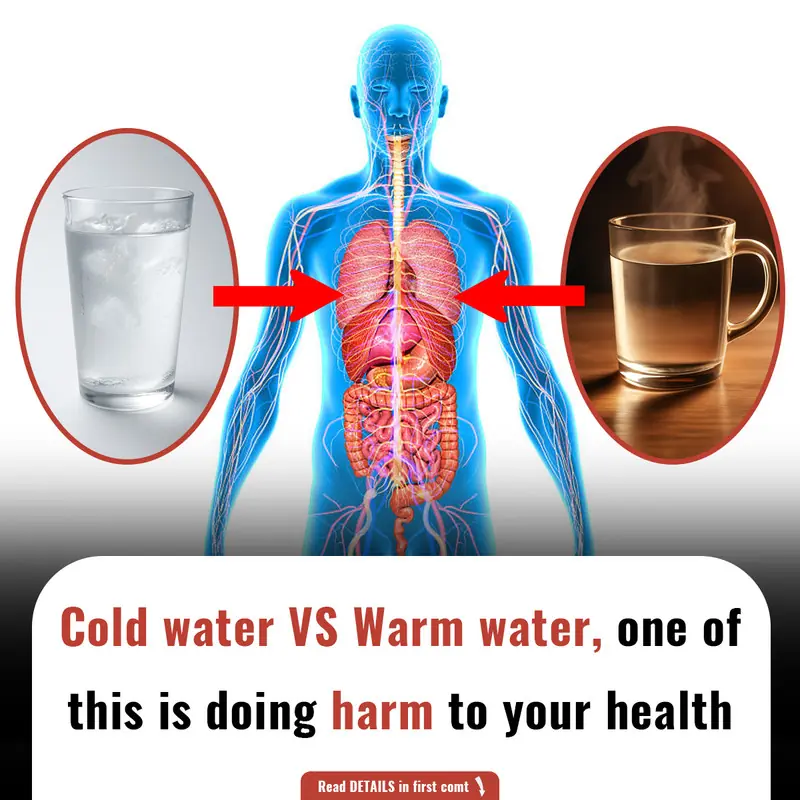
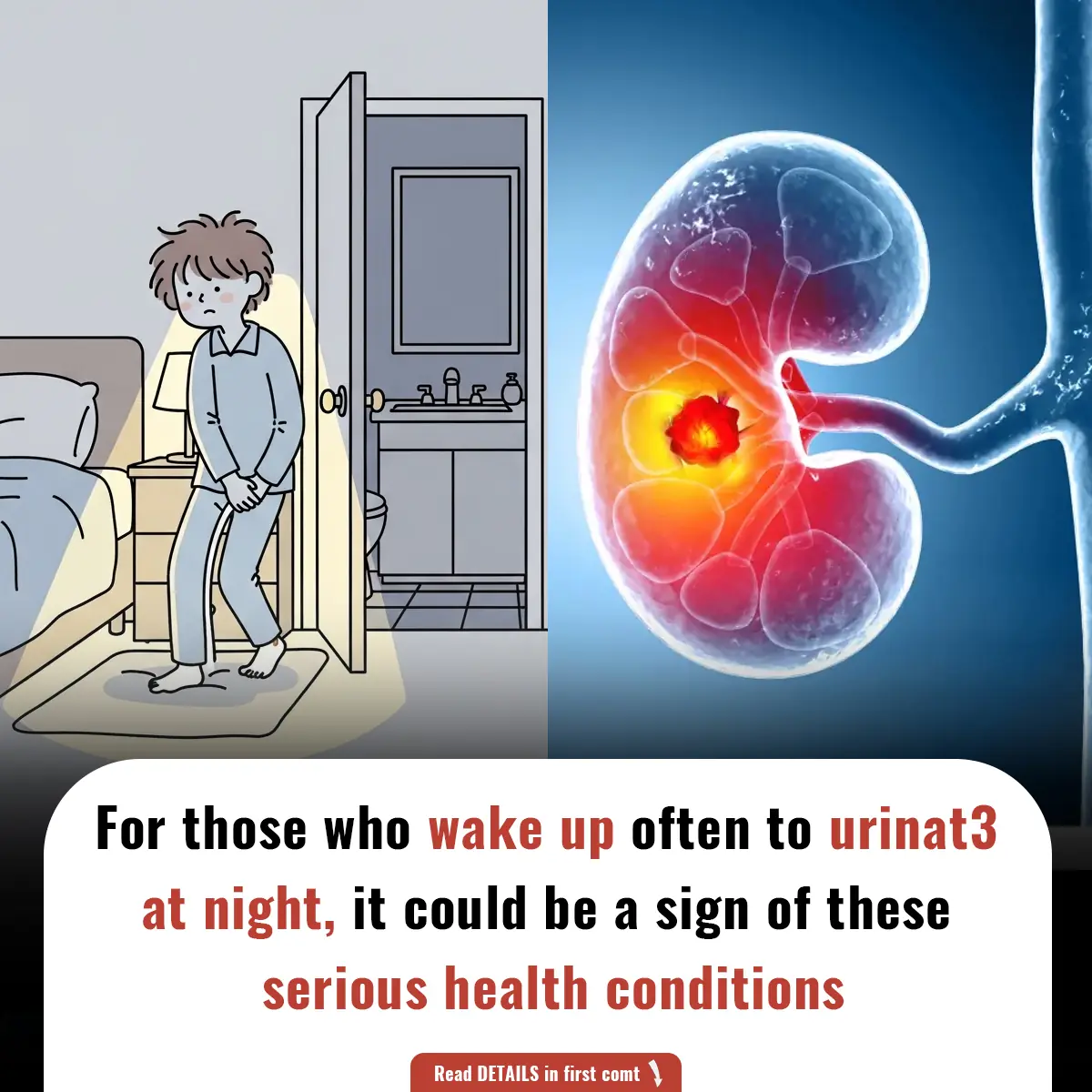
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects older adults, leading to muscle stiffness and joint pain. This condition can be debilitating, as it often restricts movement, especially in the shoulders, hips, and other major muscle groups. While it is most commonly seen in people over 65, it can still affect individuals under 50 in rare cases. Polymyalgia rheumatica is frequently mistaken for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia, due to similar symptoms, but it differs in terms of causes, treatments, and long-term management.
In this article, we will discuss the key signs and symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica and how they might help you identify the condition. We will also examine its relationship with other inflammatory diseases, particularly giant cell arteritis, and provide insights into how it can affect your daily life.
Understanding Polymyalgia Rheumatica: What You Need to Know
Polymyalgia rheumatica is a type of inflammatory disorder that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in the muscles and joints. It typically manifests in the shoulders and hips but can affect other areas of the body as well. While the exact cause of PMR remains unknown, it is believed to involve immune system dysfunction, where the body’s immune system attacks the tissues around the muscles and joints.
One of the challenges in diagnosing polymyalgia rheumatica is that its symptoms overlap with those of other conditions like fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis. However, the primary distinction is that PMR does not cause joint damage or swelling in the same way as rheumatoid arthritis. Instead, the pain and stiffness are more pronounced, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
In some cases, polymyalgia rheumatica is linked with another serious condition called giant cell arteritis (GCA), which is an inflammation of the blood vessels. This connection underscores the importance of early diagnosis and treatment, as untreated polymyalgia rheumatica can lead to complications, including permanent disability.
Early Warning Signs of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
1. Persistent Shoulder Pain
Credit: Pixabay
The hallmark symptom of polymyalgia rheumatica is persistent pain in the shoulders. This discomfort often begins gradually and can become quite severe over time. For many individuals, the pain is noticeable when performing routine activities such as dressing, reaching for objects, or lifting their arms. The pain tends to affect both shoulders simultaneously and can be particularly bothersome at night, making it hard to get a good night’s sleep.
In some cases, the pain may extend to the upper arms, causing a deep, aching sensation that seems to persist without relief. As the condition progresses, the pain might also affect the neck and upper back, further restricting movement.
2. Pain in Hips, Thighs, Buttocks, and Neck
While shoulder pain is often the first sign, polymyalgia rheumatica can also cause discomfort in other major muscle groups. Pain in the hips, buttocks, thighs, and neck is common, and this aching sensation can make daily activities, such as sitting, standing, bending, and walking, difficult.
The pain tends to worsen after periods of inactivity or after repetitive movements, making tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or even getting out of bed more challenging. The discomfort is typically a deep, aching pain rather than sharp or stabbing, and it can become more intense with time if left untreated.
3. Stiffness, Especially in the Morning

Credit: Pexels
Another key sign of polymyalgia rheumatica is muscle stiffness, which is often worst in the mornings. This stiffness can last for more than an hour and makes it hard to move around after waking up. Many people describe the sensation as their muscles "locking up" after sleep, and it can make getting out of bed or performing basic activities like brushing teeth or getting dressed very uncomfortable.
Stiffness can also occur after sitting for long periods or following physical exertion. Mild movement can help to ease the stiffness, but without treatment, the condition can lead to increased mobility issues over time, making it more difficult to complete everyday tasks.
4. Limited Range of Motion
If left untreated, the stiffness associated with polymyalgia rheumatica can lead to a reduced range of motion in the affected joints. For instance, shoulder pain may make it difficult to raise your arms above your head or extend them outward. Similarly, hip pain can limit your ability to bend over or sit down and stand up with ease.
Many individuals may begin to limit their movements unconsciously, trying to avoid the pain. Over time, this reduction in movement can cause further weakening of muscles and an overall decline in flexibility, which exacerbates the mobility issues caused by the condition.
5. Pain in Knees, Elbows, and Wrists
Though polymyalgia rheumatica primarily affects the shoulders and hips, some people experience pain and stiffness in other joints such as the knees, elbows, and wrists. This pain is often confused with the symptoms of arthritis, but PMR does not typically result in the joint swelling or deformities seen in rheumatoid arthritis.
The pain in these joints can make basic tasks, such as typing, writing, or walking, particularly difficult. For individuals with wrist pain, even holding a pen or using a computer can become a challenge, which significantly impacts their quality of life. Knee pain can make it difficult to walk or climb stairs, further limiting mobility and independence.
6. Fatigue and Low-Grade Fever
Beyond joint and muscle pain, polymyalgia rheumatica can also cause systemic symptoms, such as fatigue and a low-grade fever. Many individuals with PMR feel persistently tired, even after a full night’s rest. This exhaustion can make it difficult to maintain an active lifestyle or complete daily tasks, contributing to a feeling of being constantly drained.
Some people also experience mild fever and a general feeling of malaise, which may be accompanied by a reduced appetite and weight loss. These systemic symptoms can contribute to a sense of overall unwellness, making it even more challenging for patients to maintain a positive outlook.
7. Depression and Emotional Impact
The physical pain and limitations caused by polymyalgia rheumatica can also take a toll on a person’s emotional well-being. As mobility decreases and daily activities become more difficult, feelings of frustration, sadness, and isolation may develop. Depression is a common symptom, particularly when individuals feel like they are losing their independence.
The emotional impact of polymyalgia rheumatica can exacerbate the physical symptoms, creating a vicious cycle of pain and emotional distress. It's important to address both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition to improve overall quality of life.
How Polymyalgia Rheumatica is Diagnosed
If you experience any of the signs mentioned above, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis. Your doctor will typically begin with a physical examination and may order blood tests to check for elevated levels of inflammatory markers, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). These tests are commonly elevated in people with polymyalgia rheumatica.
In some cases, imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs may be used to rule out other conditions, such as arthritis or tendonitis. If polymyalgia rheumatica is suspected, your doctor may also look for symptoms of giant cell arteritis, as these two conditions are often linked.
Treatment Options for Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Credit: Pixabay
While there is no cure for polymyalgia rheumatica, treatment options are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The most common treatment involves corticosteroids, such as prednisone, which can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Most people experience significant improvement in symptoms within days or weeks of starting corticosteroid therapy.
However, long-term use of corticosteroids can have side effects, such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections. Therefore, doctors aim to use the lowest effective dose of steroids and may gradually taper the medication as symptoms improve.
In addition to medications, physical therapy and exercises designed to improve flexibility and strength can help patients maintain mobility and prevent further complications. Occupational therapy may also be beneficial for individuals who need assistance with performing daily activities.
Conclusion: Early Detection and Proper Management
Polymyalgia rheumatica is a challenging condition that can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms such as shoulder pain, stiffness, fatigue, or joint discomfort, it’s important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
With the right care and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with polymyalgia rheumatica can continue to lead active lives, despite the challenges posed by the condition. By working closely with healthcare providers, patients can find a treatment plan that works best for them and regain a sense of control over their health and well-being.