
Beware: These 6 Inexpensive Fish Could Be Contaminated with H@rmful Toxins

Introduction
In many households, fish is a staple food due to its affordability and nutritional value. However, not all fish are created equal when it comes to safety. Certain species, while budget-friendly, may harbor toxins that can pose health risks if consumed improperly. Understanding which fish to avoid and how to prepare them safely is crucial for maintaining good health.
1. The Hidden Dangers of Thiaminase in Fish
Thiaminase is an enzyme found in certain fish species that breaks down thiamine (vitamin B1), leading to a deficiency if consumed in large amounts. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, and nerve damage. While cooking can reduce thiaminase activity, it may not eliminate it entirely.
2. Identifying Fish Species Prone to Contamination
Certain fish are more likely to contain thiaminase and other toxins. These include:
-
Mackerel: Known for its high thiaminase content.
-
Carp: Often carries parasites and toxins.
-
Catfish: May accumulate harmful substances from polluted waters.
-
Tilapia: Susceptible to bacterial infections if not properly handled.
-
Anchovies: Small size makes them prone to contamination.
-
Herring: Can contain high levels of toxins if not stored correctly.
These species are commonly found in markets due to their low cost but may pose health risks if not prepared properly.
3. Safe Consumption Tips
To minimize health risks:
-
Cook Thoroughly: Ensure fish is cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) to kill parasites and reduce toxin levels.
-
Avoid Raw Consumption: Raw or undercooked fish can harbor harmful bacteria and parasites.
-
Diversify Your Diet: Incorporate a variety of fish species to reduce the risk of toxin accumulation.
-
Source Responsibly: Purchase fish from reputable sources that adhere to safety standards.
4. Recognizing Symptoms of Toxic Exposure
Be aware of signs that may indicate exposure to fish-borne toxins:
-
Neurological Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, or weakness.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
-
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or lethargy.
If you experience these symptoms after consuming fish, seek medical attention promptly.
5. Alternative Fish Choices
Consider these safer, nutrient-rich alternatives:
-
Salmon: High in omega-3 fatty acids and low in toxins.
-
Trout: Sustainable and less likely to contain harmful substances.
-
Cod: Lean protein source with minimal contamination risk.
-
Sardines: Rich in nutrients and less prone to toxins.
These options provide health benefits without the associated risks.
6. The Importance of Proper Fish Handling
Even safe fish can become contaminated if not handled correctly. Always:
-
Store Properly: Keep fish refrigerated or frozen until ready to cook.
-
Clean Thoroughly: Wash hands, utensils, and surfaces after handling raw fish.
-
Check Freshness: Ensure fish has a fresh smell and firm texture.
Proper handling reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Conclusion
While certain fish species are affordable and widely consumed, it's essential to be aware of potential health risks associated with their consumption. By choosing safer alternatives, preparing fish properly, and staying informed about food safety practices, you can enjoy the nutritional benefits of fish without compromising your health.
News in the same category


5 Common Electric Kettle Mistakes That Could Lead to Serious Accidents

Why Dogs Are More Sensitive and Alert During Thunderstorms Than Humans: The Science Behind Their Unique Instincts

Why Experts Recommend Putting Your Luggage in the Bathtub After Checking in: Turns Out It Has Many Unexpected Benefits

Experts reveal the effects on your body from eating one meal a day after a sh0cking simulation
Major medical breakthrough: Korean researchers discover “Undo” mechanism to transform tumor cells back to normal
If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you will suffer from ...
Drink water on an empty stomach right after waking up for 1 month and see how you transform physically and mentally
5 types of food that can do wonder for your gut health and digestion

Scientists may have uncovered the reason why weight tends to rebound after loss
The truth about cold water: 5 health concerns you should know

Should you buy straight shrimp or curved shrimp at the market? I just learned today that there's such a big difference

Should you choose purple garlic or white garlic? Many housewives think they're the same, but in reality, they're not

Why you should never insert your washing machine drain hose directly into the floor drain: expert advice
Why Do People Throw Water Bottles Under Hotel Beds? The Hidden Reasons Behind This Common Habit

Why do hotels set check-out time at 12 pm? Unveiling the practical reasons
Early warnings signs and symptoms of ovarian canc3r everywoman should be aware of

8 types of food that can fight canc3r many of you didn't know
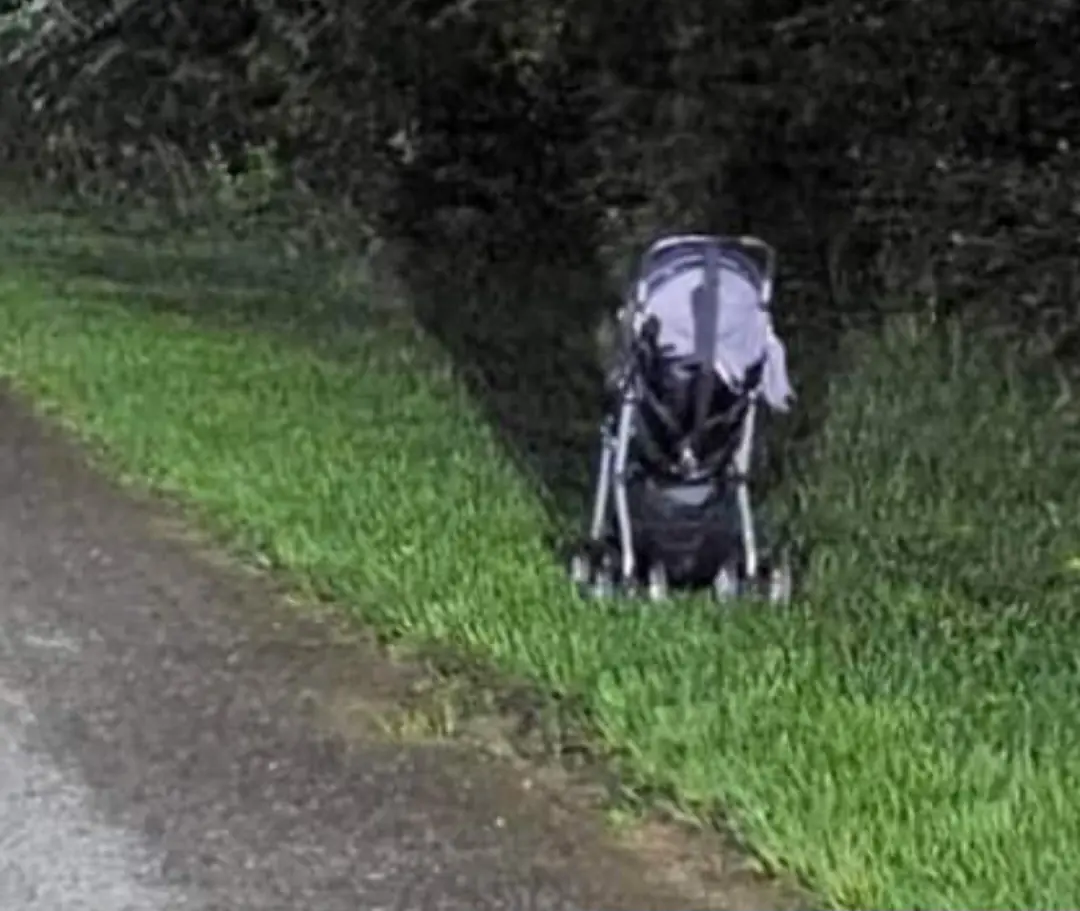

Woman’s Chilling Warning After Discovering Abandoned Pram on Remote Road
A 6-year-old boy diagnosed with late-stage canc3r, his father regrets after doctors reveal the cause linked to a popular type of beverage
News Post
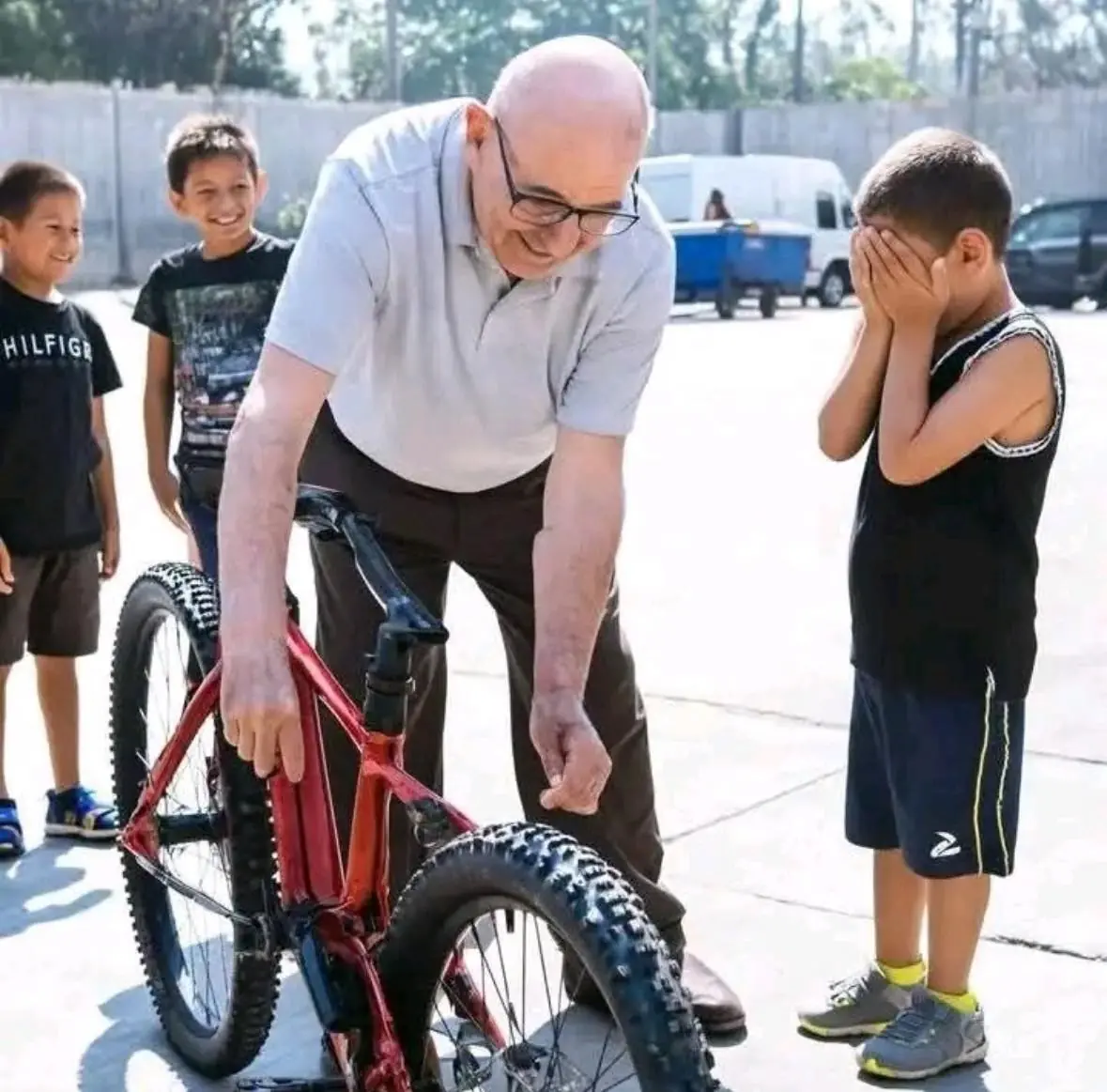

KINDNESS OVER ANGER: HOW A CAR OWNER TURNED A BOY’S MISTAKE INTO A LIFE-CHANGING LESSON
Discover the heartwarming story of a boy who d@maged a car by acc!dent and the owner’s surprising act of kindness that went beyond fixing a dent — a powerful lesson in forgiveness and generosity.
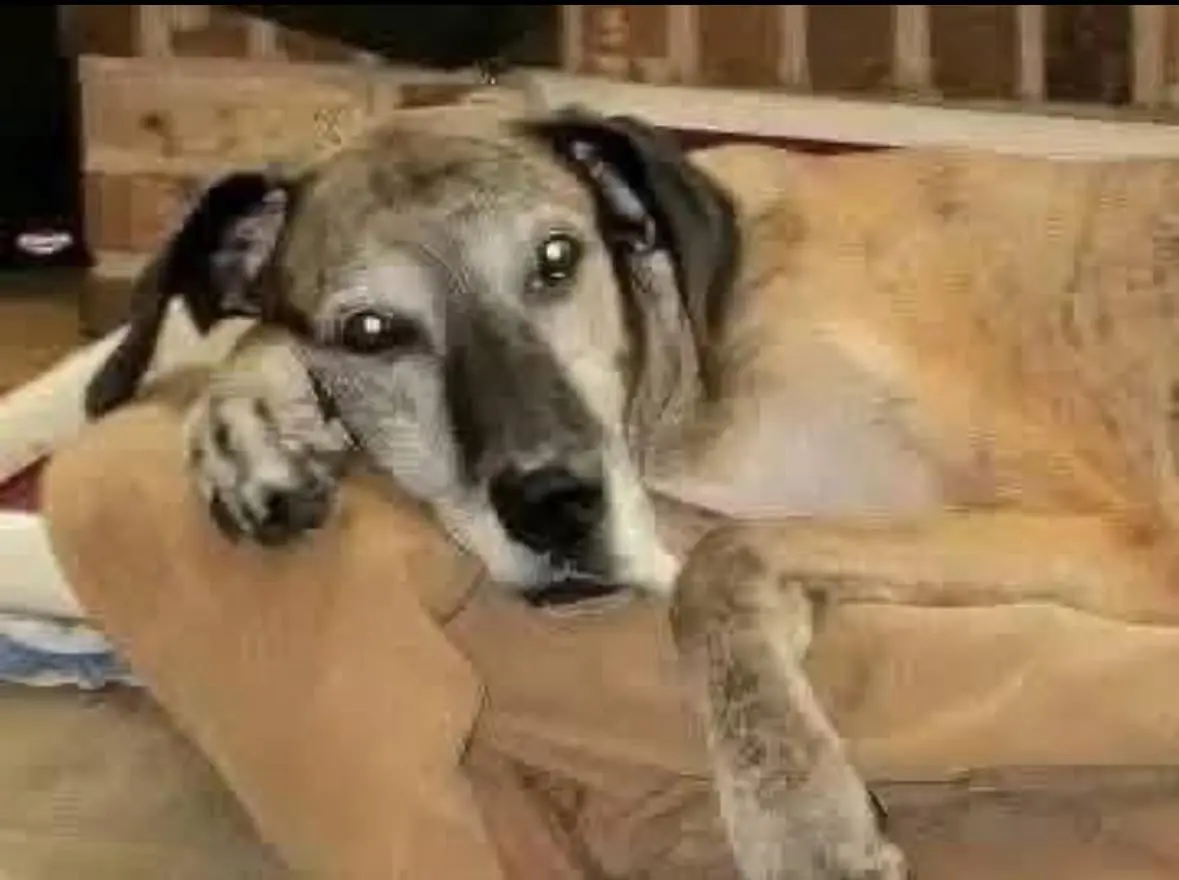

THE HEARTBRE@KING RESCUE OF ETHEL: FROM PUPPY MILL NIGHTM@RES TO A LIFE FILLED WITH LOVE
Discover the touching journey of Ethel, a 5-year-old Great Dane rescued from a cr:u:el puppy mill. Learn how patience, love, and kindness transformed her life from fear and abu$e to joy and safety.
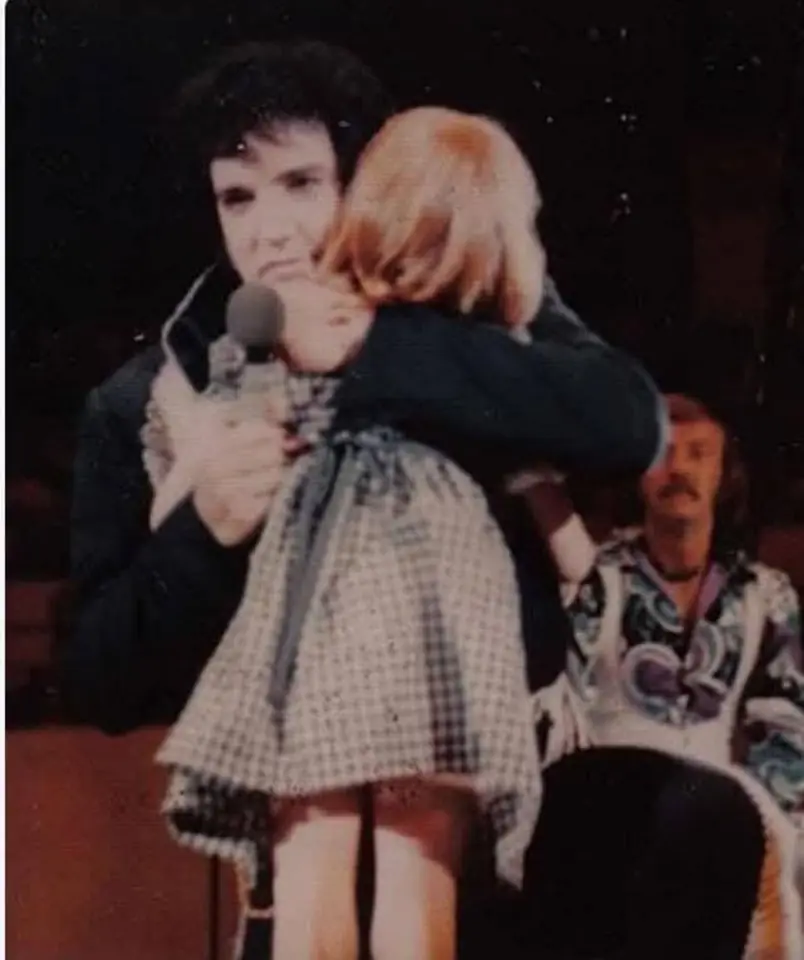

ELVIS PRESLEY'S HEARTFELT GESTURE THAT CHANGED A BLIND GIRL'S LIFE FOREVER
Discover the touching story of how Elvis Presley’s compassionate act during a 1975 concert helped a blind girl regain her sight, inspiring hope and kindness that echoes through time.
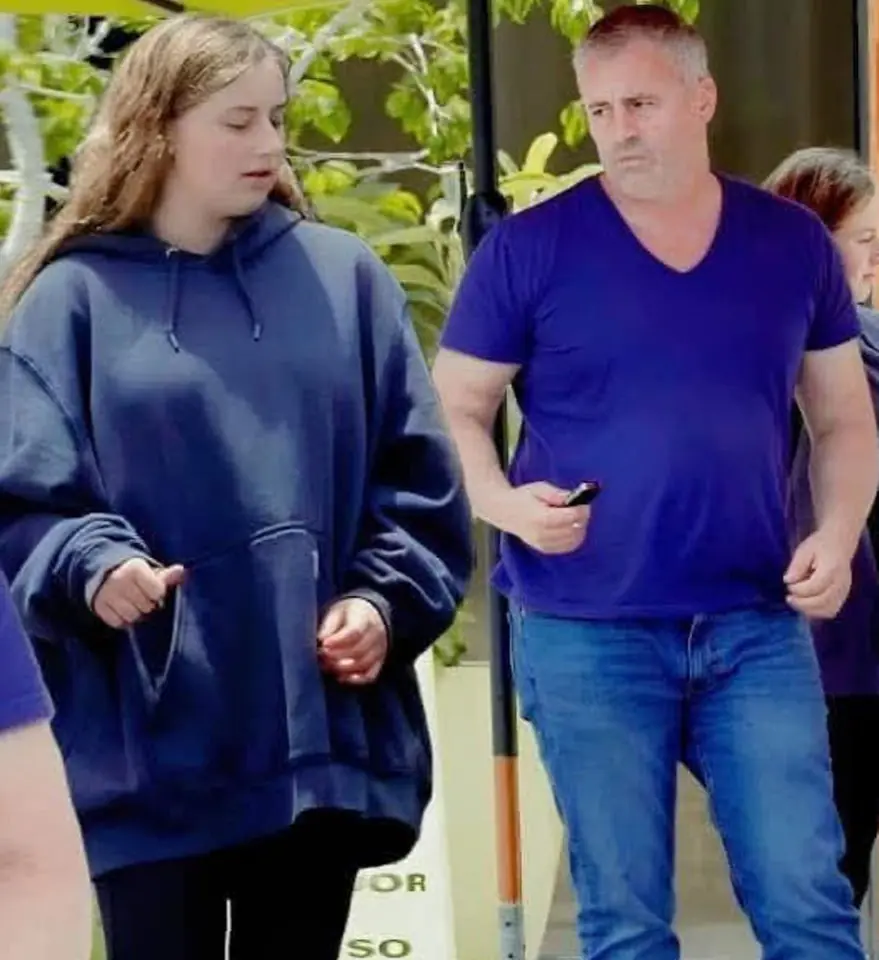

MATT LEBLANC: THE ACTOR WHO CHOSE FATHERHOOD OVER FAME – A STORY OF LOVE, SACRIFICE, AND QUIET STRENGTH
Discover the touching journey of Matt LeBlanc, the beloved actor behind Joey Tribbiani, who stepped away from Hollywood spotlight to care for his daughter diagnosed with a rare brain condition. A heartfelt story of love, sacrifice, and fatherhood.

A Heartwarming Act of Kindness: How One HVAC Owner Saved a Family’s Winter—and Honored a Deployed Soldier
When a family’s furnace failed on a freezing night, a heating company owner went above and beyond—fixing the problem and charging just $1 in a touching tribute to military service. Discover the inspiring story of generosity and gratitude that warmed m
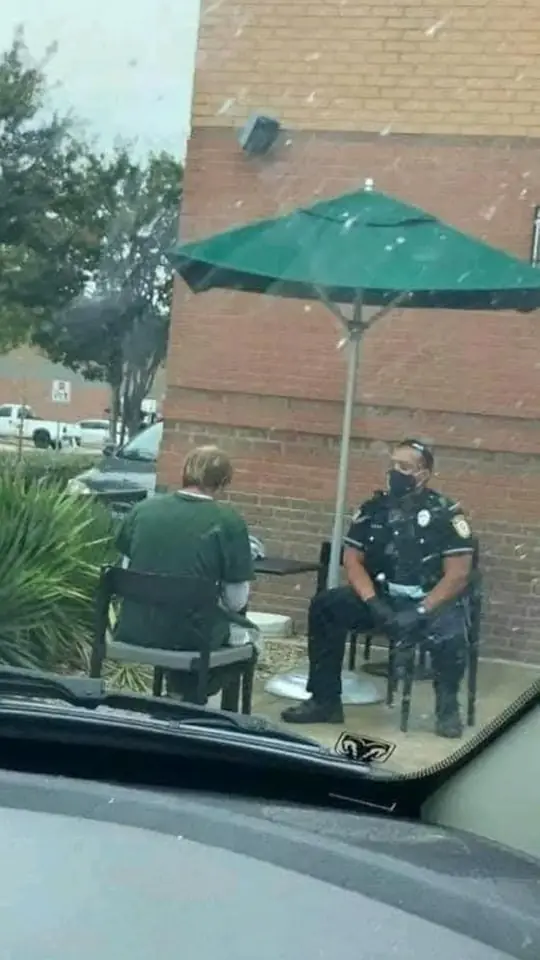

Officer Reese’s Compassionate Response: A Heartwarming Moment at Starbucks
Officer Reese calms an upset man at Starbucks with empathy, showing true kindness. Read this story! ❤️☕
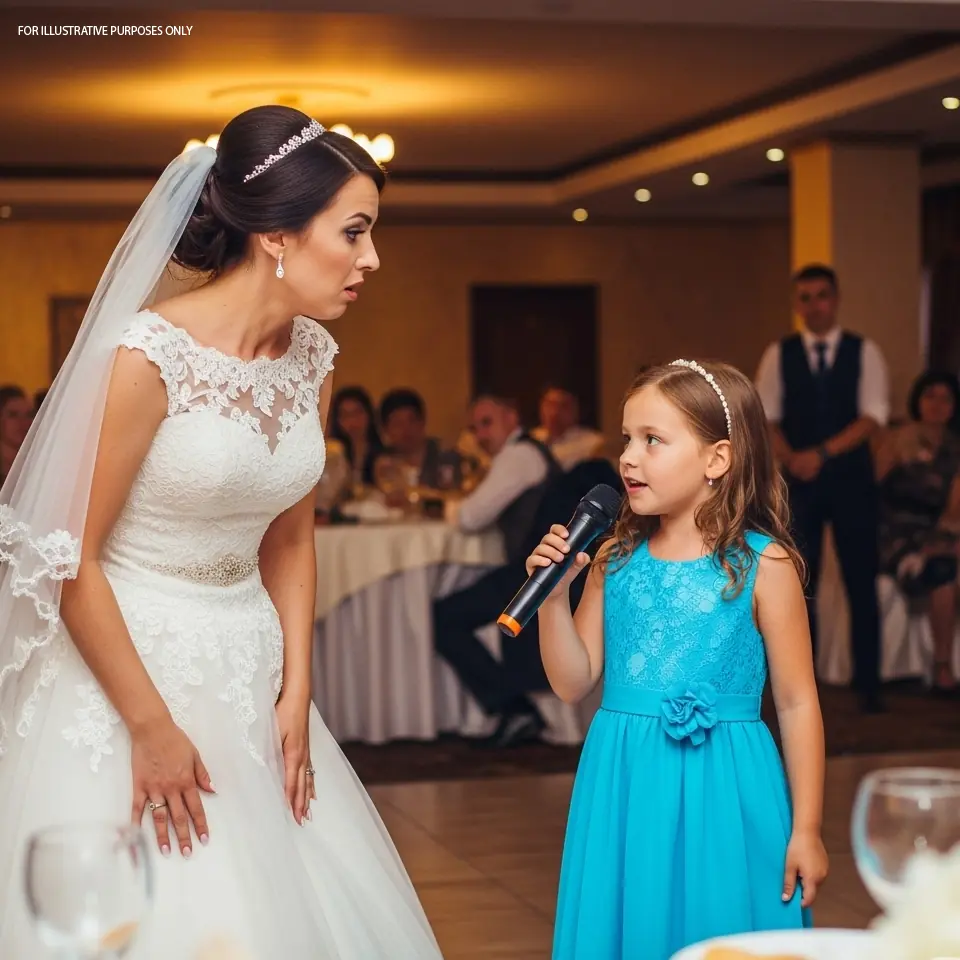

At her mother’s wedding, the girl took the microphone to congratulate her but instead showed a sh0cking video.
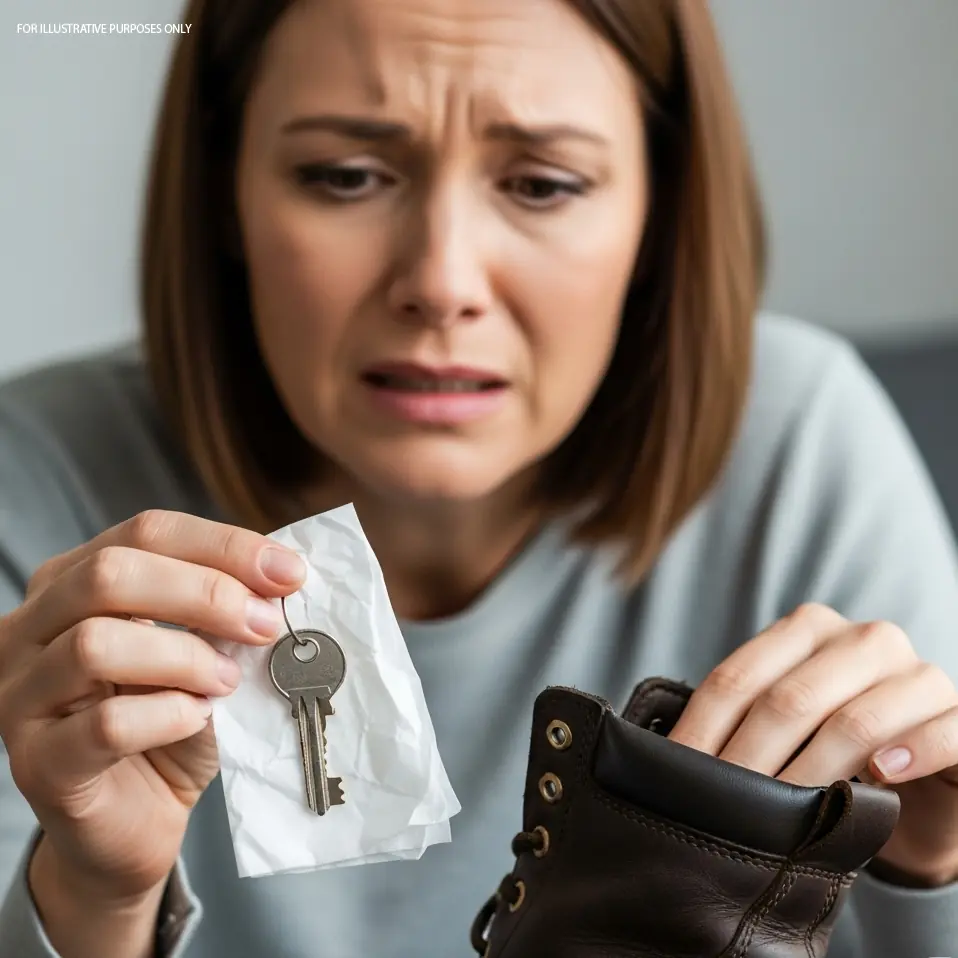

The Hidden Key in His Work Boot: Uncovering a Secret Life and the Shattered Marriage That Followed
When I found a mysterious second key hidden in my husband’s work boot, it unraveled a web of l!es, a secret child, and a hidden life. This is the gripping story of betrayal, heartbre@k, and the pa!nful journey toward truth and unexpected reconciliation.
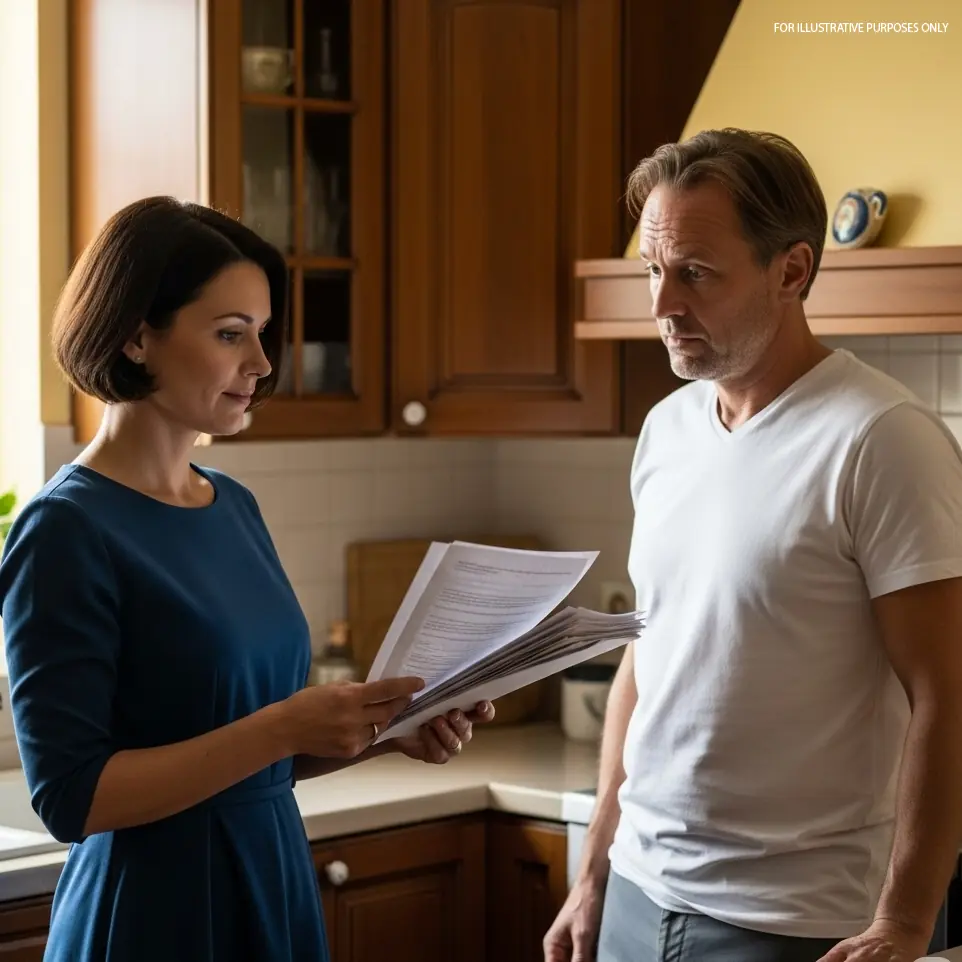

After Betrayal: How One Woman Found Strength and Reclaimed Her Life from a Br0ken Marriage
After 32 years of marriage shattered by betrayal, Lidia discovers her inner strength and dignity. This gripping story reveals her journey from heartbreak to empowerment, showing how she turned pain into a new beginning.
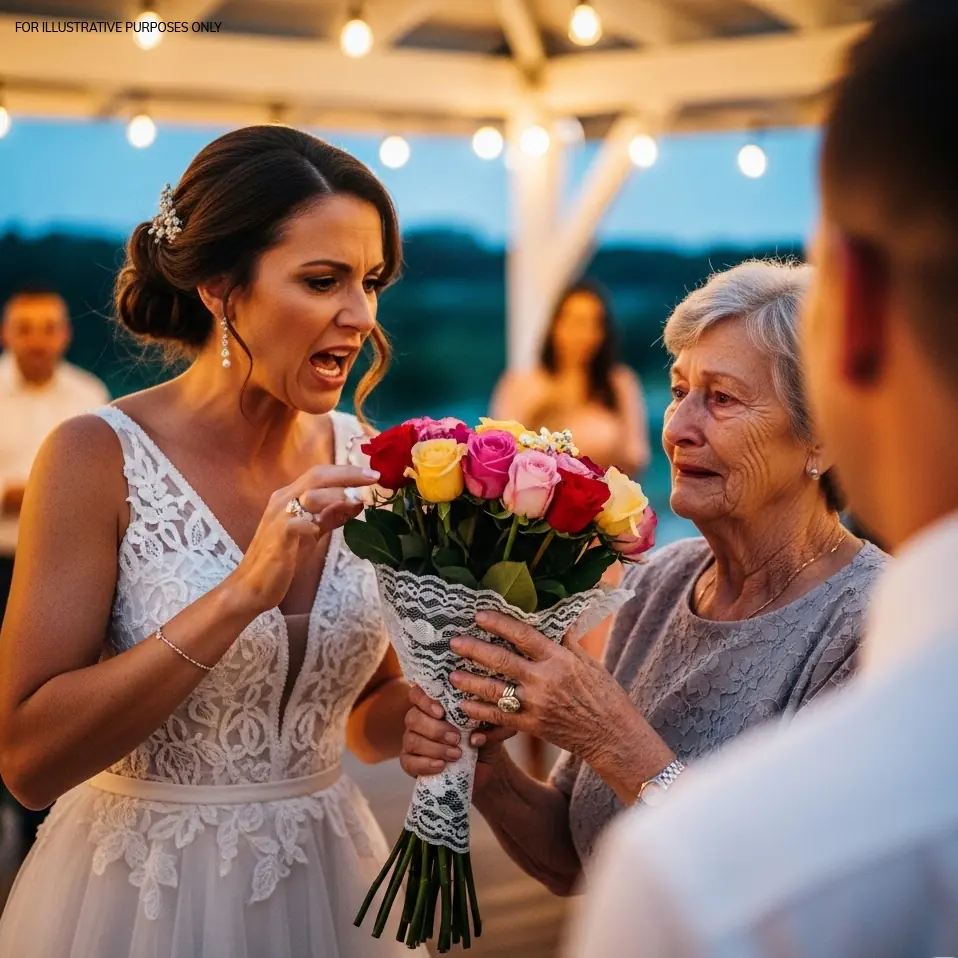

When a Wedding Gift Sparks a Family Fallout: The Sh0cking Truth Behind the Missing Wedding Video
At her niece’s lavish wedding, a grandmother’s heartfelt gift is cr:u:elly dismissed, igniting a dramatic family clash. Discover how love, legacy, and justice prevailed amid the mysterious disappearance of the wedding video and shattered illusions.
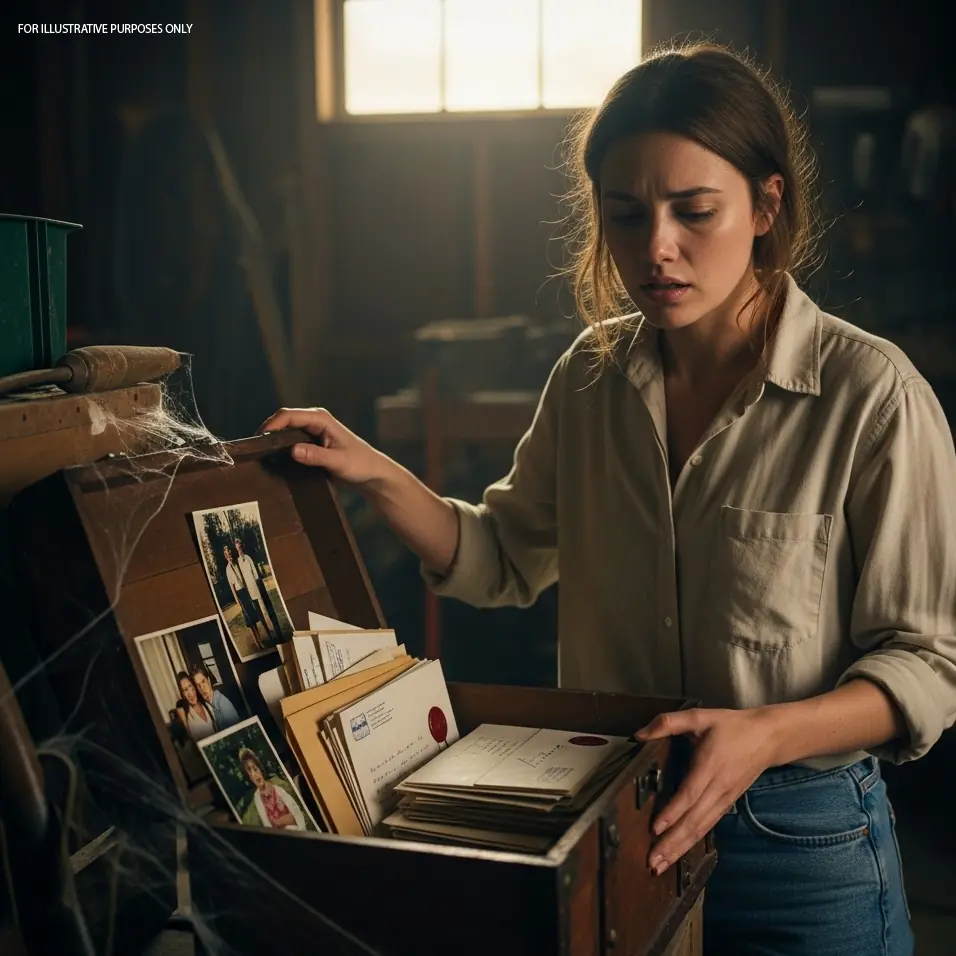

Unearthing Betrayal: How a Hidden Box Sparked My Journey from Heartbre@k to Healing and New Love
After discovering a hidden box revealing years of lies beneath my garage floorboards, I faced the crushing truth of betrayal. A year later, I found strength, reclaimed my life, and embraced new love.

4 household appliances that are energy hogs and how to tame them

5 Common Electric Kettle Mistakes That Could Lead to Serious Accidents

Why Dogs Are More Sensitive and Alert During Thunderstorms Than Humans: The Science Behind Their Unique Instincts

When a 911 Call Changed Everything: The Heartwarming Story That Proves Heroes Walk Among Us
Discover how a compassionate 911 operator went beyond duty to help a starving cancer survivor, sparking a community movement of kindness that will restore your faith in humanity.

Why Experts Recommend Putting Your Luggage in the Bathtub After Checking in: Turns Out It Has Many Unexpected Benefits

Experts reveal the effects on your body from eating one meal a day after a sh0cking simulation

Major medical breakthrough: Korean researchers discover “Undo” mechanism to transform tumor cells back to normal

If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you will suffer from ...
