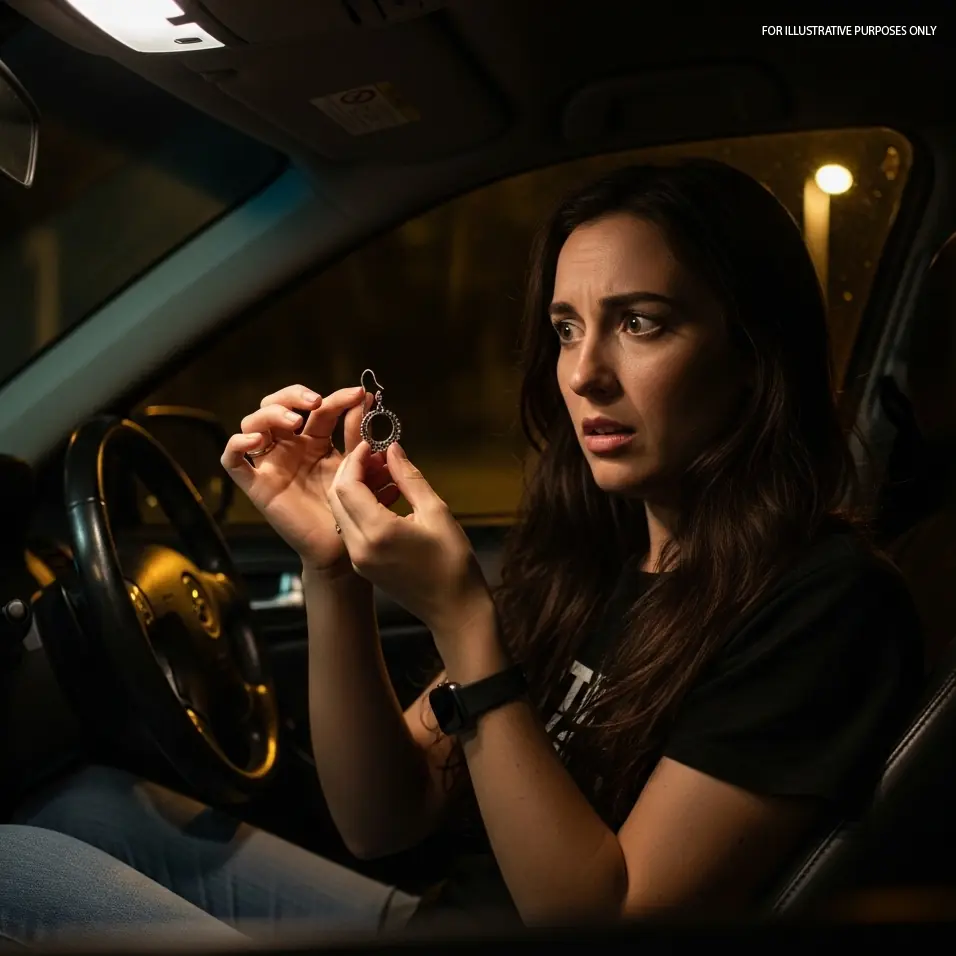

The Earring in the Passenger Seat: A Suspicious Find Leads to a Truthful Confrontation
A woman finds a sh0cking truth after discovering a mysterious child’s drawing in her fiancé’s car. Suspicion, betrayal, and secrets unravel as she confronts him, ultimately deciding the fate of their relationship.

Am I Wrong for Not Laughing at My Fiancé's "Jokes" About Calling Off Our Wedding?
A bride-to-be is questioning her relationship after her fiancé repeatedly jokes about calling off their wedding. What happens when humor crosses the line into hurtful behavior?

36-Year-Old Teacher Passed Away From Diabetes Doctors Say Was Triggered By Everyday Foods
Diabetes is a dangerous condition with numerous complications, and diet is a key factor.

Experts issue urgent warning about terrifying hidden symptom from taking Mounjaro and Ozempic
Experts have issued an urgent warning about a symptom that can come to light from taking drugs such as Mounjaro and Ozempic.

The Benefits of Epsom Salt Foot Soak: A Natural Remedy for Foot Pain and Health
Discover the health benefits of Epsom salt foot soaks, including pain relief, exfoliation, fungal infection treatment, and more. Learn how to safely use Epsom salt for foot health.

What Causes Blue Veins? Understanding the Reasons and When to Seek Help
Blue or green veins are common, but when should you worry? Learn the possible causes of visible veins, from genetics to lifestyle factors, and when it may indicate a medical condition.

DIY Rice Cream for Radiant, Youthful Skin: The Japanese Secret to Erasing Wrinkles & Fine Line
With its powerful combination of rice, almond oil, and vitamin-rich ingredients, this rice cream provides nourishment, hydration, and antioxidant protection to your skin.

7 Early Warning Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore: Act Now for Better Health
Learn about 7 early warning signs of diabetes that could be easily overlooked. Early detection can help manage diabetes, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Read on for expert insights.

5 Homemade Skin Toners for Smooth, Glowing Skin: Natural Remedies for Every Skin Type
By incorporating these toners into your daily routine, you can expect healthier, brighter, and more balanced skin without the use of harsh chemicals.

Genetic Link Between Endometriosis and Autoimmune Diseases Revealed in New Study
A new study has identified a shared genetic link between endometriosis and autoimmune conditions. Women with endometriosis are at a higher risk for diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis.

Roasted Onion Peel and Garlic Peel Remedies for Grey Hair: Natural Solutions for Dark, Vibrant Hair
. Roasted onion peel and garlic peel offer effective, safe, and natural alternatives that can help you combat grey hair and restore youthful vitality.

People Warned to See a Doctor After Sharing Photo of Concerning Dark Line on Finger
A Reddit user received warnings to see a doctor immediately after posting an image of a dark line on their finger. Learn about melanonychia and why nail discoloration can be a serious health concern.

Breakthrough in Parkinson’s Treatment: Japanese Scientists Successfully Implant Lab-Grown Brain Cells
Japanese researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery in Parkinson’s treatment using lab-grown brain cells. Early results from the clinical trial show promising improvements in movement and dopamine production.

4 Simple Steps to Cool Your Home Faster and Save on Electricity Before Turning on the Air Conditioner

Effective Cumin Seed Detox Tonic for Belly Fat Reduction: Your Ultimate Guide to a Flatter Midsection
The cumin seed detox tonic is a natural, easy-to-make remedy that can help accelerate belly fat loss, improve digestion, and enhance overall health.

3-Blade vs. 5-Blade Fans: Which Cools Better? The Truth Behind Common Misconceptions

The Alarming Rise of Bowel C@ncer in Young Adults: Is Your Diet to Blame
